Deep Learning for Computer Vision
Rajalingappaa Shanmugamani, Abdul Ghani Abdul Rahman, Stephen Maurice Moore, Nishanth Koganti
- 310 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
Rajalingappaa Shanmugamani, Abdul Ghani Abdul Rahman, Stephen Maurice Moore, Nishanth Koganti
Über dieses Buch
Learn how to model and train advanced neural networks to implement a variety of Computer Vision tasks
Key Features
- Train different kinds of deep learning model from scratch to solve specific problems in Computer Vision
- Combine the power of Python, Keras, and TensorFlow to build deep learning models for object detection, image classification, similarity learning, image captioning, and more
- Includes tips on optimizing and improving the performance of your models under various constraints
Book Description
Deep learning has shown its power in several application areas of Artificial Intelligence, especially in Computer Vision. Computer Vision is the science of understanding and manipulating images, and finds enormous applications in the areas of robotics, automation, and so on. This book will also show you, with practical examples, how to develop Computer Vision applications by leveraging the power of deep learning.
In this book, you will learn different techniques related to object classification, object detection, image segmentation, captioning, image generation, face analysis, and more. You will also explore their applications using popular Python libraries such as TensorFlow and Keras. This book will help you master state-of-the-art, deep learning algorithms and their implementation.
What you will learn
- Set up an environment for deep learning with Python, TensorFlow, and Keras
- Define and train a model for image and video classification
- Use features from a pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network model for image retrieval
- Understand and implement object detection using the real-world Pedestrian Detection scenario
- Learn about various problems in image captioning and how to overcome them by training images and text together
- Implement similarity matching and train a model for face recognition
- Understand the concept of generative models and use them for image generation
- Deploy your deep learning models and optimize them for high performance
Who this book is for
This book is targeted at data scientists and Computer Vision practitioners who wish to apply the concepts of Deep Learning to overcome any problem related to Computer Vision. A basic knowledge of programming in Python—and some understanding of machine learning concepts—is required to get the best out of this book.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
Generative Models
- The applications of generative models
- Algorithms for style transfer
- Training a model for super-resolution of images
- Implementation and training of generative models
- Drawbacks of current models
Applications of generative models
Artistic style transfer

Predicting the next frame in a video

Super-resolution of images
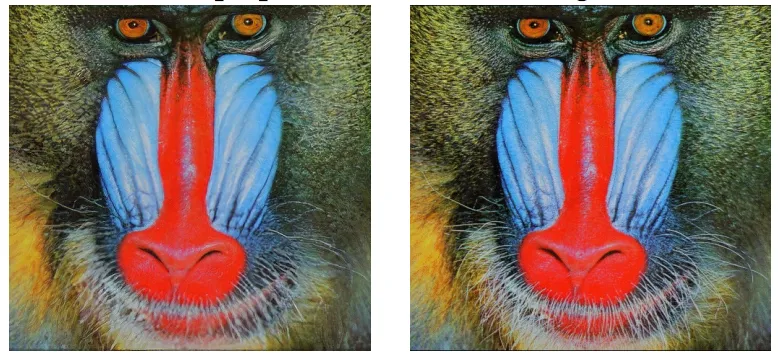
Interactive image generation