Finance for Non-Finance People
Sandeep Goel
- 430 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Finance for Non-Finance People
Sandeep Goel
Über dieses Buch
Finance is key to every business organisation as well as outside. This book makes sense of the finance world from a non-finance perspective. It introduces, explains and demystifies essential ideas of business finance to those who do not have financial background or training. Lucid, accessible, yet comprehensive, the book delineates the financial workings of businesses and offers an overview of corporate finance in the global context. The volume:
-
- Contains effective tools for financial communication, monitoring, analysis and resource allocation;
-
- Provides important learning aids such as figures, tables, illustrations and case studies;
-
- Highlights fundamental concepts and applications of finance;
-
- Surveys global corporate practices, recent trends and current data.
This updated second edition contains new sections on Tax Planning, including Income Tax and Goods and Services Tax in India. A guide to building financial acumen, this book will be a useful resource for executive and management development programmes (EDPs & MDPs) oriented towards business managers, including MBA programmes. It will benefit business executives, corporate heads, entrepreneurs, government officials, teachers, researchers, and students of management and business, as well as those who deal with finance or financial matters in their daily lives.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
Part I
Introduction
1
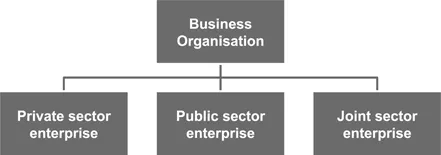
Business organisations
Meaning of business organisation
Types of business organisations