![]()
Part I
Big Picture: On 21st Century Realities
![]()
Rebuilding Economic and Political Capital for EU Integration
Silvia Merler
Europe has been divided for much of its history, until the creation of the European Union introduced a ‘new’ peaceful and cooperating reality. In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize “for over six decades [having] contributed to the advancement of peace and reconciliation, democracy and human rights in Europe”. The announcement came at a time when the hardship of navigating through the economic crisis was putting enormous strain on political cohesion within the EU. Today, as new challenges emerge, the EU appears to be more divided than ever since its creation. The divide is especially evident in the eurozone, where integration was the strongest before the crisis, and where economic, social and political divides persist today. At the broader EU level, strong centripetal forces were evident in the UK’s urgency to renegotiate its ‘status’ within the EU and in the increasingly frequent tensions over the management of the refugee crisis. This contribution focuses on the eurozone, where the sharing of a single currency induces the deepest economic integration and imposes the need for the strongest political cohesion. It will look at the recent trends of Europeans’ trust and satisfaction with the EU project and link them with the ongoing economic challenges, with the aim of highlighting relevant policy priorities.
The Fading European Political Capital
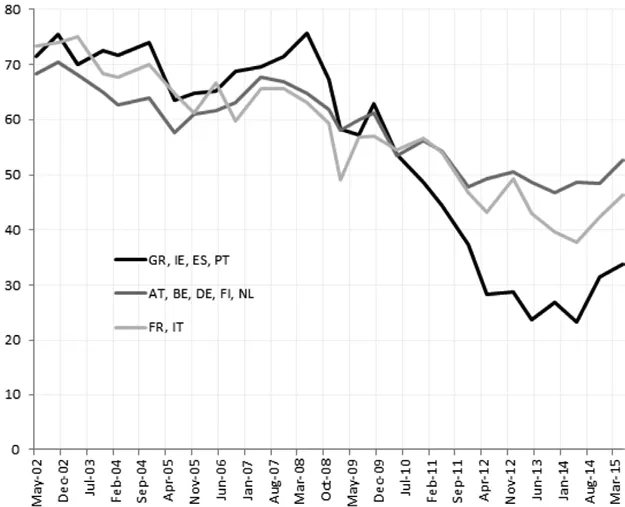
For a supranational union such as the EU, the trust of Europeans in EU institutions is an especially important metric of legitimacy. Data from the European commission’s Eurobarometer survey shows that trust in the European institutions has been declining everywhere across eurozone member states since the beginning of the crisis, although more markedly so in those countries that have undergone adjustment programmes. In 2008 – before the outbreak of the global financial crisis – almost 75 per cent of respondents across Greece, Ireland, Portugal and Spain declared they tended to trust the European parliament, the European commission and the European Central Bank (ECB). By the end of 2013, the percentage had dropped to only 25 per cent on average across the same countries. Figure 1.1 suggests that trust levels in EU institutions bounced back in 2014 and 2015 in the programme countries, as well as in France and Italy (where it had declined but less markedly). Across those countries on which the impact of the eurozone crisis was less traumatic – ie Austria, Belgium, Germany, Finland and the Netherlands – trust in EU institutions decreased between 2008 and 2011 and has remained flat since then (see Figure 1.1).
Figure 1.1 Percentage of Respondents Who Declare to Trust in EU Institutions.
Source: Author’s calculations based on data from Eurobarometer; percentages are computed out of those who expressed a clear opinion (“don’t know” answers are not counted). Note: Groups are constructed as averages weighted by population.
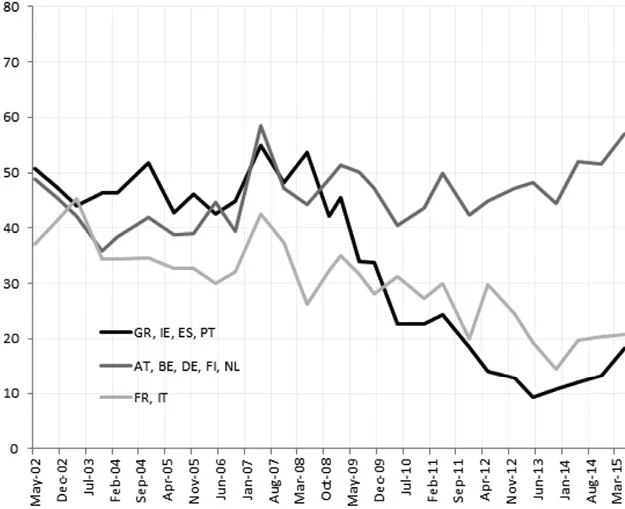
Trust in national institutions appears to have been historically lower than trust in European institutions, with only 55–60 per cent of respondents declaring trust at the pre-crisis peak in 2007. Since then, things have evolved very differently across Europe. National institutions have lost sizable amount of trust in programme countries as well as in France and Italy, whereas they have gained in trust compared to EU institutions across those countries that were less severely affected by the crisis (see Figure 1.2).
Figure 1.2 Percentage of Respondents Who Declare to Trust in National Institutions.
Source: Author’s calculations based on Eurobarometer data.
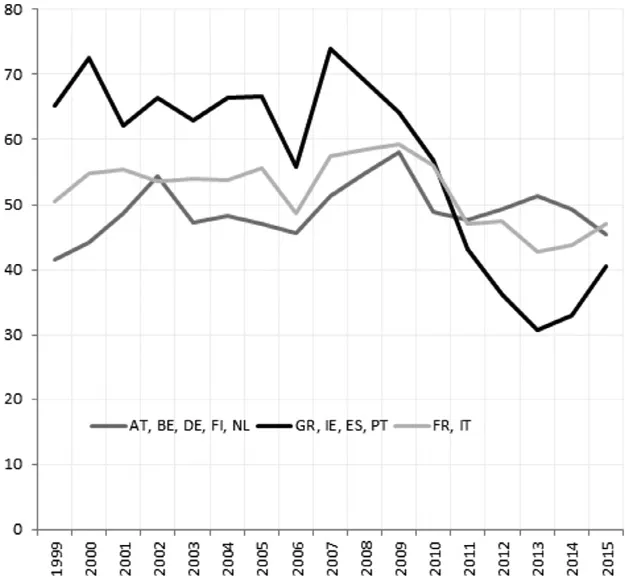
Figure 1.3 Percentage of Respondents Who Declare to Be Satisfied with Democracy in the EU. Source: Author’s calculations based on Eurobarometer data.
Particularly worrisome for a union that holds democracy among its core founding values, Europeans appear very dissatisfied with the way democracy works in the EU and in their own countries. The percentage of Eurobarometer respondents declaring to be “very satisfied” or “fairly satisfied” with “democracy in the EU” dropped from 75 per cent in 2007 to 30 per cent in 2013 across those countries that underwent macroeconomic adjustment programmes. Satisfaction with democracy in citizens’ home countries has been in free fall since 2007, dropping from 70 per cent to 25 per cent in 2013. The latest data suggests a rebound in satisfaction with democracy at both the EU and country level, but the rebound is from a very low level and it might still be fragile (Figure 1.3).
The Economic and Social Roots of the Divide
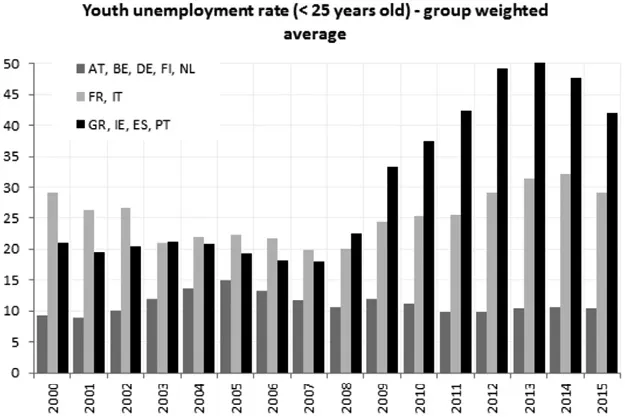
Europeans’ evident distrust and dissatisfaction with the EU is strongly grounded in the economic crisis and its sizable social impact. The crisis brought back unemployment levels that had not been seen for a very long time. The unemployment rate for the Eurozone as a whole grew from 7.5 per cent in 2007 to 12 per cent in 2013, but the increase was very unbalanced across countries, with the figure reaching as high as 26–27 per cent in Greece and Spain. Moreover, unemployment hit the young generations especially hard. Across Greece, Ireland, Spain and Portugal, youth unemployment rates reached as high as 50 per cent on average in 2013 (Figure 1.4).
In the programme countries, as well as in France and Italy, youth unemployment has not only increased, but it has also become more persistent. The percentage of those who have been unemployed for longer than one year has increased considerably, and the entire distribution has shifted towards longer unemployment periods. In 2007 those who had been unemployed for longer than one year constituted less than 20 per cent of the total unemployed on average across the programme countries, whereas in 2014 they accounted for 42 per cent. A similar (although less sizable) increase is also found in France and Italy, whereas it is not common across countries in the so-called ‘north’ of the eurozone.
Prolonged youth unemployment can have very serious consequences. The longer young people stay out of the labour market, the more their skills deteriorate and become obsolete, making it more difficult to be re-employed. The increasing duration of youth unemployment is thus especially worrying, as it points to the risk that with unchanged policies some countries could be facing a future of structurally higher unemployment. Faced with few opportunities at home, many people are leaving those countries that have been hit harder by the crisis: an analysis of the index of brain drain computed by the World Economic Forum in their Global Competitiveness Reports1 shows that those countries that have been hit harder by the crisis have become less able to attract or even retain talent.
Figure 1.4 Youth Unemployment Rates. Source: Author’s calculation based on Eurostat data.
The economic crisis affected Europeans’ distrust in the EU through its sizable social repercussions, which appear to have radically changed the meaning of the EU in the eyes of Europeans. The Eurobarometer survey also asks people what the EU means to them personally, and reports the percentage of people mentioning in their answers selected words such as “economic prosperity”, “democracy”, “unemployment” or “bureaucracy”. Between 2008 and 2014, the percentage of respondents for whom the EU appears to be associated with the idea “unemployment” has increased while the percentage of people who associate the EU with the idea of “economic prosperity” and “democracy” has declined steadily across the programme countries as well as in Italy and France.
Policy Priorities
Europeans’ distrust of EU institutions is a major threat to EU integration. While trust has shown sign of improvement recently, this rebound may be still too fragile to justify complacency. For trust to be solidly rebuilt, policy changes should aim at addressing the underlying social and economic roots of this discontent, in the attempt to rebuild a positive meaning for the EU in the eyes of Europeans.
Restarting growth requires financing for the real economy, which was severely reduced during the crisis. Banks in the countries that came under market stress tightened their lending to firms, with serious pro-cyclical consequences for those countries where firms’ financing remains mostly bank-based. The effect was amplified by the fact that SMEs – the hardest-hit by the credit crunch – constitute a large share of the non-financial corporate sector in several eurozone countries. Banks have slowly restarted to lend to the real economy, but the credit recovery is uneven across countries. In this context, it is essential to broaden and diversify the financing opportunity of European firms. This will not only help in terms of financing the recovery but it will also enhance the resilience of the eurozone corporate sector to potential future crises, by fostering diversification in firms’ funding sources. The project of a capital markets union, put forward by the European commission in September 2015, aims at achieving this objective. However, implementation to date has not been sufficiently ambitious and major obstacles to the integration of capital markets – including divergent accounting enforcement regimes, fragmented market infrastructure, or incompatible frameworks for the taxation of financial investment – remain untouched.2
Productivity is the cornerstone of economic growth. According to data from the Conference Board, the level of eurozone labour productivity is about 75 per cent of the US one when measured in terms of employment and 85 per cent when measured in terms of hours worked. Labour productivity growth in the eurozone has been positive after the crisis but yearly growth is below one per cent. After the substantial contraction in total factor productivity (TFP) growth during 2008 and 2009, the eurozone had a positive TFP growth only in 2010 and 2011. The growth rate of TFP has been around zero in 2014, after two years of negative growth. It should be noted that significant variation exists in productivity across the eurozone, but improving productivity growth appears key to ensure sustainable growth.
Fostering productivity growth requires ultimately an understanding that competitiveness is essentially a firm-level phenomenon3 and that looking at the aggregate average picture could be misleading and ineffective. An OECD4 study comparing the contribution of firms to employment growth across 18 (mostly EU) countries over a 10-year period found that a small cohort of young and high-growth firms are net job creators and are responsible for a large proportion of employment growth.5 Internationalisation and in...