
eBook - ePub
Environmental Monitoring and Characterization
Janick Artiola, Ian Pepper, Mark L. Brusseau
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 410 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Environmental Monitoring and Characterization
Janick Artiola, Ian Pepper, Mark L. Brusseau
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Environmental Monitoring and Characterization is an integrated, hands-on resource for monitoring all aspects of the environment. Sample collection methods and relevant physical, chemical and biological processes necessary to characterize the environment are brought together in twenty chapters which cover: sample collection methods, monitoring terrestrial, aquatic and air environments, and relevant chemical, physical and biological processes and contaminants.
This book will serve as an authoritative reference for advanced students and environmental professionals.
- Examines the integration of physical, chemical, and biological processes
- Emphasizes field methods and real-time data acquisition, made more accessible with case studies, problems, calculations, and questions
- Includes four color illustrations throughout the text
- Brings together the concepts of environmental monitoring and site characterization
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Environmental Monitoring and Characterization als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Environmental Monitoring and Characterization von Janick Artiola, Ian Pepper, Mark L. Brusseau im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Ciencias biológicas & Ciencia medioambiental. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
1 MONITORING AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE ENVIRONMENT
THE ENVIRONMENT
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING
ENVIRONMENTAL REMEDIATION AND RESTORATION
SCALES OF OBSERVATION
AGENCIES
CURRENT AND FUTURE STATUS OF ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING
PURPOSE OF THIS TEXTBOOK
REFERENCES AND ADDITIONAL READING
THE ENVIRONMENT
Environmental changes occur naturally and are a part of or the result of multiple cycles and interactions. Numerous natural cycles of the earth’s environment have been studied within the framework of three major scientific disciplines: chemistry, physics, and biology. Environmental scientists study the dynamics of cycles, such as the nitrogen and water cycles, and their relationships to soil-geologic materials, surface waters, the atmosphere, and living organisms. The untrained observer may see the atmosphere as being separated from the earth’s surface. However, to the trained observer the environment is composed of integrated and interconnected cycles and domains. We now know that the environment is a continuum of physical, chemical, and biological processes that cannot be easily separated from one another. Water, for example, exists in three states and is found inside and on the surface of earth’s crust, in the atmosphere, and within living organisms. It is difficult to separate the physical, chemical, and biological processes of water within any particular environment, because water is transferred across boundaries.
Humans now have a more holistic view of the environment and recognize that many factors determine its health and preservation. This in turn has led to the new term biocomplexity, which is defined as “the interdependence of elements within specific environmental systems, and the interactions between different types of systems.” Thus, research on the individual components of environmental systems provides limited information on the system itself. We are now also concerned with sustainable and renewable versus non-renewable natural resources as well as with biodiversity in relation to our own survival.
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING
Environmental monitoring is the observation and study of the environment. In scientific terms, we wish to collect data from which we can derive knowledge (Figure 1.1). Thus, environmental monitoring has its role defined in the first three steps of the staircase and is rooted in the scientific method. Objective observations produce sound data, which in turn produce valuable information. Information-derived knowledge usually leads to an enhanced understanding of the problem/situation, which improves the chances of making informed decisions. However, it is important to understand that other factors, including political, economic, and social factors, influence decision making.
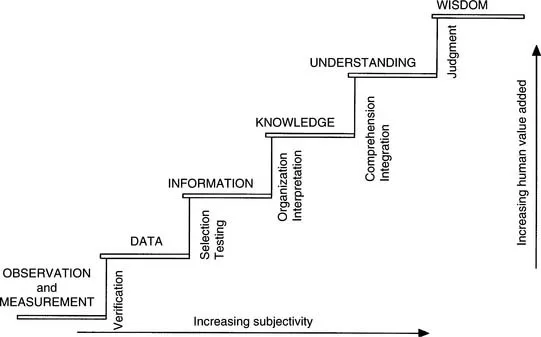
FIGURE 1.1 The staircase of knowing. Science-based observations and measurements improve our understanding of the environment and lead to wise decision-making.
(From Roots, E.F. (1997) Inclusion of different knowledge systems in research. In: Terra Borealis. Traditional and Western Scientific Environmental Knowledge. Workshop Proceedings, Northwest River, Labrador 10 & 11 Sept. 1997. No. 1. Manseau M. (ed), Institute for Environmental Monitoring and Research, P.O. Box 1859, Station B Happy Valley–Goose Bay Labrador, Newfoundland, AOP E10. Terra Borealis 1:42–49, 1998.)
The information generated from monitoring activities can be used in a myriad of ways, ranging from understanding the short-term fate of an endangered fish species in a small stream, to defining the long-term management and preservation strategies of natural resources over vast tracts of land. Box 1.1 lists some recognizable knowledge-based regulations and benefits of environmental monitoring.
BOX 1.1 Knowledge-Based Regulation and Benefits of Environmental Monitoring
Protection of public water supplies: Including surface and groundwater monitoring; sources of water pollution; waste and wastewater treatment and their disposal and discharge into the environment
Hazardous, nonhazardous and radioactive waste management: Including disposal, reuse, and possible impacts to human health and the environment
Urban air quality: Sources of pollution, transportation, and industrial effects on human health
Natural resources protection and management: Land and soil degradation; forests and wood harvesting; water supplies, including lakes, rivers, and oceans; recreation; food supply
Weather forecasting: Anticipating weather, long- and short-term climatic changes, and weather-related catastrophes, including floods, droughts, hurricanes, and tornadoes
Economic development and land planning: Resources allocation; resource exploitation
Population growth: Density patterns, related to economic development and natural resources
Delineation: Mapping of natural resources; soil classification; wetland delineation; critical habitats; water resources; boundary changes
Endangered species and biodiversity: Enumeration of species; extinction, discovery, protection
Global climate changes: Strategies to control pollution emissions and weather- and health-related gaseous emissions
Although Box 1.1 is not exhaustive, it does give an idea of the major role that environmental monitoring plays in our lives. Many of us are rarely aware that such regulations exist and that these are the result of ongoing monitoring activities. Nonetheless, we all receive the benefits associated with these activities.
Recently, environmental monitoring has become even more critical as human populations increase, adding ever-increasing strains on the environment. There are numerous examples of deleterious environmental changes that result from population increases and concentrated human activities. For example, in the United States, the industrial and agricultural revolutions of the last 100 years have produced large amounts of waste by-products that, until the late 1960s, were released into the environment without regard to consequences. In many parts of the developing world, wastes are still disposed of without treatment. Through environmental monitoring we know that most surface soils, bodies of waters, and even ice caps contain trace and ultratrace levels of synthetic chemicals (e.g., dioxins) and nuclear-fallout components (e.g., radioactive cesium). Also, many surface waters, including rivers and lakes, contain trace concentrations of pesticides because of the results of agricultural runoff and rainfall tainted with atmospheric pollutants. The indirect effects of released chemicals into the environment are also a recent cause of concern. Carbon dioxide gas from automobiles and power plants and Freon (refrigerant gas) released into the atmosphere may be involved in deleterious climatic changes.
Environmental monitoring is very broad and requires a multi-disciplinary scientific approach. Environmental scientists require skills in basic sciences such as chemistry, physics, biology, mathematics, statistics, and computer science. Therefore, all science-based disciplines are involved in this endeavor.
ENVIRONMENTAL REMEDIATION AND RESTORATION
Environmental remediation and restoration focus on the development and implementation of strategies geared to reverse negative environmental impacts. Anthropogenic activities often perturb environments and severely limit their capacity for regeneration. For exam...