
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Features recent trends and advances in the theory and techniques used to accurately measure and model growth
Growth Curve Modeling: Theory and Applications features an accessible introduction to growth curve modeling and addresses how to monitor the change in variables over time since there is no "one size fits all" approach to growth measurement. A review of the requisite mathematics for growth modeling and the statistical techniques needed for estimating growth models are provided, and an overview of popular growth curves, such as linear, logarithmic, reciprocal, logistic, Gompertz, Weibull, negative exponential, and log-logistic, among others, is included.
In addition, the book discusses key application areas including economic, plant, population, forest, and firm growth and is suitable as a resource for assessing recent growth modeling trends in the medical field. SAS® is utilized throughout to analyze and model growth curves, aiding readers in estimating specialized growth rates and curves. Including derivations of virtually all of the major growth curves and models, Growth Curve Modeling: Theory and Applications also features:
• Statistical distribution analysis as it pertains to growth modeling
• Trend estimations
• Dynamic site equations obtained from growth models
• Nonlinear regression
• Yield-density curves
• Nonlinear mixed effects models for repeated measurements data
Growth Curve Modeling: Theory and Applications is an excellent resource for statisticians, public health analysts, biologists, botanists, economists, and demographers who require a modern review of statistical methods for modeling growth curves and analyzing longitudinal data. The book is also useful for upper-undergraduate and graduate courses on growth modeling.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES
1.1 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSION
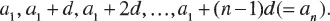
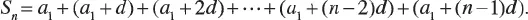
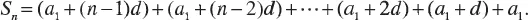
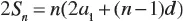
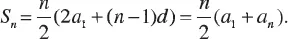
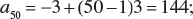
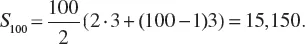
1.2 GEOMETRIC PROGRESSION
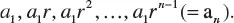
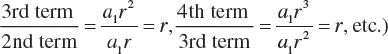
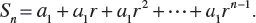
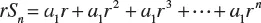
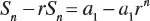
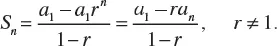
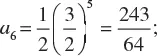
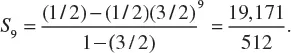
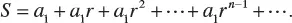
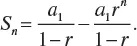
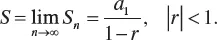
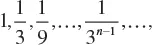
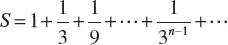
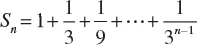
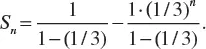
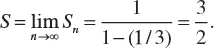
1.3 THE BINOMIAL FORMULA
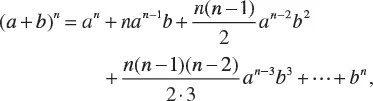
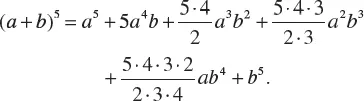
Table of contents
- COVER PAGE
- CONTENTS
- TITLE PAGE
- COPYRIGHT
- DEDICATION
- PREFACE
- 1 MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES
- 2 FUNDAMENTALS OF GROWTH
- 3 PARAMETRIC GROWTH CURVE MODELING
- 4 ESTIMATION OF TREND
- 5 DYNAMIC SITE EQUATIONS OBTAINED FROM GROWTH MODELS
- 6 NONLINEAR REGRESSION
- 7 YIELD–DENSITY CURVES
- 8 NONLINEAR MIXED–EFFECTS MODELS FOR REPEATED MEASUREMENTS DATA
- 9 MODELING THE SIZE AND GROWTH RATE DISTRIBUTIONS OF FIRMS
- 10 FUNDAMENTALS OF POPULATION DYNAMICS
- APPENDIX A
- REFERENCES
- INDEX