
eBook - ePub
Oral Medicine and Pathology at a Glance
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Oral Medicine and Pathology at a Glance
About this book
Oral Medicine and Pathology at a Glance, 2nd Edition offers a comprehensive overview of essential aspects of oral medicine and pathology, with an emphasis on oral health care provision in general practice.
- Updated new edition, covering the most important conditions and commonly encountered oral pathologies and their clinical management
- Presented in the popular, highly-illustrated At a Glance style with clinical photographs throughout
- Written by an international author team
- Includes a companion website with self-assessment MCQs, further reading and downloadable images
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Oral Medicine and Pathology at a Glance by Pedro Diz Dios,Crispian Scully,Oslei Paes de Almeida,José V. Bagán,Adalberto Mosqueda Taylor in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Médecine & Santé bucco-dentaire et chirurgie. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
Examination of extraoral tissues
This book does not include the basics of history taking, only specific relevant points in the text. Bear in mind that the history gives the diagnosis in about 80% of cases.
Following the history, during which the clinician will note the patient’s conscious level, any anxiety, appearance, communication, posture, breathing, movements, behavior, sweating, weight loss or wasting (Figure 1.1), physical examination is indicated. This necessitates touching the patient; therefore, informed consent and confidentiality are required, a chaperone available, and religious and cultural aspects should be borne in mind (see Scully and Wilson).
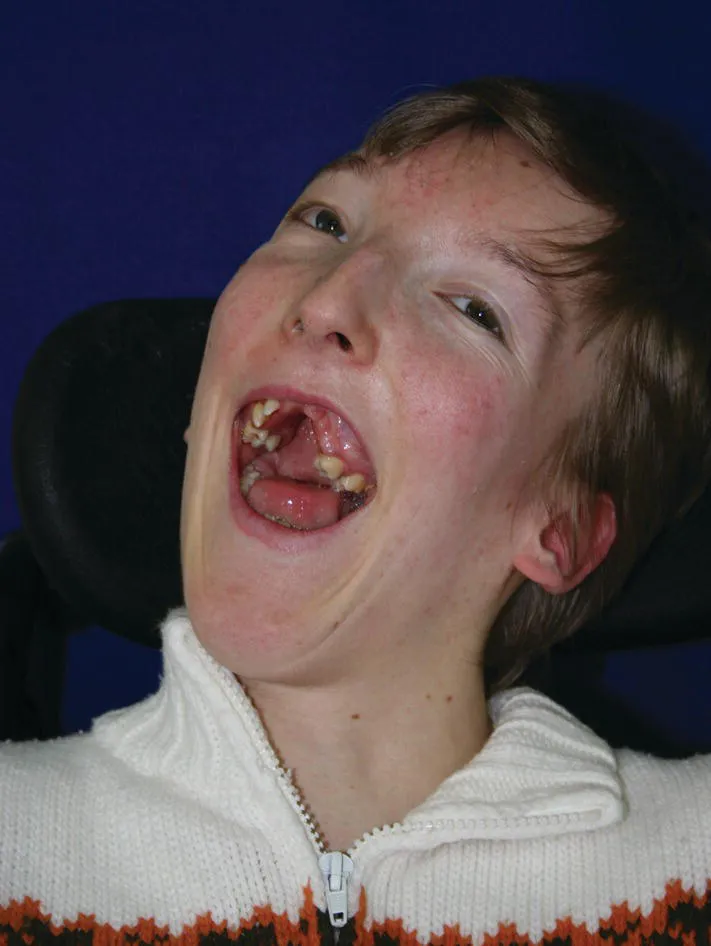
Figure 1.1 Cerebral palsy head.
Relevant medical problems may even be manifest in the fully clothed patient – where changes affect the head and neck, cranial nerves, or limbs. Therefore, while there is no rigid system for examination, the clinician should ensure that these areas are checked.
Head and neck
Pupil size should be noted (e.g. dilated in anxiety or cocaine abuse, constricted in heroin abuse).
Facial color should be noted:
- pallor (e.g. anemia)
- rashes (e.g. viral infections, lupus) (Figure 1.2)
- erythema (e.g. anxiety, alcoholism, polycythemia)
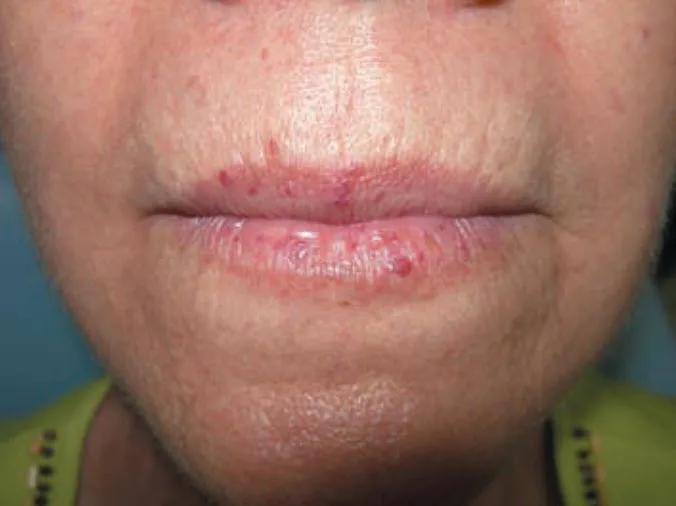
Figure 1.2 Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.
Swellings, sinuses or fistulas should be noted (Figure 1.3).
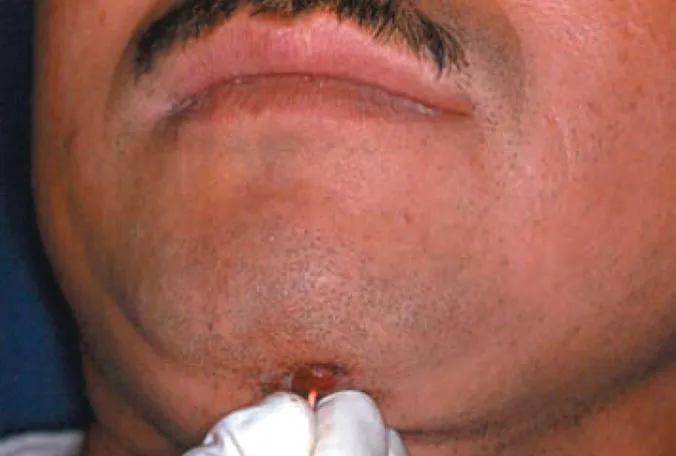
Figure 1.3 Cutaneous odontogenic fistula.
Facial symmetry is examined for evidence of enlarged masseter muscles (masseteric hypertrophy) suggestive of clenching or bruxism.
Neck swellings should be elicited, followed by careful palpation of lymph nodes (and salivary and thyroid glands), searching for swelling and/or tenderness, by observing the patient from in front, noting any obvious asymmetry or swelling (Figure 1.4a and b), then standing behind the seated patient to palpate the nodes. Systematically, each region needs to be examined lightly with the pulps of the fingers, trying to roll the nodes against harder underlying structures.
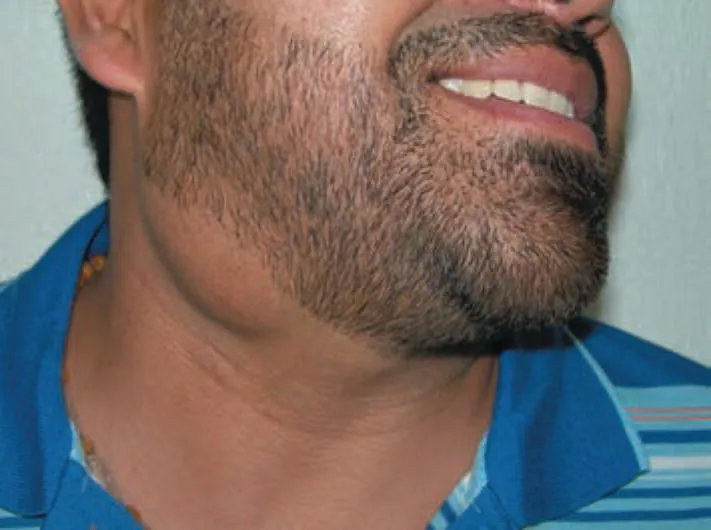
Figure 1.4a Lipoma.
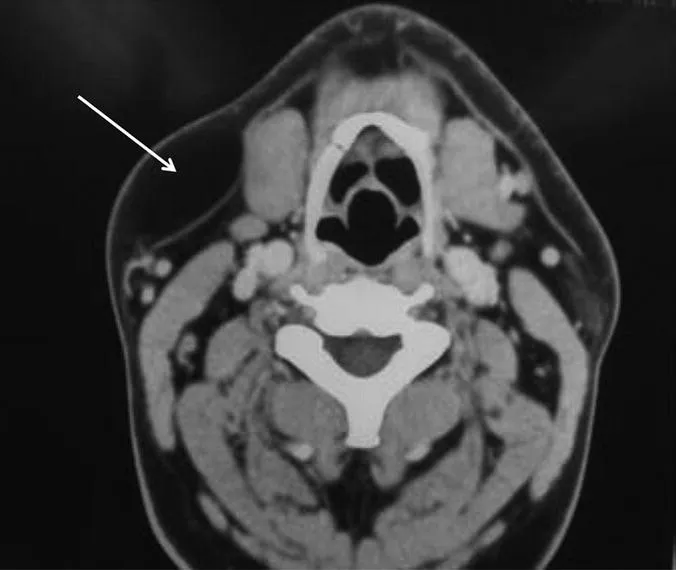
Figure 1.4b Scan of lipoma (arrow on lesion).
Some information can be gained by the texture and nature of the lymphadenopathy; nodes that are tender may be inflammatory (lymphadenitis), while those that are increasing in size and are hard, or fixed to adjacent tissues, may be malignant.
Cranial nerves
The cranial nerves should be examined, in particular facial movement and corneal reflex should be tested and facial sensation determined (Table 1.1). Movement of the mouth as the patient speaks is important, especially when they allow ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- About the companion website
- 1 Examination of extraoral tissues
- 2 Examination of mouth, jaws, temporomandibular region and salivary glands
- 3 Investigations: Histopathology
- 4 Investigations: Microbiology
- 5 Investigations: Imaging
- 6 Investigations: Blood tests
- 7 Anatomical variants and developmental anomalies
- 8 Blisters
- 9 Blisters, infections: Herpes simplex virus
- 10 Blisters, infections: Varicella zoster virus
- 11 Blisters, skin diseases: Pemphigus
- 12 Blisters, skin diseases: Pemphigoid
- 13 Pigmented lesions
- 14 Pigmented lesions: Ethnic pigmentation and tattoos
- 15 Pigmented lesions: Melanotic macule
- 16 Pigmented lesions: Nevus and others
- 17 Pigmented lesions: Malignant melanoma
- 18 Red and purple lesions
- 19 Red and purple lesions: Desquamative gingivitis, mucositis
- 20 Red and purple lesions: Erythematous candidosis
- 21 Red and purple lesions: Angiomas
- 22 Red and purple lesions: Proliferative vascular lesions, Kaposi sarcoma
- 23 Red and purple lesions: Erythroplakia
- 24 Red and purple lesions: Erythema migrans (lingual erythema migrans; benign migratory glossitis; geographical tongue; continental tongue)
- 25 Swellings: Hereditary conditions, drug-induced swellings
- 26 Swellings: Infections, Human Papilloma Virus
- 27 Swellings: Granulomatous conditions
- 28 Swellings: Reactive lesions
- 29 Swellings: Malignant neoplasms, oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
- 30 Swellings: Malignant neoplasms, lymphoma, metastatic neoplasms
- 31 Ulcers and erosions: Local causes, drug-induced ulcers
- 32 Ulcers and erosions: Aphthae
- 33 Ulcers and erosions: Aphthous-like ulcers
- 34 Ulcers and erosions: Blood diseases, gastrointestinal disorders
- 35 Ulcers and erosions: Infections
- 36 Ulcers and erosions: Erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- 37 White lesions: Candidosis (candidiasis)
- 38 White lesions: Keratosis, leukoplakia
- 39 White lesions: Hairy leukoplakia, lichen planus
- 40 Salivary conditions: Salivary swelling and salivary excess
- 41 Salivary conditions: Dry mouth
- 42 Salivary conditions: Sjögren syndrome
- 43 Salivary conditions: Sialolithiasis, sialadenitis
- 44 Salivary conditions: Neoplasms
- 45 Salivary conditions: Mucoceles, sialosis
- 46 Neck swelling
- 47 Neck swelling: Cervical lymphadenopathy in generalized lymphadenopathy
- 48 Neurological conditions: Bell palsy, and trigeminal sensory loss
- 49 Neurological conditions and pain: Local, referred and vascular
- 50 Neurological conditions and pain: Trigeminal neuralgia
- 51 Neurological conditions and pain: Psychogenic (idiopathic facial pain, idiopathic odontalgia, and burning mouth syndrome (oral dysesthesia))
- 52 Jaw conditions: Temporomandibular pain-dysfunction
- 53 Jaw bone conditions: adiolucencies and radiopacities
- 54 Jaw bone conditions: Odontogenic diseases and cysts
- 55 Jaw bone conditions: Odontogenic tumors
- 56 Jaw conditions: Bone disorders
- 57 Jaw bone conditions: Fibro-osseous lesions
- 58 Maxillary sinus conditions
- 59 Oral malodor
- 60 Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and AIDS
- Index
- End User License Agreement