![]()
Part I
Management Influences in a Virtual Global Landscape
The theme for Part I is understanding and managing the influences and drivers present in an unpredictable and increasingly complex digital environment; where survival and success is often founded on innovation and creating the next advantage from within. This requires an unprecedented measure of risk taking, cleverness, ingenuity and flexibility on the part of managers. They need to foresee and make sense of threats in the changing landscape that is typical of the virtual global environment, whilst being highly creative and inventive in seeking out new opportunities.
To put this in context, Chapter 1 explores a number of challenges facing management in the changing world of today; many of which can be overcome though innovation. It explains some of the skills, new mindsets and roles of managers that are necessary to be innovative in meeting these challenges.
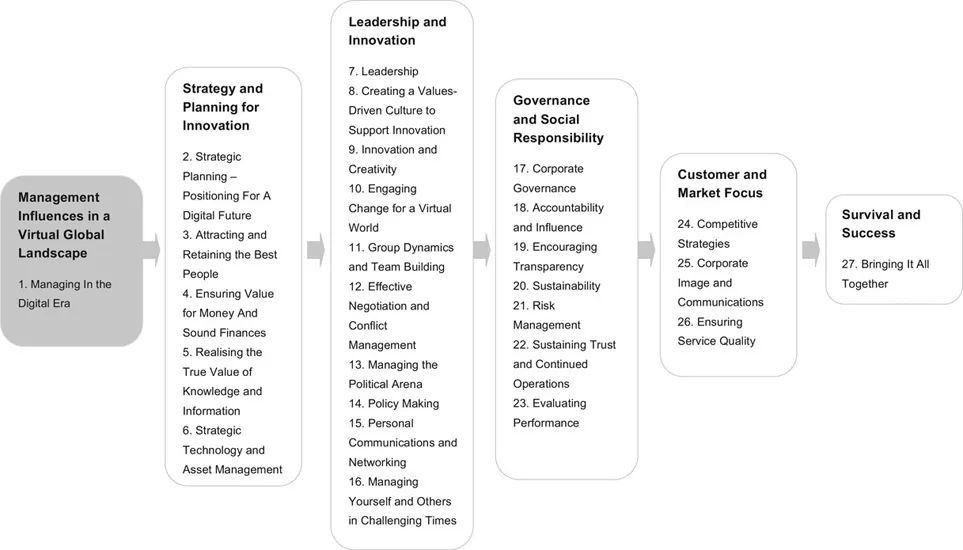
Figure PI.1 Management influences in a virtual global landscape
![]()
1
Managing in the Digital Era
Challenges for Information Services
As the virtual world unfolds and Web capabilities expand, libraries and information services must undergo radical change to survive and grow. The online or virtual world is challenging basic assumptions in economies, societies and lifestyles and leading to paradigm shifts in service delivery. For example, Web 2.0 allowed users to interact with and create resources with one another through crowd sourcing, social media and online resources such as Wikipedia. Web 3.0 enabled online shopping that has created a global market place, basically free of import duties and no longer reliant on built infrastructure. This presents an alternative model for library and information services, where the physical presence, the high street library, is being replaced by the virtual presence, e-services. Once ordered via a smart phone application, books and other materials can be shipped from library warehouses direct to the consumer’s location, which is itself identified through geospatial technology loaded on the smart phone. Even at the ordering stage, e-services can offer a chat component where questions can be answered about products and services by a library or information expert online. This global market place offers greater convenience, variety and choice, often at a cheaper price.
Web 4.0 developments go even further. Global integration that delivers global transparency, governance, distribution, collaboration and participation enables libraries to participate in global, information-centric, collaborative ventures to deliver 24×365 services. Such global alliances between libraries and information services means that when one service is closed, their and their partners’ client needs are satisfied online by another partner operating in its normal business hours in a + or – 8 hour time zone.
Web 4.0 technology will further change the way we do business and communicate and are entertained. The web of things – inanimate objects such as household items (fridges, security systems) or cars that currently can communicate with each other – will be supplemented by the web of thoughts – ultra-intelligent agents embedded in wearable technology devices that will read human emotions and intelligence.
Embracing these radical changes means that libraries and information services are reliant on innovative ideas that:
- are future oriented and challenge the status quo;
- significantly shift strategic direction (paradigm shift);
- involve new uses for floor space, as bricks and mortar are being replaced by mobile networks;
- maximize the use of crowd sourcing and social media; and
- necessitate different skills and knowledge such as digital rights management, social media management, online community management and other monitoring skills that safeguard an organization’s brand and online reputation.
To illustrate this, Parker et al. (2005:176) quotes Troll (2002) on the future of libraries, a statement that is still relevant today.
As libraries struggle with the fallout of the digital age, they must find a creative way to remain relevant to the twentieth century user who has the ability and means of finding vast amounts of information without setting foot in a brick and mortar library.… The freely accessible information on the web, in conjunction with the escalating costs of library materials, threatens the traditional mission of libraries to create and sustain large, self-sufficient collections for their patrons.
By seeking and shaping opportunities, generating new ideas and producing creative outcomes in e-services, libraries and information services can remain relevant in the virtual world. Indeed, their abilities to create, share and use knowledge remain key factors in the creation of wealth and high-value employment, in stimulating creativity and sustainability, and in improving the quality of life and social value.
Managing for the Future and Survival
To manage today’s challenges, leaders and organizations have to understand technology developments and impacts, be entrepreneurial, and think and act in new ways to anticipate change and:
- sustain their impetus and operations;
- develop new business opportunities and advantages;
- attract and retain people who are creative, have innovative mindsets and skills in ideas generation;
- better utilize their knowledge and information, including social networking tools;
- transform and rejuvenate existing products and services; and
- prepare for sudden, unprecedented shocks.
Whilst customers now expect to see seamless e-services across multiple channels that are tailored to need, not all customers have the same needs and expectations. Employees’ as well as customers’ needs and expectations will differ according to their age group or generation, physical locality and personal circumstances. Therefore the information service must be prepared to deliver different solutions for different generations to meet different circumstances and sustain these in an environment of dwindling financial resources.
Integrated channel services that include push e-services to tablets and smart phones, social networking and Web tools such as chat lines, e-journals and e-books, traditional one-on-one service delivery and Web-enabled transactions increase the level of customer convenience and can reduce costs. Moving customers to physical self-service such as checkouts or online Web self-service, e-journals and e-books reduces counter staff and other overhead costs as well as the amount of travel, time and expense for the customer.
No matter what their title, as Chief Information or Knowledge Officer or Library and Information Services Manager, the occupants of these roles will be innovators and strategic change managers. They will need to re-conceptualize their function and reinvent themselves as challenges, needs and opportunities come along. Those supporting business and corporate environments, research and development institutions will be at the forefront of change as their abilities to offer new information and e-services, as well as other creative uses of ICT will be critical to the sustainability and entrepreneurial success of their parent organization. They will need to be imaginative, resourceful, proactive and versatile.
Uncertainty and change present new challenges that need to be managed from different perspectives in order to survive and prosper in the future. Progressive organizations have recognized that their imagination, creativity and consequential business advantage are predicated on educated and skilled people who can create ideas, share and use knowledge well. They look for ways to increase the level of innovation by establishing corporate values that encourage openness and originality. Information technology and business applications are also important to connect and harness collective intelligence.
The funding base for many information services is dwindling, whilst at the same time there is greater demand for knowledge and information in the corporate environment and by people making lifestyle and other decisions concerning their future. Managing in this environment requires the ability to make smarter and resourceful decisions; especially in ensuring the sustainability of services in an era of decreasing financial contributions and loss of corporate knowledge.
At a local community level social media is being used to share knowledge about community events, understand issues surrounding environmental sustainability and support diversity in lifestyle. In these environments, the opportunity also exists for information services to be valuable social entrepreneurs that develop social capital by developing e-services that help people live, learn, grow and connect.
New Skills, Mindsets and Approaches
Management today embraces a way of thinking, an attitude and behavioural style that is global and innovative. Whilst strategic thinking, technical, interpersonal, knowledge-enabling, conceptual and analytical skills are still used, they are applied with a different mindset; for it is personal drive and initiative, a passion and an openness of mind that makes a difference. Those that really transform organizations incite a passion in others, build an organizational capability to view adversity as a challenge, and look for new opportunities in fast-changing environments.
Creating and Sharing the Vision
First and foremost, leaders and managers have to inspire others to think creatively – building and sharing a vision for the future of the information service in a virtual world. As well as painting a picture that describes what future e-services may look like, good managers exhibit leadership and build total commitment, enabling everyone to identify personally with and own the vision, working as a team to achieve it. In inspiring others and in creating a common identity amongst individuals, managers will use creative flair as well as communicating, networking, motivating and leadership skills.
Effective managers are able to create a mental picture of different future scenarios and to visualize the library, its organization and community in a preferred future space. Strategic thinking skills are also necessary in order to capitalize on these ideas through opportunity and innovation, as well as in considering the implications, interdependencies and possibilities of a huge range of issues.
Strategic thinking skills also include inspiring a sense of purpose and direction for others, and encouraging people to think beyond their traditional boundaries to a very different future. Advocacy and championing are also important roles in developing an understanding in others of the organization’s vision, purpose, value and usefulness. Finally, good judgement, intelligence and common sense are required to make the right call and to manage the many varied and sometimes competing issues.
Creating Creative Environments
A creative environment is fostered through leadership and management skills and mindsets that support and actively encourage people to think differently and bring their creative talents and ideas to work. It is based on the philosophy that everyone has the capacities to solve problems in unique ways, to conceive bright ideas and to use entrepreneurial thinking, but many are discouraged to do so. The management role is to encourage creative thinking, and, unlock or free up know-how, talents, skills and expertise in people so that they can be used for everyone’s benefit.
Developing creative and innovative thinking is an activity that should be employed at all levels of management. Senior management need to be innovative in their thinking, whilst building and demonstrating their commitment to a corporate culture that values ideas generation, open communication and entrepreneurial thinking. Management also need to sustain this commitment through their actions year after year – championing their cause, motivating and preparing others to readily accept innovation and change.
Having a Global Perspective
The increasing global focus on external contexts and stakeholder relationships that is a result of the virtual world is driving the need for an innovative and international perspective to e-service delivery. Whilst information has historically been sourced globally, service delivery has tended to be localized. Multinational corporations, virtual operations, international collaboration in approaches to research and development and universal access now mean that service delivery spans continents with its associated management and technical implications for libraries and information centres.
Having a global perspective or mindset entails the ability to look world-wide for opportunities and threats that will have an impact on service delivery and the organization itself. Examples include being prepared to seek answers from elsewhere, delivering e-services to portable devices any time any place in the world, considering best practice in e-service delivery that has worked in other places, being comfortable in managing multicultural environments, being open to ideas and having a global view of the library and information service market.
Instilling a Passion
Instilling passion into organizations is part of the visionary mindset and talent of a good leader. In shaping and driving the strategic directions for the organization, effective leaders demonstrate a passion for what they believe the organization can achieve and instil this in others, whilst having the capacity to remain focused on strategic outcomes in turbulent and changing environments. Passion is also necessary to create enthusiasm. People who have passion demonstrate a natu...