![]()
Part I
SELL WALKABILITY
SELLING WALKABILITY as a community goal is not as hard as it used to be, but there is always opposition, typically from the usual suspects: the automotive hordes, tinfoil-hat-wearing Agenda-21 conspiracy theorists, tea-baggers, and the like. Somehow, while a central government investing in highways and subsidizing oil companies constitutes freedom, any local investment in sidewalks and bike lanes smacks of a communist takeover.
The inevitability of some pushback, however ill-informed, means that walkability proponents need to be armed with the best arguments in its support. Five stand out: Economics, Health, Climate, Equity, and Community. The first three are discussed at great length in Walkable City; the last two are recent additions for more sophisticated audiences. All are helpful at winning converts.
![]()
1
Sell Walkability on Wealth
There are powerful economic reasons to invest in walkability.
IMPROVING WALKABILITY costs money, and budgets are tight. The first step in convincing community leaders to invest in walkability is to demonstrate that such investments pay off. Evidence abounds and can be mustered in support of a handful of powerful arguments.
Walkability powers property values. One of the clearest correlations in real estate is between walkability and home value. As a typical example, homes in Denver’s walkable neighborhoods sell at a 150% premium over those in drivable sprawl.2 In Charlotte, each Walk Score point (on a scale of 100) translates into about a $2,000 increase in home value.3 Home values determine local property-tax revenue, justifying investments in walkability. Additionally, office space in walkable zip codes has a considerable leasing rate premium over suburban locations, and much lower vacancy rates.4
Walkability attracts talent. Educated millennials value walkability, and are moving to more walkable places. 64% of them choose first where they want to live, and only then do they look for work;5 77% say they plan to live in an urban core.6 According to a recent study, a full 63% of millennials (and 42% of baby boomers) want to live in a place where they don’t need a car.7 Companies and cities that wish to attract young talent need to provide the walkable urban lifestyle they desire.
Investments in walkability create more, and better, jobs. A study of transportation projects in Baltimore found that, compared to highway investments, each dollar spent on pedestrian facilities created 57% more jobs, and each dollar spent on bicycle facilities created 100% more jobs.8 Once built, walkable places have stronger economies. One recent study documents that America’s most walkable metros generate 49% more GDP per capita than its least walkable metros.9
Car-dependent cities make their citizens poorer… but they also make themselves poorer through the large hidden subsidies that automobiles require.
Car culture doesn’t pay. It has been estimated that, between 1970 and 2010, we have doubled the amount of roadway in America. Over the same years, the typical American family has doubled the percentage of its income spent on transportation—from 10% to 20%.10 By burdening most Americans with mandatory car ownership, our suburban landscape has contributed markedly to the cash-strapped condition of contemporary life.
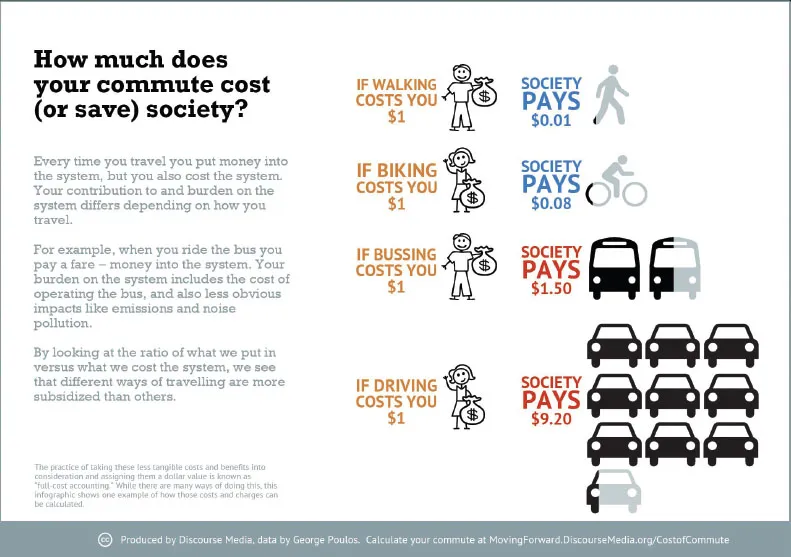
Walking creates positive externalities. All transportation is subsidized—the question is, how much? Walking and biking require sidewalks and bike lanes, but these represent little more than a rounding error when compared to the cost of our roads. Meanwhile, the externalities of driving are clear and huge, including the costs of policing, ambulances, hospitals, time wasted in traffic, and climate change. The externalities of walking and biking are principally those that come from a healthier population. The City of Copenhagen calculates that every mile driven by car costs the city 20 cents, while each mile biked earns the city 42 cents.11 While not all externalities can be monetized, their substantial long-term impacts—like sea-level rise—represent an economic future that cities ignore at their peril.
RULE 1: When advocating for walkability, use the arguments of property value, talent attraction, job creation, transportation costs, and subsidies/externalities.
![]()
2
Sell Walkability on Health
There are powerful health reasons to invest in walkability.
THE BEST DAY TO BE A CITY PLANNER IN AMERICA was July 9, 2004, when Howard Frumkin, Lawrence Frank, and Richard Jackson came out with their book, Urban Sprawl and Public Health. In it, the authors made it clear that so much of American morbidity was a result of the fact that, in much of this country, we have designed out of existence the useful walk. That important book, and others that have been published since, document how the American health care crisis is largely an urban design crisis, with walkability at the heart of the cure.
The health benefits of having a more walkable community are measurable and huge, and include the following:12
Americans are almost four times as likely to die in a car crash than Britons or Swedes.
Walkable communities are slimmer communities. America faces an obesity epidemic that can be linked directly to suburban sprawl. The lower a community’s Walk Score, the more likely its residents are to be overweight.13 Any investment that makes a city more walkable is likely to make it less obese as well.
Slimmer communities have lower health care costs. While a concern in its own right, obesity is most costly due to the diseases that it causes or makes worse. These include diabetes, coronary disease, hypertension, gallstones, osteoarthritis, and a variety of cancers. Treating these maladies is extraordinarily expensive, and most of these costs are borne by society and by municipalities themselves. When cities become more walkable, we all benefit.
The fact that we don’t think twice about taking the car to the parking lot to the escalator to the treadmill in order to walk is one reason why we now have the first generation of Americans expected to live shorter lives than their parents.
Walkable communities save lives. Car crashes kill a remarkable 1.25 million humans each year. In 2017, more than 40,000 of these were Americans—a new record. While most of us take such deaths for granted, it is eye-opening to compare the United States to other developed nations that are less car-dependent. Americans are almost four times as likely to die in a car crash as Britons or Swedes.14 This is due principally to the design of our cities: the more walkable, the fewer deaths. For this same reason, you are almost four times as likely to die on the road in Memphis or Orlando as in New York or Portland.15 Year after year, the evidence shows us that it is the cities shaped around automobiles that are the most effective at smashing them into each other.
Air pollution deaths are also an outcome of community design. Approximately 40 million Americans—13% of us—suffer from asthma, and its economic cost is estimated at $56 billion in the United States alone.16 But asthma is responsible for only a fraction of the 200,000 annual “premature deaths” that are attributed to air pollution. One M.I.T. study found that the leading cause of these deaths was vehicle emissions.17 Unlike a generation ago, most air pollution now comes not from factories, but from driving.18 To the lives potentially saved by reducing car crashes, we can add even a larger number saved by reducing auto exhaust. Both are outcomes of making more walkable cities.
RULE 2: When advocating for walkability, use public health arguments including those related to obesity, health care costs, and the death rates from car crashes and air pollution.
![]()
3
Sell Walkability on Climate Change
There are powerful environmental reasons to invest in walkability.
AS LOVERS OF CITIES, most urban planners have had their challenges dealing with environmentalists, because, ...