![]()
CHAPTER 1
An introduction to blood groups
What is a blood group?
In 1900, Landsteiner showed that people could be divided into three groups (now called A, B, and O) on the basis of whether their red cells clumped when mixed with separated sera from other people. A fourth group (AB) was soon found. This is the origin of the term ‘blood group’.
A blood group could be defined as, ‘An inherited character of the red cell surface, detected by a specific alloantibody’. Do blood groups have to be present on red cells? This is the usual meaning, though platelet- and neutrophil-specific antigens might also be called blood groups. In this book only red cell surface antigens are considered. Blood groups do not have to be red-cell specific, or even blood-cell specific, and most are also detected on other cell types. Blood groups do have to be detected by a specific antibody: polymorphisms suspected of being present on the red cell surface, but only detected by other means, such as DNA sequencing, are not blood groups. Furthermore, the antibodies must be alloantibodies, implying that some individuals lack the blood group.
Blood group antigens may be:
- proteins;
- glycoproteins, with the antibody recognising primarily the polypeptide backbone;
- glycoproteins, with the antibody recognising the carbohydrate moiety;
- glycolipids, with the antibody recognising the carbohydrate portion.
Blood group polymorphisms may be as fundamental as representing the presence or absence of the whole macromolecule (e.g. RhD), or as minor as a single amino acid change (e.g. Fya and Fyb) or a single monosaccharide difference (e.g. A and B).
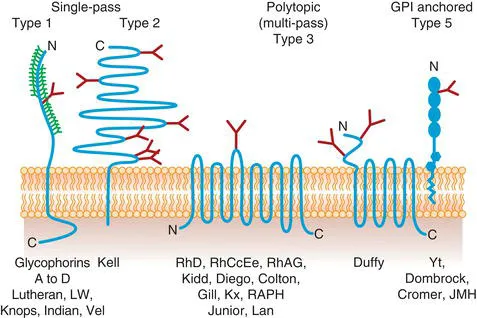
Blood group proteins and glycoproteins are integral structures of the red cell membrane. Diagrammatic representations of some blood group proteins and glycoproteins in the membrane are shown in Fig. 1.1. Some pass through the membrane once. These generally have an external N-terminal domain and a cytoplasmic C-terminal domain (Type 1), though in one case (the Kell glycoprotein) the C-terminus is external and the N-terminus internal (Type 2). Some are polytopic (Type 3); that is, they cross the membrane several times. Usually both termini are cytoplasmic, but the Duffy glycoprotein has an odd number of membrane-spanning domains and an extracellular N-terminal domain. Finally, some have no membrane-spanning domain, but are anchored to the membrane by a lipid tail (called a glycosylphosphatidylinositol or GPI anchor), which is attached to the C-terminus of the protein through carbohydrate (Type 5). There are no Type 4 glycoproteins, which have no external domain, in the red cell membrane.
Most red cell surface proteins are glycosylated, the only exceptions being the Rh and Kx proteins. This glycosylation may be (1) N-glycosylation, large, branched sugars attached to asparagine residues of the amino acid backbone, or (2) O-glycosylation, smaller glycans (usually tetrasaccharides) attached to serine or threonine residues.
Blood group antibodies
Blood groups are antigens and, by definition, a molecule cannot be an antigen unless it is recognised by an antibody (or T cell receptor); therefore, all blood group specificities are defined by antibodies. Most adults have antibodies to the A or B antigens, or to both; that is, they have ‘naturally occurring’ antibodies to those ABO antigens they lack. For most other blood groups, corresponding antibodies are not ‘naturally occurring’, but are only formed as a result of immunisation by transfused red cells or by fetal red cells leaking into the maternal circulation during pregnancy or childbirth.
Blood group antibodies are usually IgM or IgG, although some may be IgA (Chapter 6). ‘Naturally occurring’ antibodies are usually predominantly IgM, whereas ‘immune’ antibodies are predominantly IgG. As a general rule, IgM antibodies will directly agglutinate antigen-positive red cells in a saline medium, whereas most IgG antibodies require potentiators or anti-human globulin to effect agglutination (Chapter 2).
Clinical importance of blood groups
Blood groups are of great clinical importance in blood transfusion and in transplantation. In fact, the discovery of the ABO system was one of the most important factors in making the practice of blood transfusion possible. Many blood group antibodies have the potential to cause rapid destruction of transfused red cells bearing the corresponding antigen, giving rise to a haemolytic transfusion reaction (HTR), either immediately or several days after the transfusion. At their worst, HTRs give rise to disseminated intravascular coagulation, renal failure, and death. At their mildest, they reduce the efficacy of the transfusion (Chapter 6).
IgG blood group antibodies can cross the placenta during pregnancy and haemolyse fetal red cells expressing the corresponding antigen. This may cause alloimmune fetal haemolytic anaemia, more commonly known as haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN). Many blood group antibodies have the potential to cause HDFN, but the most common culprits are D and c of the Rh system and K of the Kell system.
Biological importance of blood groups
The biological importance of many blood group antigens is either known or can be surmised from their structure. The following functions have been attributed to blood group antigens: transporters of biologically important molecules across the red cell membrane; receptors of external stimuli and cell adhesion; regulators of autologous complement to prevent red cell destruction; enzymes; anchors of the red cell membrane to the cytoskeleton; and providers of an extracellular carbohydrate matrix to protect the cell from mechanical damage and microbial attack. Very little is known, however, about the functions of the blood group polymorphisms, but it is likely that they arose from selection pressures created by pathogens exploiting blood group molecules for attachment to the cells and subsequent invasion.
Blood group systems
The International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) recognises 339 blood group antigens; 297 of these are classified into 1 of 33 blood group systems (Table 1.1 and see the Red Cell Immunogenetics and Blood Group Terminology Working Party area of the ISBT website: www.isbtweb.org). Each blood group system represents either a single gene or a cluster of two or three closely linked genes of related sequence and with little or no recognised recombination occurring between them. Consequently, each blood group system is a genetically discrete entity. The MNS system comprises three genes, Rh, Xg, and Chido/Rodgers, two genes each, and each of the remainder represents a single gene. Rh and MNS are the most complex systems, with 54 and 46 antigens, respectively; nine systems consist of just a single antigen.
Blood group terminology and classification
Since the discovery of the ABO system in 1900, a multitude of blood group antigens have been identified and many different styles of terminology have been used. These include the following to represent alleles: upper case letters (e.g. A, B; M, N); upper and lower case letters to represent antithetical antigens, the products of alleles (S, s; K, k); superscript letters (Fya, Fyb), and numbers (Lu6, Lu9). A variety of different styles of terminology have been us...