
Signaling Pathways in Liver Diseases
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Signaling Pathways in Liver Diseases
About this book
Signaling Pathways in Liver Diseases, Third Edition again provides hepatologists and hepatology researchers with an expert overview of the complex and novel cellular/extracellular signaling pathways in the liver, and their role in liver diseases. The last few years have seen a great number of developments in this field, which in turn have led to new opportunities for innovative treatments; however, the intricacy of these pathways and their interactions continue to provide a real challenge for clinicians. This outstanding book compiles the emerging knowledge into a single expert resource, cataloguing and organizing it into an accessible and understandable format.
With increased focus on the comprehension of cellular mechanisms involved in steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver tumors, which has led to changes in the management of these diseases, this new edition also sees the introduction of exciting new chapters on key emerging areas such as:
- Autophagy
- Notch Pathway
- P13K/PTEN Signaling in Liver Diseases
- Sirtuins
- Hepcidin and Iron
- Epigenetic Regulation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Liver Fibrosis
- Oxidative Stress and Signaling in the Liver.
Professors Dufour and Clavien have assembled an all-star cast of chapter authors, each of whom has provided clear and appropriate illustrations to reinforce the text, with a key points box offering a concise and handy summary. Self-assessment questions and answers allow the reader to test their own knowledge.
Signaling Pathways in Liver Disease, Third Edition is the perfect educational and reference tool to bridge the information exchange between the laboratory, the clinical ward, and the operating room, and an essential tool for the modern-day hepatologist.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
Hepatocytes
KEY POINTS
- The liver is the largest metabolic organ of the human body with a multitude of physiological functions.
- Hepatocytes differentiate from cells of the anterior entoderm under the influence of fibroblast growth factors and bone morphogenic proteins.
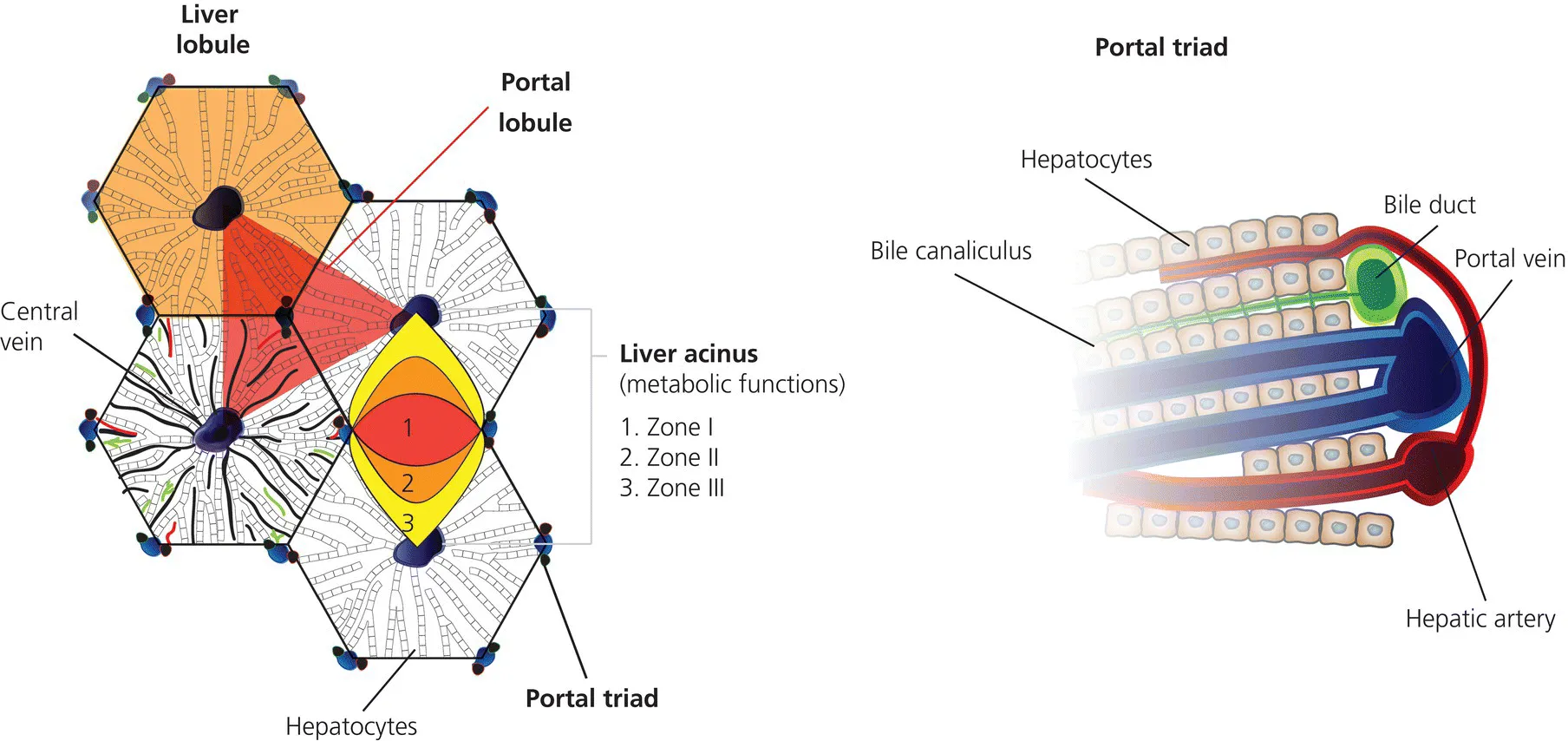
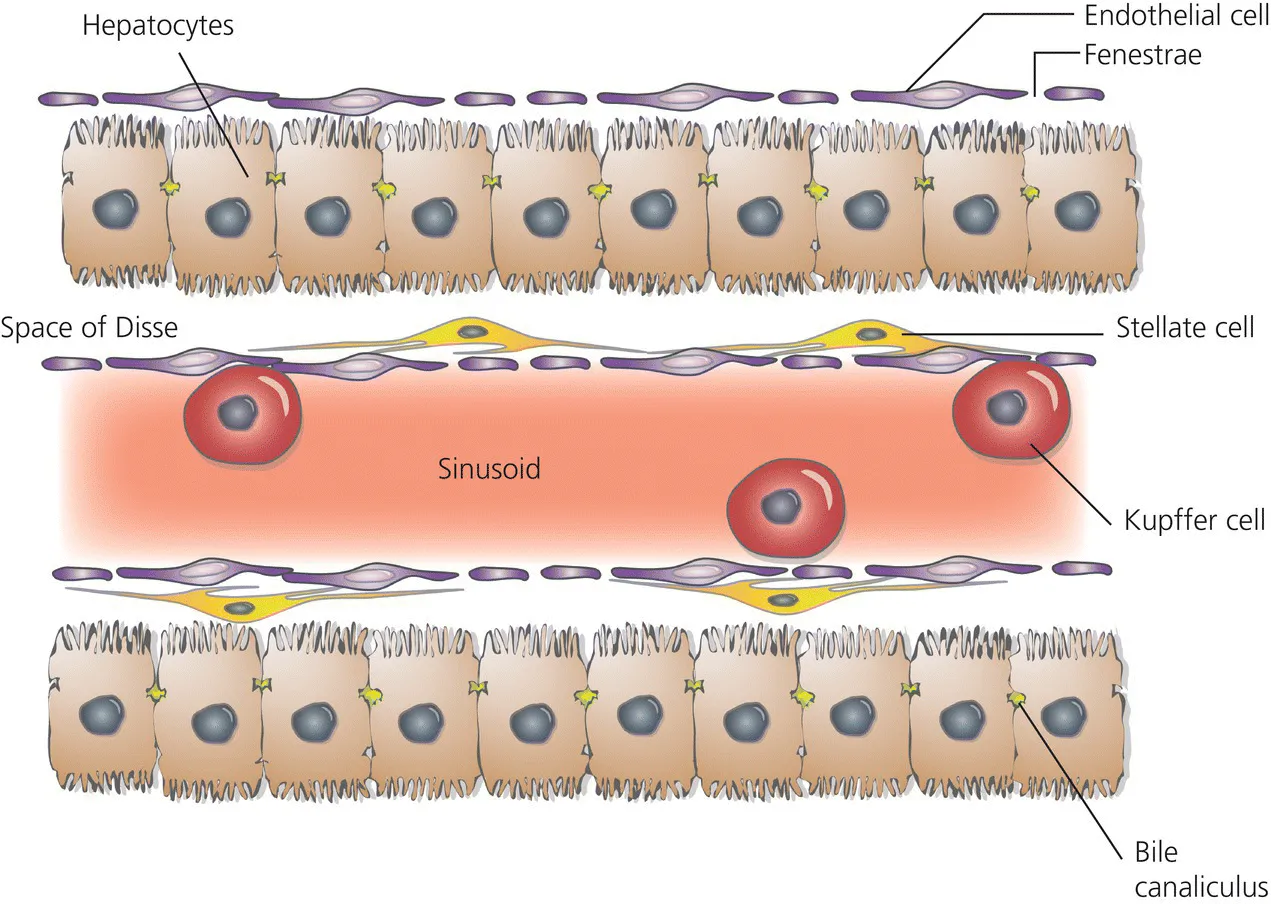
- The hepatocytes are the central parenchymal cells, performing all important biochemical processes in close contact with the bloodstream, forming a network of bile canaliculi with their cell membranes that excrete biliary fluid and its various contents into the small bowel.
- The cell membranes of the hepatocyte show distinct domains equipped with specific transporters essential for the uptake of molecules from the bloodstream and on the opposite side of the cell for secretion into the bile.
- The hepatocyte is an important storage compartment for carbohydrates and lipids, the main site of amino acid metabolism and protein synthesis (i.e. serum albumin, transport proteins and many coagulation factors) as well as the site of the two stages of biotransformation facilitating excretion of many toxins and xenobiotics.
Introduction
- Resorption and storage
- Synthesis and secretion
- Detoxification and excretion
Liver and hepatocyte development
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- List of Contributors
- CHAPTER 1: Hepatocytes
- CHAPTER 2: Signaling pathways in biliary epithelial cells
- CHAPTER 3: Stellate cells
- CHAPTER 4: Kupffer cells
- CHAPTER 5: Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells
- CHAPTER 6: Extracellular matrix
- CHAPTER 7: Platelets: a new cell type in liver physiology
- CHAPTER 8: Immune cell communication in liver disease and liver regeneration
- CHAPTER 9: Extracellular vesicle RNA in liver disease
- CHAPTER 10: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- CHAPTER 11: Autophagy
- CHAPTER 12: CXC chemokine receptor signaling in liver repair and regeneration
- CHAPTER 13: Metabolic regulation of liver regeneration
- CHAPTER 14: TNF signaling
- CHAPTER 15: Fas/FasL
- CHAPTER 16: Interferon signaling
- CHAPTER 17: Endocannabinoid signaling in liver pathologies
- CHAPTER 18: The WNT/β-catenin pathway
- CHAPTER 19: Hedgehog signaling in the liver
- CHAPTER 20: Notch pathway
- CHAPTER 21: PI3K/PTEN signaling in liver diseases
- CHAPTER 22: mTOR signaling in liver disease
- CHAPTER 23: LKB1/AMPK pathway in the control of hepatic energy metabolism
- CHAPTER 24: NF-κB
- CHAPTER 25: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases in liver diseases
- CHAPTER 26: p53
- CHAPTER 27: Sirtuins
- CHAPTER 28: Bile acids and their receptors
- CHAPTER 29: Hepcidin and iron
- CHAPTER 30: Gut microbiome and liver diseases
- CHAPTER 31: Epigenetic regulation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis
- CHAPTER 32: Signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
- CHAPTER 33: Interplay between hepatitis B virus and innate immune signaling pathways
- CHAPTER 34: Signaling of hepatitis C virus
- CHAPTER 35: Oxidative stress and signaling in the liver
- Answers to MCQs
- Index
- End User License Agreement