
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
The Advanced Fixed Income and Derivatives Management Guide
About this book
The Advanced Fixed Income and Derivatives Management Guide provides a completely novel framework for analysis of fixed income securities and portfolio management, with over 700 useful equations. The most detailed analysis of inflation linked and corporate securities and bond options analysis available;, this book features numerous practical examples that can be used for creating alpha transfer to any fixed income portfolio. With a framework that unifies back office operations, such as risk management and portfolio management in a consistent way, readers will be able to better manage all sectors of fixed income, including bonds, mortgages, credits, and currencies, and their respective derivatives, including bond and interest rate futures and options, callable bonds, credit default swaps, interest rate swaps, swaptions and inflation swaps. Coverage includes never-before-seen detail on topics including recovery value, partial yields, arbitrage, and more, and the companion website features downloadable worksheets that can be used for measuring the risks of securities based on the term structure models.
Many theoretical models of the Term Structure of Interest Rates (TSIR) lack the accuracy to be used by market practitioners, and the most popular models are not mathematically stable. This book helps readers develop stable and accurate TSIR for all fundamental rates, enabling analysis of even the most complex securities or cash flow structure. The components of the TSIR are almost identical to the modes of fluctuations of interest rates and represent the language with which the markets speak.
- Examine unique arbitrage, risk measurement, performance attribution, and replication of bond futures
- Learn to estimate recovery value from market data, and the impact of recovery value on risks
- Gain deeper insight into partial yields, product design, and portfolio construction
- Discover the proof that corporate bonds cannot follow efficient market hypothesis
This useful guide provides a framework for systematic and consistent management of all global fixed income assets based on the term structure of rates. Practitioners seeking a more thorough management system will find solutions in The Advanced Fixed Income and Derivatives Management Guide.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Review of Market Analytics
1.1 BOND VALUATION
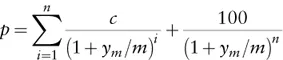
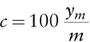
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Table of Contents
- List of Tables
- List of Figures
- Abbreviations
- Notation
- Preface
- Acknowledgement
- Foreword
- About the Author
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Review of Market Analytics
- Chapter 2: Term Structure of Rates
- Chapter 3: Comparison of Basis Functions
- Chapter 4: Risk Measurement
- Chapter 5: Performance Attribution
- Chapter 6: Libor and Swaps
- Chapter 7: Trading
- Chapter 8: Linear Optimization and Portfolio Replication
- Chapter 9: Yield Volatility
- Chapter 10: Convexity and Long Rates
- Chapter 11: Real Rates and Inflation Expectations
- Chapter 12: Credit Spreads
- Chapter 13: Default and Recovery
- Chapter 14: Deliverable Bond Futures and Options
- Chapter 15: Bond Options
- Chapter 16: Currencies
- Chapter 17: Prepayment Model
- Chapter 18: Mortgage Bonds
- Chapter 19: Product Design and Portfolio Construction
- Chapter 20: Calculating Parameters of the TSIR
- Chapter 21: Implementation
- References
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app