Introduction to Sensors
Ambika Nagaraj Abstract
Sensors are tiny, low-cost devices engaging themselves to monitor the environment in many applications. Their assembly is programmed to gather sensory information and move data to the predefined destination. The readings received by the sensors are gathered by the gateway node and redirected to the data processing module. They further parse the directions and send the information to the Sink node. This chapter details the working of these devices in various applications and the challenges faced by them. It also provides an overview of the book. Like any domain or sensors that have shortcomings are worked upon to provide flexibility and ease.
Keywords: Applications, Challenges, Wireless sensor network.
INTRODUCTION
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) [1] known as Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) [2] is the collection of smart devices. The nodes in this distribution are spatial to perform an application-oriented task. This development is a result of the miniaturization of computing and sensing technologies that enables the growth of low-power and inexpensive instruments. These tiny devices are deployed in the environment to monitor or track any object of interest. Their deployment in the network is in an inactive state. They self-configure, communicate with the nodes within the short-range, and constitute their topology. Sensors are assembly collection of the conceivably high number of detecting nodes, imparting remote multi-jump design [3]. Exceptional nodes called cluster heads [4] assemble the results and forward them to the next available hop. They aid in infrastructure failures, conserve natural resources, increase productivity, enhance security, and enable the growth of a new series of applications. Depending on the type of network they are deployed in, the sink and the node count vary in number. It collects the required readings, processes them, and disseminates them. They monitor real-time physical conditions, including temperature, humidity, sound, intensity, and vibration. Another positive aspect is that these devices can go global by giving live readings of the environment. Like every technology, these sensors also carry the burden of their drawbacks. Energy, power, security, storage space are some of the disadvantages that need working.
BACKGROUND
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) can understand the short-distance correspondence between their community devices by building remote systems in impromptu habits. It is troublesome to associate them and versatile correspondence systems (Internet). It is because of its absence of uniform institutionalization in correspondence conventions. The detection advancements and the information from WSN cannot be transmitted in long separation considering the constraint of WSN transmission conventions. Internet-of-Things (IoT) provided an answer to these questions. Thus, with the improvement of the Internet-of-Things, another system gear called the Internet-of-Things Gateway is developed. Their objective is to settle with the heterogeneity between different sensor systems and portable correspondence systems. It also fortifies the administration of the WSN with the terminal device and scaffolds customary correspondence systems with sensor systems. The procedure makes it easier to deal with the gadgets of sensor systems.
Internet-of-Things is a dynamic and a Global Networked Infrastructure arrangement that manages self-designing nodes with high Intelligence. Intelligent sensors work together to convert this present reality variable and transmit the estimated values into a digital information stream for transmission to a passage. The inherent microchip unit knowledge usage in different capacities has made it acceptable. It can decrease the heap on its progressively focal assets. They can detect any creation parameters that begin to float past satisfactory standards and produce alerts in like manner. These devices made of large little items are with a constrained Memory stockpiling and computing limit. Their description of an authentic world is noteworthy in regards to Privacy, Performance, Scalability, and Reliability.
Another issue that the sensors face is low memory capacity. Cloud infrastructure provides answers to these issues faced by the sensor technology. Cloud Computing is an immense future with unlimited storage, considering stockpiling and calculation controls. Distributed computing is a plan of action to engage ubiquitously, on-request organization access to an assortment of configurable figuring assets. Some of the examples include stockpiling, administrations, maintaining servers, and applications that can immediately provide noteworthy administration. Cloud computing has been innovative with notable suggestions for the conveyance of the Internet. Information supervision by cloud administrations secures the system. It can supervise an enormous number of gadgets and hence help the maintenance of large scale assembly and its applications.
Distributed computing, on wheels, is known as Mobile cloud computing. With the blast of portable applications and the help of Cloud computing, the system handles an assortment of administrations for versatile clients. Mobile clients amass rich experience of different administrations from versatile applications. These systems run on the gadgets as well as on remote servers through the isolated systems. Lately, practices focused on cell phones have begun getting inexhaustible with applications of different classes. Some examples include amusement, games, business, informal communication, travel, and news.
The fog adds extra fuel to cloud technology. It empowers the computation at the edge of the system. It can convey new executions and administrations. In fog processing, offices or foundations that are assets to administrations on the verge of the system are called fog devices. The switches can work as the latest servers.
WORKING OF SENSORS IN DIFFERENT APPLICATIONS
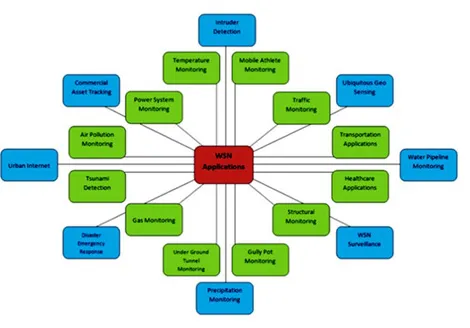
The ongoing development of the Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) [1, 5, 6] and remote correspondence innovation makes it to convey on an enormous scale, low power, reasonable sensory organization. Such a methodology guarantees an advantage over the traditional detecting techniques in numerous ways. The large-scale organization has not just expanded spatial inclusion and accomplishes higher goals, but it also builds the adaptation to non-critical failure of the framework. The system makes it much increasingly appealing in military applications [7] and other hazard related applications like territory checking and ecological perception [8]. Fig. (1) portrays the implementation of the wireless sensor network. The exercise in the blue box uses different technologies in an assembly. The applications in the green box can use the same category of devices. The practice is widely used and explained below.
Intrusion Detection
An intrusion identification framework recognizes and reports a suspected activity in its discovery region. These frameworks are regularly coordinated with other physical security frameworks and depend on IT frameworks with Internet abilities. Three crucial parts of this kind of system are the sensor, control unit, and annunciator. Sensors distinguish invasion using various measures. The control unit gets the caution warning from the sensor and afterward actuates a quiet alert, or the annunciator will create a warning (e.g., in the form of a light or alarm).
Many detection systems are suggested by various authors to protect the system from intrusion. In the first scheme [10], the authors detail the assault resistance issue as a two-player, nonzero-sum, non-agreeable game between an assailant and a sensor. In the first stage, a non-helpful game between the assailant and sensor hub's suggestion highlights the work. By utilizing the game hypothesis structure, the game accomplishes Nash equilibrium for the two- aggressors and IDS. The second scheme is known as the interruption discovery structure. It is dependent on Markov Decision Process. The system consolidates a learning system. In the starting, IDS watches the framework and learns the conduct of the adversary, and attempts to choose which hub that needs insurance. If it ensures that the assailant is trying to assault, the assault is made ineffective. However, if an aggressor strikes an unexpected hub in comparison to the sensor device, then it becomes fruitful. The third scheme has the utilization of a natural measurement. Traffic load is measured, and IDS decides to secure the hub, which has the most elevated measure of traffic load. The work simulation has 20-200 cluster heads. Pentium III having CPU 1133 MHz usage collects the readings in the required environment.
Fig. (1)) Applications of wireless sensor network [
9].
The interruption location framework [11] follows an appropriate design. It makes indistinguishable IDS customers running in every hub of the system. At that point, the IDS customers speak with one another to arrive at a resolution on an interruption occasion. Every customer follows a particular based methodology to recognize assaults. It distinguishes deviations from typical conduct given in the client characterized rules. The system director needs to differentiate and insert the bits by comparing each strike that the IDS ought to identify. Because of its nearsighted vision around its neighborhood, a hub will most likely be unable to settle on an executive choice. The proposal contains 100 randomly distributed nodes. It runs 1000 times to arrive at the watchdog with a unique ID. Mica2 (TinyOS) required 1.5KB of RAM and 3.9KB of ROM. The nodes are connected using MintRoute.
Ubiquitous Geo Sensing
Universal Geo-detection empowers the comprehension of the perplexing connections between aggregate human movement and climate designs. It can give bits of knowledge into essential procedures or cause-impact association. Some examples include instances of crisis supervisors who require time-basic choice help, open transportation administrators require the successful assignment of assets to upgrade the traffic stream, for project leads to help business insight.
One of the works [12] recognizes the impediments of existing impromptu based methodologies for preparing numerous total questions. It proposes emerged materialized in-network (MINVs) and related access procedures. The procedures include full scanning, replication cluster, and prefix sum.
GeoSENS [13] is a pairwise key foundation convention utilizing the zone data of the district in with sensor systems deployment. Dozens of utilization in a locale is considerably enormous than the sensor remote transmission territory with an overhead of putting away more keys in sensors.
Commercial Asset Tracking
Mechanized stock administration and resource tracking issues with traditional techniques include collecting, storing, and recovering data.
This procedure implementation is an enormous number of components in an organization, association, or foundation. A benefit portrayed by these systems is that they are remarkably identifiable. Some examples include framework depiction, physical area, or proprietor data. The advantage has a lot of recognizing attributes related to the defined identification number (series of numbers, characters, or a mix of both). As a couple, this information mapping (identification number and qualities) commonly goes into a database physically or utilizing a standardized tag framework.
The RFID framework and the remote sensor assembly have been coordinated in a study [14]. The commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) RFID framework gave various choices to coordinate with a remote sensor. The RS232 association fulfills the purpose of information, correspondence since the secluded sensor foundation offers a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) at a similar piece rate. The additional circuit acquaints with the interface. The UART of the remote sensor with the RS232 association of the ...