
VoLTE and ViLTE
Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile Network
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This book presents the architecture of two networks that make up the backbone of the telephone service VoLTE and video service ViLTE. The 4G mobile network makes it possible to construct bearers through which IP packets, containing either telephone signals (SIP, SDP) or voice or video media (RTP stream), are transported.
The IMS network performs the processing of the telephone signal to provide VoLTE and ViLTE services, including call routing and the provision of additional services. Different procedures are described: the set-up and termination of a session, interconnection with third-party networks, roaming and intra-system handover.
The inter-system handover PS-CS is a special case that occurs when the mobile loses 4G network coverage over the course of a session. The e-SRVCC mechanism enables continuity of the service during the switch of the telephone communication to the 2G or 3G networks. The SMS service for short messages, which is a special telephone service in itself, is provided by two structures, one relying on the IMS network, and a second on the CSFB functionality.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Network Architecture
1.1. EPS network
1.1.1. Functional architecture
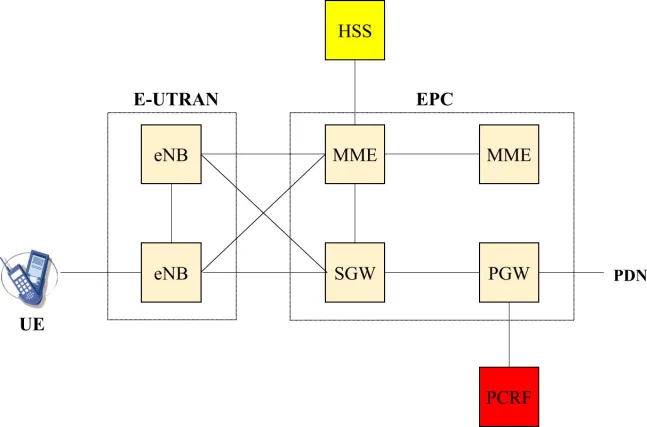
1.1.1.1. eNB entity
1.1.1.2. MME entity
1.1.1.3. SGW entity
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- List of Abbreviations
- 1 Network Architecture
- 2 Signaling Protocols
- 3 Basic Procedures
- 4 Radio Interface Procedures
- 5 Service Profiles
- 6 Interconnections
- 7 Handover
- 8 Roaming
- 9 Service Centralization and Continuity
- 10 Short Message Service
- Bibliography
- Index
- End User License Agreement