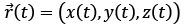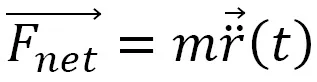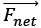Extending and Modifying LAMMPS Writing Your Own Source Code
Dr. Shafat Mubin, Jichen Li, Dr. Steven Plimpton
- 394 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Extending and Modifying LAMMPS Writing Your Own Source Code
Dr. Shafat Mubin, Jichen Li, Dr. Steven Plimpton
Über dieses Buch
Understand the LAMMPS source code and modify it to meet your research needs, and run simulations for bespoke applications involving forces, thermostats, pair potentials and more with easeKey Features• Understand the structure of the LAMMPS source code• Implement custom features in the LAMMPS source code to meet your research needs• Run example simulations involving forces, thermostats, and pair potentials based on implemented featuresBook DescriptionLAMMPS is one of the most widely used tools for running simulations for research in molecular dynamics. While the tool itself is fairly easy to use, more often than not you'll need to customize it to meet your specific simulation requirements. Extending and Modifying LAMMPS bridges this learning gap and helps you achieve this by writing custom code to add new features to LAMMPS source code. Written by ardent supporters of LAMMPS, this practical guide will enable you to extend the capabilities of LAMMPS with the help of step-by-step explanations of essential concepts, practical examples, and self-assessment questions. This LAMMPS book provides a hands-on approach to implementing associated methodologies that will get you up and running and productive in no time. You'll begin with a short introduction to the internal mechanisms of LAMMPS, and gradually transition to an overview of the source code along with a tutorial on modifying it. As you advance, you'll understand the structure, syntax, and organization of LAMMPS source code, and be able to write your own source code extensions to LAMMPS that implement features beyond the ones available in standard downloadable versions. By the end of this book, you'll have learned how to add your own extensions and modifications to the LAMMPS source code that can implement features that suit your simulation requirements.What you will learn• Identify how LAMMPS input script commands are parsed within the source code• Understand the architecture of the source code• Relate source code elements to simulated quantities• Learn how stored quantities are accessed within the source code• Explore the mechanisms controlling pair styles, computes, and fixes• Modify the source code to implement custom features in LAMMPSWho this book is forThis book is for students, faculty members, and researchers who are currently using LAMMPS or considering switching to LAMMPS, have a basic knowledge of how to use LAMMPS, and are looking to extend LAMMPS source code for research purposes. This book is not a tutorial on using LAMMPS or writing LAMMPS scripts, and it is assumed that the reader is comfortable with the basic LAMMPS syntax. The book is geared toward users with little to no experience in source code editing. Familiarity with C++ programming is helpful but not necessary.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
Section 1: Getting Started with LAMMPS
- Chapter 1, MD Theory and Simulation Practices
- Chapter 2, LAMMPS Syntax and Source Code Repository
Chapter 1: MD Theory and Simulation Practices
- Introducing MD theory
- Understanding the dynamics of point particles
- Performing iterative updates using the Velocity Verlet algorithm
- Understanding rotational motion
- Examining temperature and velocity distribution of particles
- Implementing MD simulation practices including cutoff, periodic boundaries, and neighbor lists
Technical requirements
Introducing MD theory
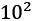
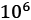
Understanding the dynamics of point particles