![]()
Part I
Overview of modern gas turbine systems
![]()
1
Introduction to gas turbines
A.J.A. Mom, European Turbine Network ETN, Belgium
Abstract:
This chapter provides an overview of the importance of gas turbines for the power generation and oil and gas sector and – in less detail – the aviation sector. Worldwide trends in power generation and electricity conversion processes and the role of gas turbines to minimise CO2 emissions are addressed. Gas turbines are essential and crucial to reduce emissions both in aviation and in power production. Technologies for improving gas turbine and system efficiency, through higher turbine inlet temperatures, improved materials, cooling methods and thermal barrier coatings are described. New thermodynamic approaches, including intercooling, water and steam injection and hybrid cycles are addressed. Major issues are also fuel and operational flexibility, reliability and availability, cost reduction and power density, especially for the offshore sector. Market trends have been sketched. In the coming decades, gas turbines will be one of the major technologies for CO2 emission reductions in the power generation, aviation, oil and gas exploration and transport sectors. This prognosis is based on their high current efficiency and further efficiency improvement potential, both for simple cycle as for combined-cycle applications.
Key words
aircraft propulsion
simple and combined cycle efficiency
NOx reduction
450 scenario
global warming
zero carbon emission
IGCC
CO2 capture
life cycle costs
hybrid cycles
bottoming cycles
fuel flexibility
operational flexibility
carbon capture and storage
hydrogen
1.1 Introduction
In modern society there is still little appreciation of what a gas turbine is or does. This is in contrast to diesel or gasoline engines, the so-called reciprocating engines, since most people know that these are the motors which drive our cars and trucks. Despite this general lack of recognition, gas turbines are essential to everyday life. Modern air traffic would not exist without gas turbines, and we would also have serious shortages in electricity production without them.
So what is a gas turbine? It is an internal combustion engine that burns gaseous or liquid fuel. It delivers the energy of this combustion either by means of thrust, in an aircraft jet engine; or – by means of a rotating shaft – it provides (a) electricity via a generator, or (b) mechanical power for driving compressors or ship propulsion.
Most aircraft engines are now gas turbines. In the early part of the twentieth century reciprocating (gasoline) engines were used as the main propulsion units for aircraft, but this changed after the World War II. Nowadays, civil and military airplanes, helicopters and business jets all use gas turbines because of their superior thrust/weight ratio. Only the small general aviation aircraft still use reciprocating engines.
In the power generation sector, gas turbines have also become the main technology for conversion of fossil fuels into electricity. Conventional gas- and oil- fired steam plants have been replaced by very efficient combined-cycle power plants using gas turbines for the combustion of gas or oil. The combined-cycle works as follows. Firstly, the gas turbine drives a generator, delivering two-thirds of the total power output. Secondly, the hot exhaust gas from the turbine passes through a boiler to produce steam that drives a steam turbine and a coupled generator. This secondary system delivers the remaining third of the total power output of the combined-cycle power plant. An important variation is cogeneration, or combined heat and power. In this case, the steam produced in the boiler is used for process heat. There are many applications for co-generation, for example, in the paper, process and food and beverage industries.
Apart from these major areas, gas turbines are also used in a variety of other applications. In the oil and gas sector, gas turbines drive compressors or pumps for gas- and oil-processing and transport. Furthermore, gas turbines often power fast ferries and military vessels owing to their superior power/weight ratio. There is also a new trend to apply very small gas turbines for pre-firing in central heating systems.
1.2 The importance of gas turbines for worldwide CO2 reduction
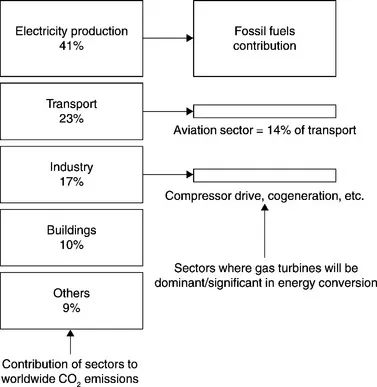
Gas turbine technology is very important in terms of future worldwide reduction of CO2 emissions. In the power generation sector, which is the greatest contributor to CO2 emissions, CO2 reduction is currently the driving factor, see Fig. 1.1. If worldwide CO2 emissions have to be reduced by 20% in 2020, and by more than 50% in 2050, then gas turbines will surely play a crucial role, owing to their high efficiency and fuel flexibility.
1.1 Sources of worldwide CO2 emissions and potential of gas turbines (in 2010).
In the aviation sector, propulsion is delivered principally by gas turbines, as mentioned earlier. There is massive political pressure to make air transport cleaner, both in terms of noise reduction as well as fuel reduction, and hence reduced CO2 and NOx emissions. Gas turbine technology improvements will be crucial here too.
Overall, it can be seen from Fig. 1.1 that gas turbines play, or will play, an important role in the sectors, responsible for about 50% of the total worldwide CO2 emissions. It is evident that these very ambitious goals for reducing CO2 emissions cannot be achieved without full exploitation of advanced gas turbine technology.
Although this book addresses ...