
Modeling of Photovoltaic Systems Using MATLAB
Simplified Green Codes
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Modeling of Photovoltaic Systems Using MATLAB
Simplified Green Codes
About this book
Provides simplified MATLAB® codes for analysis of photovoltaic systems, describes the model of the whole photovoltaic power system, and shows readers how to build these models line by line.
This book presents simplified coded models for photovoltaic (PV)-based systems using MATLAB® to help readers understand the dynamic behavior of these systems. Through the use of MATLAB®, the reader has the ability to modify system configuration, parameters, and optimization criteria. Topics covered include energy sources, storage, and power electronic devices. The book contains six chapters that cover systems' components from the solar source to the end user. Chapter 1 discusses modeling of the solar source, and Chapter 2 discusses modeling of the PV source. Chapter 3 focuses on modeling of PV systems' power electronic features and auxiliary power sources. Modeling of PV systems' energy flow is examined in Chapter 4, while Chapter 5 discusses PV systems in electrical power systems. Chapter 6 presents an application of PV system models in systems' size optimization. Common control methodologies applied to these systems are also modeled in this book.
- Covers the basic models of the whole PV power system, enabling the reader modify the models to provide different sizing and control methodologies
- Examines auxiliary components to PV systems, including wind turbines, diesel generators, and pumps
- Contains examples, drills, and codes
Modeling of Photovoltaic Systems Using MATLAB®: Simplified Green Codes is a reference for researchers, students, and engineers who work in the field of renewable energy, and specifically in PV systems.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
MODELING OF THE SOLAR SOURCE
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 MODELING OF THE SUN POSITION
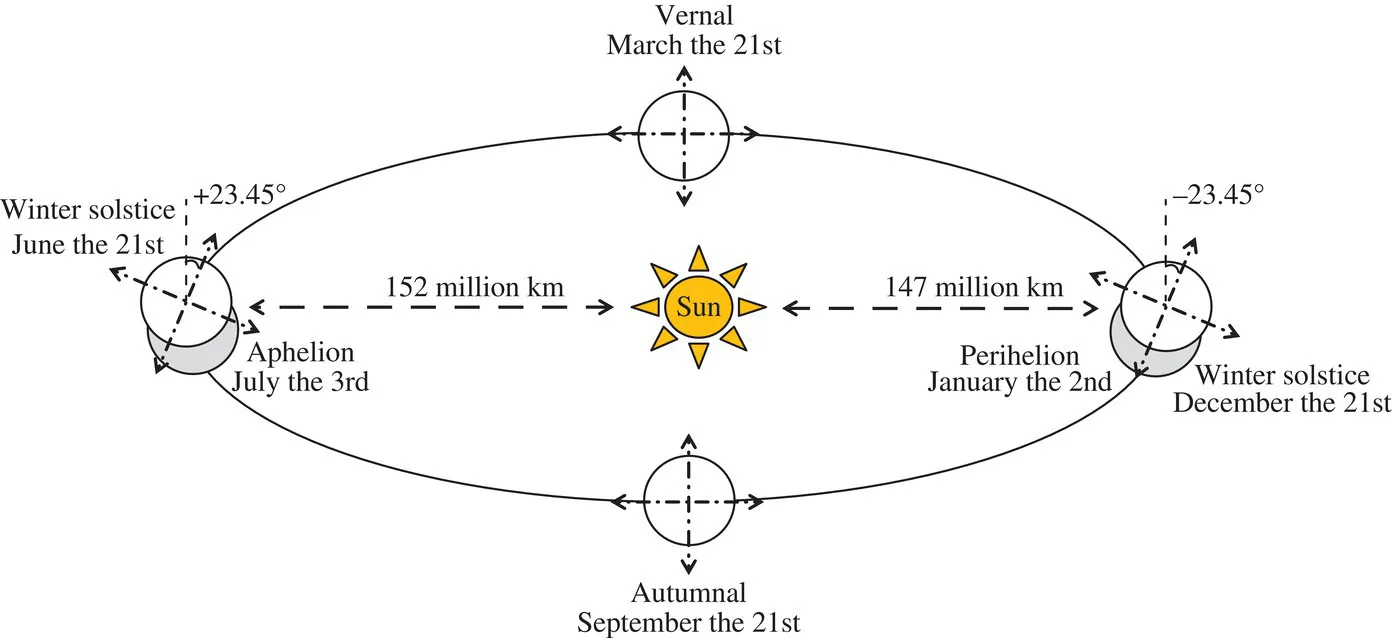
Table of contents
- COVER
- TITLE PAGE
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
- ABOUT THE AUTHORS
- FOREWORD
- ACKNOWLEDGMENT
- 1 MODELING OF THE SOLAR SOURCE
- 2 MODELING OF PHOTOVOLTAIC SOURCE
- 3 MODELING OF PV SYSTEM POWER ELECTRONIC FEATURES AND AUXILIARY POWER SOURCES
- 4 MODELING OF PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM ENERGY FLOW
- 5 PV SYSTEMS IN THE ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEM
- 6 PV SYSTEM SIZE OPTIMIZATION
- INDEX
- END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT