
eBook - ePub
Nanotechnology in the Defense Industry
Advances, Innovation, and Practical Applications
Madhuri Sharon, Angelica S. L. Rodriguez, Chetna Sharon, Pio Sifuentes Gallardo
This is a test
Buch teilen
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Nanotechnology in the Defense Industry
Advances, Innovation, and Practical Applications
Madhuri Sharon, Angelica S. L. Rodriguez, Chetna Sharon, Pio Sifuentes Gallardo
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
This book will be about various aspects related to applications and use of knowledge of nanotechnology in promoting defense activities. The area in which scientists are focusing includes (i) nano-devices such as sensors, GPS & computers, chemical & biological weapons, nano-fabrics, bulletproof materials, nano-stealth coating, use of nanotechnology in various areas of aerospace. It is intended to cover available methodologies and understanding of technologies for these applications. Not only for destructive but also to improve medical and casualty, safety care for soldiers, and to produce lightweight, strong and multi-functional materials for use in body armour, both for protection and to provide enhanced connectivity will be covered.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Nanotechnology in the Defense Industry als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Nanotechnology in the Defense Industry von Madhuri Sharon, Angelica S. L. Rodriguez, Chetna Sharon, Pio Sifuentes Gallardo im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Technik & Maschinenbau & Werkstoffwissenschaft. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Chapter 1
Nanotechnology’s Entry into the Defense Arena
Madhuri Sharon
Walchand Centre for Research in Nanotechnology & Bionanotechnology, WCAS, W.H. Marg, Ashok-Chowk, Solapur, Maharashtra, India
Science is based solely on doubt-based, disinterested examination of the natural and physical world. It is entirely independent of personal belief. There is a very important, fundamental concomitant - that is to accept absolutely nothing whatsoever, for which there is no evidence, as having any fundamental validity.
Nobel Laureate Sir Harold W. Kroto
Nobel Laureate Sir Harold W. Kroto
1.1 Introduction
When nanotechnology emerged as a new science, it had attracted the attention of scientists from all branches of science the world over. Similarly, people from different domains of life and governance started realizing the impact of nanotechnology. Authorities from the military, security and defense arena also started thinking about the use of this technology. It was realized that nanotechnology would make a big difference in areas such as troop functionality, high-speed conveyance and capacity, safety of soldiers, betterment of aircraft, systems for command, control, communication and surveillance, automation and robotics, innovative sensors, advanced war fighter and battle systems capability, electrochemical power, such as batteries or fuel cells, and many more. Nanotechnology is seen as being a technology of national importance to the economy and security by many developed countries especially in the defense sectors. This chapter is about the area of defense that is being impacted by nanotechnology. Almost all countries across the globe are experimenting to understand how this Small Science will help protect their country.
1.2 What Is Nanotechnology
Let us very briefly look at this topic. One may write volumes on what nanotechnology is. But that would be beyond the scope of this book, because this book is about the specific application of nanotechnology in defense. However, in a nut shell, the emergence of nanotechnology, which is a science that deals with the properties of materials with dimensions of 1–100 nm (Figure 1.1), is a result of the fruitful thinking of the visionary Nobel laureate Professor Richard Feynman. Nanotechnology has revolutionized almost every field such as medicine, electronics, information technology, geology, space technology, material science, etc. Enough evidence on this subject has been provided to be able to state that at macroscale and microscale objects behave differently than that at nanoscale. The behavioral as well as the structural properties of a nano-object change. When one starts reducing the size of a solid from micro-level to nano-level, its appearance completely changes, especially where metals are concerned. Gold appears lustrous yellow at macroscale, but when brought to nano-level its color turns to red or blue depending on the size.
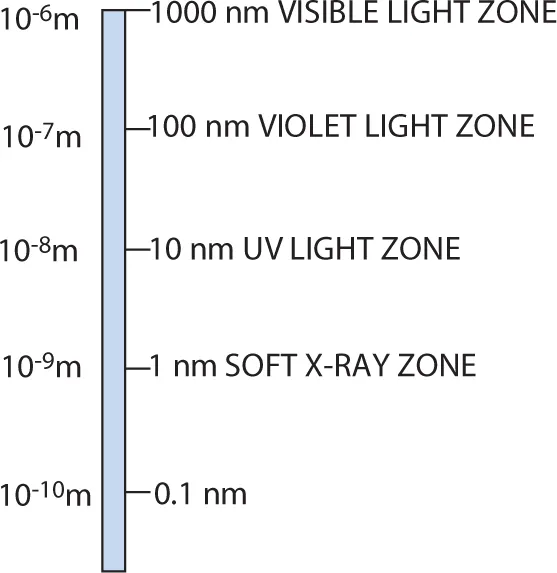
Figure 1.1 Nanometer scale.
Such alterations in properties of nanomaterials have created vast applications in Physics, Chemistry, Materials Science, Computers, Engineering, Medical and Biosciences, etc. No wonder venturing into the tiny domain of atoms and molecules is catching on. The main aim and objectives of Nanotechnology and Nanoscience is to unravel as well as comprehend the appearance of strange but useful traits in nanoparticles when they venture into the realm of nanoscale (1–100 nm). The emergence of the physicochemical and optoelectronic properties of nanoparticles is primarily due to confinement of electrons within particles of dimensions smaller than the bulk electron delocalization length. This ability to tune the optical absorption or emission properties (quantum dots) by simple variation in nanoparticle size is particularly attractive in the facile bandgap engineering of material and the growth of quantum dots.
In a nutshell, nanotechnology is the branch of technology that deals with dimensions and tolerances of less than 100 nanometers, especially the manipulation of individual atoms and molecules, or is the manipulation of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale. Such small engineered materials exhibit unique properties that are not found in their bulk counterparts.
The unique properties of nanomaterials that are being utilized for various applications are their chemical reactivity, mechanical strength, electrical properties, optical properties, thermal properties, and durability and quantum effects.
It is difficult to say which country’s defense department was first to start working out the possibility of using nanotechnology. However, strong participation of the United States Department of Defense in areas such as sensitive spectrum analyzer 3Hz – 50 GHz, quantum dots for nanoelectronics and sensors, highest Q mechanical resonator (cantilever, nanowire) for chemical sensing, nanomagnetic materials for DNA detection, nanoscale aluminium particles for energetic materials, smallest individual organic light emitting diodes (OLED) device, long shelf life packaging for food (nanoclay PE composite), high strength fibers from twisted nanotube yarns and maskless lithographic process for semiconductors are evidence that they have been investing in working out the applications of nanotechnology.
Out of the Asian countries, Japan is the leading up-and-coming nation investing in nanotechnology, followed by China and Taiwan.
In European countries, Germany, Russia, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, etc., are running programs in nanotechnology.
1.3 Nanotechnology Offers Innovative Opportunities for Defense
Initially, many thought that nanotechnology applications offered more hype than hope. But as many fantasies started becoming realities, the considerations and joint as well as separate efforts of scientists have reached a consensus that nanotechnology can provide strength and enhanced efficacy to many requirements of the defense arena. The area in which nanotechnology inputs are being envisaged as a must are its applications for (i) soldiers, (ii) security, (iii) weapons, (iv) aeronautics, (v) naval vessels, (vi) vehicles, (vii) satellites and (viii) logistics.
1.4 Nanotechnology for Soldiers
At the moment the maximum focus for the safety of soldiers is on developing a nano combat suit, which should be as thin as spandex and contain health monitors and communications equipment, acts as a shield from bullets, and can protect from biological and chemical attacks. This is for the well-being and security of soldiers. Nanotechnology is crucial for such development because without miniaturization such functionalities cannot be adapted to lightweight, wearable systems.
1.4.1 Smart Clothing Using Nanotechnology for Various Applications
Using the process of manipulating materials on an atomic or molecular scale, clothes are manufactured that have the following characteristics:
- Because it has greater tolerance to temperature change, nanotechnology-based fabric can warm or cool the body.
- It is possible to charge a phone using a fabric that is solar-powered and to recharge a cell phone or iPod. The change in temperature can open or tighten the weaving pattern of the fabric because the fibers of the fabrics can be modified so their physical properties change with temperature.
- Anti-microbial nanofabrics coated with antimicrobial nanoparticles can be used to protect soldier’s bodies from microbial infection.
- Another possibility that is being envisaged is to use fabrics coated with encapsulated insecticides to eliminate mosquitoes.
- In case a soldier faces smog or toxic gas, scientists are working on fabrics loaded with encapsulated gases that can be released to combat the condition.
- High-strength fiber made up of a composite of carbon nanotube impregnated in polymer can be used in nonwoven mats.
- Multi-Functional Textiles is another fantasy for the protection of soldiers that is being considered by modifying and functionalizing the surface properties by mixing yarn with nanomaterial and then weaving fabric from it. The new properties that can be exploited will be for the purposes of sensing, energy harvesting and energy storage.
1.4.2 Invisibility and Adaptive Camouflage
One of the ongoing dreams of scientists that has been dramatized and presented in many works of fiction and movies is a disappearing or invisible man. For this, one approach that is being considered is to make a cloak or fabric by manipulating light so that the soldiers wearing it cannot be seen or disappear. An “ultrathin invisibility skin cloak for visible light” is an outcome of this idea [1]. It is also kn...