
LTE Small Cell Optimization
3GPP Evolution to Release 13
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
LTE Small Cell Optimization
3GPP Evolution to Release 13
About this book
LTE network capabilities are enhanced with small cell deployment, with optimization and with new 3GPP features. LTE networks are getting high loaded which calls for more advanced optimization. Small cells have been discussed in the communications industry for many years, but their true deployment is happening now. New 3GPP features in Release 12 and 13 further push LTE network performance.
This timely book addresses R&D and standardization activities on LTE small cells and network optimization, focusing on 3GPP evolution to Release 13. It covers LTE small cells from specification to products and field results; Latest 3GPP evolution to Release 13; and LTE optimization and learnings from the field.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Introduction
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 LTE Global Deployments and Devices
- 1.3 Mobile Data Traffic Growth
- 1.4 LTE Technology Evolution
- 1.5 LTE Spectrum
- 1.6 Small Cell Deployments
- 1.7 Network Optimization
- 1.8 LTE Evolution Beyond Release 13
- 1.9 Summary
- References
1.1 Introduction
1.2 LTE Global Deployments and Devices
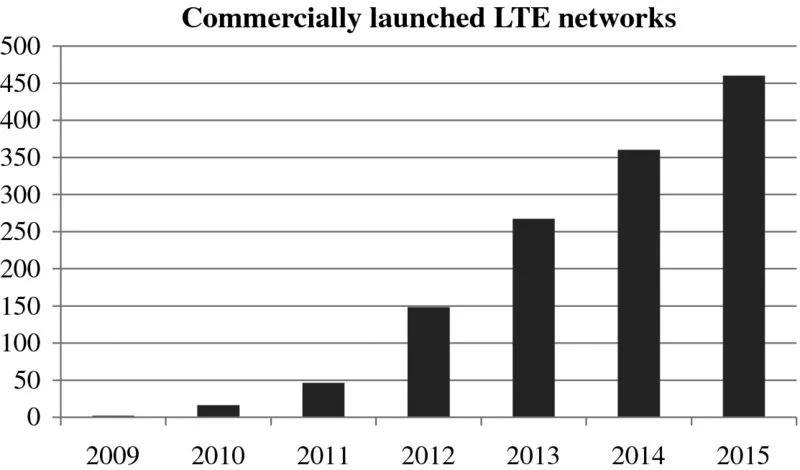


1.3 Mobile Data Traffic Growth

1.4 LTE Technology Evolution
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- List of Abbreviations
- 1 Introduction
- 2 LTE and LTE Advanced in Releases 8–11
- 3 LTE-Advanced Evolution in Releases 12–13
- 4 Small Cell Enhancements in Release 12/13
- 5 Small Cell Deployment Options
- 6 Small Cell Products
- 7 Small Cell Interference Management
- 8 Small Cell Optimization
- 9 Learnings from Small Cell Deployments
- 10 LTE Unlicensed
- 11 LTE Macro Cell Evolution
- 12 LTE Key Performance Indicator Optimization
- 13 Capacity Optimization
- 14 VoLTE Optimization
- 15 Inter-layer Mobility Optimization
- 16 Smartphone Optimization
- 17 Further Outlook for LTE Evolution and 5G
- Index
- EULA
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app