
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
The main aim of the book is to present new constructive methods of delay differential equation (DDE) theory and to give readers practical tools for analysis, control design and simulating of linear systems with delays. Referred to as "systems with delays" in this volume, this class of differential equations is also called delay differential equations (DDE), time-delay systems, hereditary systems, and functional differential equations. Delay differential equations are widely used for describing and modeling various processes and systems in different applied problems
At present there are effective control and numerical methods and corresponding software for analysis and simulating different classes of ordinary differential equations (ODE) and partial differential equations (PDE). There are many applications for these types of equations, because of this progress, but there are not as many methodologies in systems with delays that are easily applicable for the engineer or applied mathematician. there are no methods of finding solutions in explicit forms, and there is an absence of generally available general-purpose software packages for simulating such systems.
Systems with Delays fills this void and provides easily applicable methods for engineers, mathematicians, and scientists to work with delay differential equations in their operations and research.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Linear time-delay systems
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 Linear systems with delays
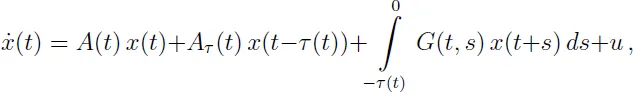
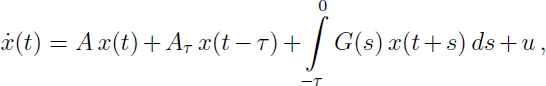
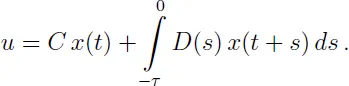
1.1.2 Wind tunnel model
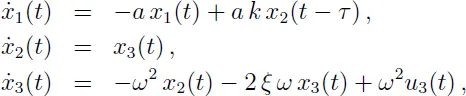
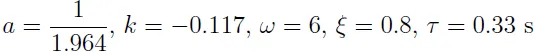
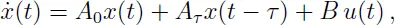
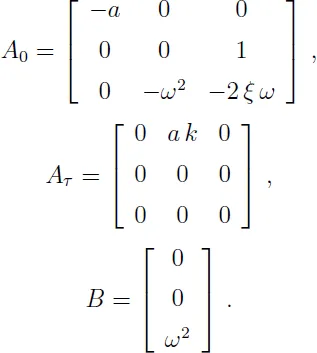
1.1.3 Combustion stability in liquid propellant rocket motors
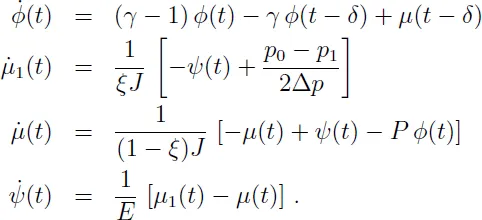
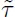
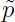
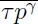
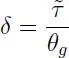
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title page
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Linear Time-Delay Systems
- Chapter 2: Stability Theory
- Chapter 3: Linear Quadratic Control
- Chapter 4: Numerical Methods
- Chapter 5: Appendix
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app