Phytomicrobiome Interactions and Sustainable Agriculture
Amit Verma, Jitendra Kumar Saini, Harikesh Bahadur Singh, Abd El-Latif Hesham, Amit Verma, Jitendra Kumar Saini, Harikesh Bahadur Singh, Abd El-Latif Hesham
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Phytomicrobiome Interactions and Sustainable Agriculture
Amit Verma, Jitendra Kumar Saini, Harikesh Bahadur Singh, Abd El-Latif Hesham, Amit Verma, Jitendra Kumar Saini, Harikesh Bahadur Singh, Abd El-Latif Hesham
Über dieses Buch
A guide to the role microbes play in the enhanced production and productivity of agriculture to feed our growing population
Phytomicrobiome Interactions and Sustainable Agriculture offers an essential guide to the importance of 'Phytomicrobiome' and explores its various components. The authors – noted experts on the topic – explore the key benefits of plant development such as nutrient availability, amelioration of stress and defense to plant disease. Throughout the book, the authors introduce and classify the corresponding Phytomicrobiome components and then present a detailed discussion related to its effect on plant development: controlling factors of this biome, its behaviour under the prevailing climate change condition and beneficial effects.
The book covers the newly emerging technical concept of Phytomicrobiome engineering, which is an advanced concept to sustain agricultural productivity in recent climatic scenario. The text is filled with comprehensive, cutting edge data, making it possible to access this ever-growing wealth of information. This important book:
- Offers a one-stop resource on phytomicrobiome concepts
- Provides a better understanding of the topic and how it can be employed for understanding plant development
- Contains a guide to sustaining agriculture using phytomicrobiome engineering
- Presents information that can lead to enhanced production and productivity to feed our growing population
Written for students, researchers and policy makers of plant biology, Phytomicrobiome Interactions and Sustainable Agriculture offers a clear understanding of the importance of microbes in overall plant growth and development.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
1
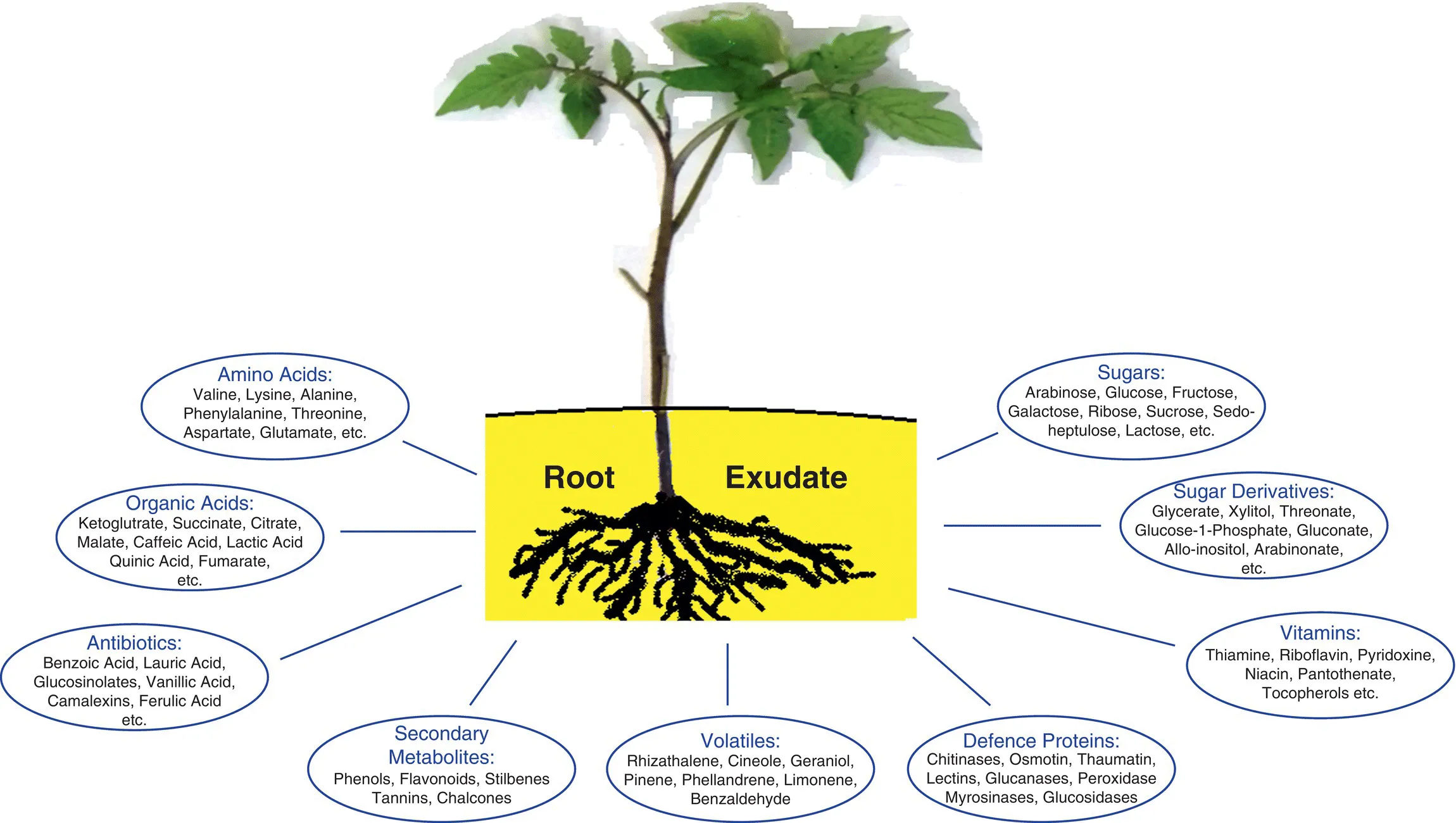
Plant Root Exudate Analysis: Recent Advances and Applications
1.1 Introduction