
Dictionary of Computer Vision and Image Processing
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Dictionary of Computer Vision and Image Processing
About this book
Written by leading researchers, the 2nd Edition of the Dictionary of Computer Vision & Image Processing is a comprehensive and reliable resource which now provides explanations of over 3500 of the most commonly used terms across image processing, computer vision and related fields including machine vision. It offers clear and concise definitions with short examples or mathematical precision where necessary for clarity that ultimately makes it a very usable reference for new entrants to these fields at senior undergraduate and graduate level, through to early career researchers to help build up knowledge of key concepts. As the book is a useful source for recent terminology and concepts, experienced professionals will also find it a valuable resource for keeping up to date with the latest advances.
New features of the 2nd Edition:
- Contains more than 1000 new terms, notably an increased focus on image processing and machine vision terms;
- Includes the addition of reference links across the majority of terms pointing readers to further information about the concept under discussion so that they can continue to expand their understanding;
- Now available as an eBook with enhanced content: approximately 50 videos to further illustrate specific terms; active cross-linking between terms so that readers can easily navigate from one related term to another and build up a full picture of the topic in question; and hyperlinked references to fully embed the text in the current literature.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information


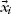
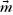
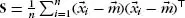
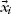

Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Preface
- Numbers
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
- References
- Supplemental Images
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app