
A Practical Guide to Quasi-elastic Neutron Scattering
Mark T F Telling
- 152 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
A Practical Guide to Quasi-elastic Neutron Scattering
Mark T F Telling
Über dieses Buch
The technique of Quasi-Elastic Neutron Scattering (QENS) is a powerful experimental tool for extracting temporal and spatial information at the nanoscale from both soft and hard condensed matter systems. However, while seemingly simple, the method is beset with sensitivities that, if ill considered, can hinder data interpretation and possibly publication. By highlighting key theoretical and data evaluation aspects of the technique, this specialised 'primer style' training resource encourages research success by guiding new researchers through a typical QENS experiment; from planning and sample preparation considerations to data reduction and subsequent analysis. Research examples are referenced throughout to illustrate the concepts addressed, with the book being written in such a way that it remains accessible to chemists, biologists, physicists, and materials scientists.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
Basics
The technique of quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) is a powerful experimental tool for extracting dynamical information at the nanoscale from both soft and hard condensed matter systems. However, while seemingly simple, the method is beset with sensitivities that, if ill considered, can hinder data interpretation and possibly publication. To start, however, this chapter simply asks “What can QENS do for me?” Key parameters and preliminary experimental considerations necessary to plan a successful neutron scattering experiment are presented, as are research case studies in the areas of chemistry, biology, physics and materials science which expand upon the information that might be extracted using the QENS method.
- Whether the QENS method is suitable for your research.
- Key parameters and preliminary experimental considerations necessary to plan a successful experiment.
- Research examples in the areas of chemistry, biology, physics and materials science.
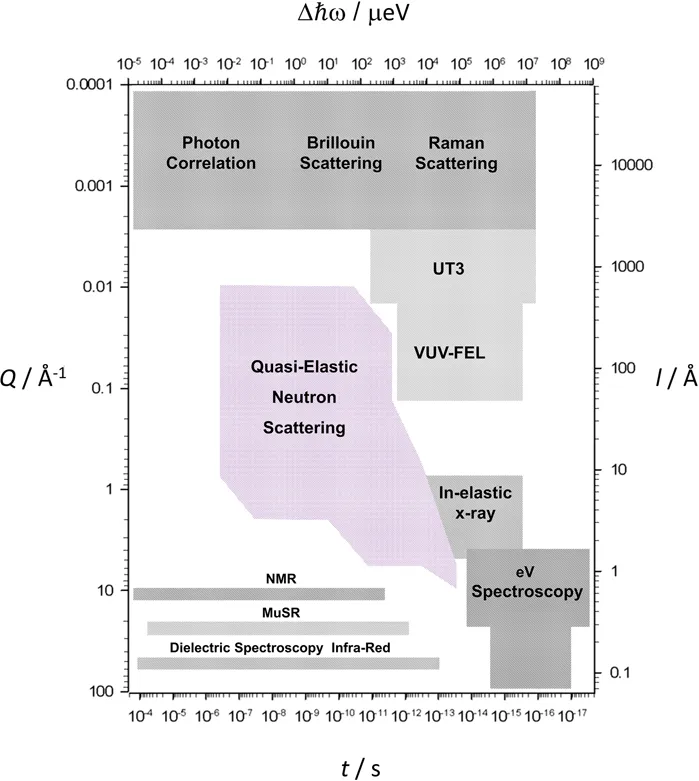
1.1 “What can Quasi-elastic Neutron Scattering Do for Me?”
| Biology | High hydrostatic pressure specifically affects molecular dynamics and shape of low-density lipoprotein particles.27 |
| Research aim | To study the effect of hydrostatic pressure (20–3000 bar) on the molecular dynamics, and shape, of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles; the physicochemical characteristics being relevant for proper functioning of lipid transport in blood circulation. |
| Why QENS? | To assign motions observed on different timescales to different dynamical populations, specific molecules or molecular groups within LDL and under pressure. |
| Additional characterisation/supporting methods |
|
| Main result reported | LDL copes well under high pressure conditions, although the lipid composition impacts the molecular dynamics and shape arrangement of the lipoprotein. |
| Instrument(s)/facility(ies) used and reported upper experimental observation time(s) |
|
| Biolo... |