
eBook - ePub
Transboundary Water Resources Management
A Multidisciplinary Approach
Jacques Ganoulis, Alice Aureli, Jean Fried, Jacques Ganoulis, Alice Aureli, Jean Fried
This is a test
Buch teilen
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Transboundary Water Resources Management
A Multidisciplinary Approach
Jacques Ganoulis, Alice Aureli, Jean Fried, Jacques Ganoulis, Alice Aureli, Jean Fried
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Based on an international symposium addressing a key issue in global development, this reference includes both the latest methodologies for and practical examples of effective management of transboundary water resources. Its multidisciplinary approach combines hydrology and environmental science with economic and political approaches, in line with new UNESCO and EU recommendations, which have been formulated and implemented with the active involvement of all three editors.
By providing a theoretical framework as well as abundant case studies from southern Europe, Africa, Asia and South America, this handbook provides hydrologists, geologists, engineers and decision-makers with all the knowledge they need for their daily work.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Transboundary Water Resources Management als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Transboundary Water Resources Management von Jacques Ganoulis, Alice Aureli, Jean Fried, Jacques Ganoulis, Alice Aureli, Jean Fried im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Physical Sciences & Hydrology. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction and Structure of the Book
This book is a practical guide that suggests methodological tools and answers to different questions related to Transboundary Water Resources Management (TWRM), including both surface and groundwater aquifer resources. Some of these questions may be formulated as follows:
- How could data and information from riparian countries be harmonized to better understand the physical characteristics of transboundary hydro-systems?
- Are hydrological and hydrogeological models available to predict different scenarios in TWRM?
- What methodology is available to delineate transboundary aquifers?
- What is the current status of international law in terms of sharing transboundary surface waters and groundwater aquifers between riparian countries and what are the main legal issues?
- How could international law improve the utilization and effective protection of shared water resources?
- How could public and stakeholder participation contribute to the implementation of integrated TWRM?
- What methodology is available for integrating different collaborative models of TWRM?
- How could potential conflicts in sharing transboundary waters be transformed into collaborative actions?
In this practical guide, different collaborative models and TWRM tools are identified and explained, not just theoretically or conceptually but through specific case studies from around the world. These case studies are grouped together in such a way that the wide range of tools available to effectively explain, address, assess, understand and resolve TWRM problems in the real world become apparent.
The book is organized in four parts, which are described below.
1.1 Part I – A Global View
Part I is divided into two chapters (Chapters 2 and 3). Chapter 2 presents the importance of transboundary waters worldwide and the need for collaborative approaches to address global challenges of TWRM. The role of different disciplinary tools and regulatory instruments (technical, environmental, legal and socio-economical) for an effective collaborative approach is also explained.
Chapter 3 describes significant worldwide initiatives, such as the INBO (International Network of Basin Organizations) network, the UNECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe) Transboundary Waters Convention (1992), the UN Watercourses Convention (1997), the UN International Law Commission articles on shared natural resources (oil, gas and including shared groundwaters in 2002), UNESCO's International Hydrological Programme (IHP) components dealing with transboundary surface and groundwater resources, the UN CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity, 1992) and the European Union Water Framework Directive (EU-WFD, 2000). The importance of building international cooperation and management networks at the transboundary river catchment scale is emphasized (Chapter 3.1) and the role of international laws for transboundary water courses and aquifers is analysed (Chapters 3.2–3.4). The EU-WFD as a driving force for implementing the concept of Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) in transboundary regions is further explained (Chapters 3.5 and 3.6) and illustrated by characteristic case studies both from the EU and non-EU countries (Chapters 3.7–3.9).
1.2 Part II – Physical, Environmental and Technical Approaches
Part II is divided into two chapters, the first of which (Chapter 4) describes physical, environmental and technical approaches for transboundary aquifers, and the second (Chapter 5) covers transboundary lake and river basins. Chapters 4.1–4.3 are quite general and explain how hydrologic and hydrogeological approaches may be used to assess not only porous transboundary aquifers (Chapter 4.1) but also karst aquifers, which are globally very important sources for water supply (Chapter 4.2). The need to share information between neighbouring countries and to harmonize data is emphasized in these sections and the use of mathematical modelling as a tool for assessing groundwater hydrodynamics in transboundary aquifers is highlighted (Chapter 4.3).
Characteristic case studies from around the world, illustrating the application of the hydrogeological and scientific tools previously analysed, are reported in the second part of Chapter 4. In these case studies further details are given on how to assess and model transboundary aquifer systems, with examples from South America (Chapter 4.4), Africa (Chapter 4.5), Asia (Chapter 4.6) and Europe (Rhine Valley, Chapter 4.7), an aquifer shared by Hungary and Romania (Chapter 4.8), an aquifer shared by Serbia and Hungary (Chapter 4.9) and aquifers around Slovenia (Chapter 4.10).
For transboundary surface waters (Chapter 5), such as lakes and rivers, the hydrological monitoring data collected by individual countries are usually non-comparable, and even incomplete. This unfortunate situation is documented in (Chapter 5.1) and is also the case for the majority of hydrogeological data of groundwater aquifers. The non-comparability of monitoring data is a major obstacle in harmonizing information available from individual countries and applying global directives like the EU-WFD. International guidelines, such as those published by UN organizations like the WMO (World Meteorological Organization), could help remediate this situation.
However, despite the lack of systematic comparable monitoring systems, three case studies illustrating successful collaboration models are presented in Chapter 5: Lake Maggiore, shared between Italy and Switzerland (Chapter 5.2), Prespa Lakes, shared between Greece, Albania and FYR of Macedonia (Chapters 5.3 and 5.4), and the Kobilje River, shared between Slovenia and Austria (Chapter 5.5). This chapter also illustrates other problems in transboundary river basins, such as impacts from climate change (Chapters 5.6 and 5.7), identification of water bodies according to the EU-WFD (Chapter 5.8), sediment transport (Chapter 5.9) and river flow periodicities (Chapter 5.10).
1.3 Part III – Legal, Socio-Economic and Institutional Approaches
This part is also divided into two chapters (Chapters 6 and 7. Chapter 6 deals mainly with legal approaches; in Chapter 6.1 explanations are offered as to how international law on transboundary aquifers may be used. In Chapter 6.2 it is shown how adequate water policies may reduce over use of water in agriculture.
Regional and bilateral legal agreements can enhance effective cooperation between countries. Examples of this are given for the Aral Sea basin, Central Asia (Chapter 6.3), for the Kidron Valley, Middle East (Chapter 6.4) and for the Prespa Lakes basin in the Balkans (Chapter 6.5). A comparison between the rivers Mekong in SE Asia and Maritsa/Evros/Meriç in SE Europe illustrates how regional agreements can contribute to transform conflicts into cooperation (Chapter 6.6).
Adequate delineation of water resources regions adapted to specific regional conditions is also an important issue. The EU-WFD stipulates that water resources management should be performed on a river basin basis. Different criteria may be used to define water resources management regions in order to better promote the application of IWRM and contribute to transboundary water conflicts resolution. Examples are provided from the USA (Chapter 6.7) and Greece (Chapter 6.8).
Chapter 7 focuses on socio-economic and institutional approaches, which are very important for the implementation of technical and legal collaborative models in transboundary waters. Stakeholder participation, social learning and institutional design are important tools for achieving effective TWRM and reducing water insecurities and this is analysed in Chapters 7.1 and 7.2. Case studies from South America (Chapter 7.3) and the Balkans (Chapters 7.4–7.6) demonstrate particular issues and problems in transboundary cooperation.
Economic governance, such as the model of common pool management of transboundary water resources (Chapter 7.7) and applications of game theory (Chapters 7.8–7.10), all important tools for facilitating negotiations in conflict resolution issues, is also discussed.
1.4 Part IV – Bridging the Gaps
To deal with the complexity of real world problems, where no distinction is made between different dependent physical and socio-economic processes, there is a need for the various approaches described in Parts II and III to be integrated. This process of integration could be facilitated in two main ways. Firstly, through education and capacity building, where special training programmes can show how multidisciplinary approaches can be coordinated to achieve an integrated view of a problem and solve it effectively in the real world (Chapter 8.1). Secondly, by taking into account a general framework for risk analysis in conflict resolution, where risks and benefits could be shared between riparian countries and “win-win” solutions to transboundary disputes can be achieved (Chapter 8.2). Both these processes are based on specific programmes developed by UNESCO.
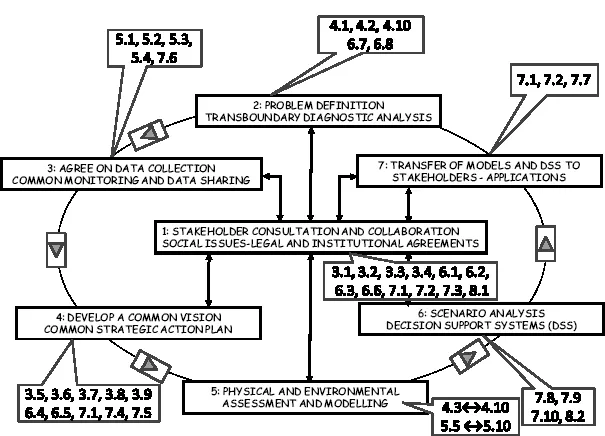
Figure 1.1 illustrates a collaborative model for TWRM based on the various contributions to this book. This uses the following seven steps and may be adapted to any particular case study of transboundary waters:
1. Stakeholder consultation and collaboration, social issues, legal and institutional agreements: this should interact with every one below;
2. problem definition: Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis (TDA);
3. agree on data collection, common monitoring and data sharing;
4. develop a common vision and common Strategic Action Plan (SAP);
5. physical and environmental assessment and modelling;
6. scenario analysis and Decision Support Systems (DSS);
7. transfer of models and DSS to stakeholders, applications.
Figure 1.1 Seven steps of the TWRM collaborative model, showing the relevant chapter/section numbers of the individual contributions from this book.
Part One
A Global View
Chapter 2
Transboundary Water Resources Management: Needs for a Coordinated Multidisciplinary Approach
2.1 Introduction
The global increase of population together with steady socio-economic development, especially of emerging economies, and the subsequent increase in water demand combined with the acceleration of water pollution from various point and diffuse sources, mean that transboundary water resources, located both on the surface (rivers and lakes) and in groundwater aquifers, are very important sources of water for different uses at global and regional scales, and form a significant part of the precious available water on earth.
Although the total amount of water on earth is substantial, only a very small fraction of it is not saline and can be directly used by man. According to the latest UN World Water Development Reports [1, 2] this amount is only 2.5% of the total water available on earth. When economically available renewable water resources are taken into account, global water availability is estimated at about 13 500 km3 per year that is only 2300 m3 per person per year. This is approximately 37% less than in 1970.
About 60% of global river flow lies within transboundary river basins [3], the surface area of which amount to almost half of the world's land surface (Figure 2.1). The significance of transboun...