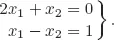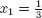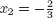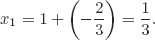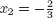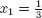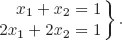Linear Algebra as an Introduction to Abstract Mathematics
Isaiah Lankham, Bruno Nachtergaele, Anne Schilling
- 208 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Linear Algebra as an Introduction to Abstract Mathematics
Isaiah Lankham, Bruno Nachtergaele, Anne Schilling
Über dieses Buch
This is an introductory textbook designed for undergraduate mathematics majors with an emphasis on abstraction and in particular, the concept of proofs in the setting of linear algebra. Typically such a student would have taken calculus, though the only prerequisite is suitable mathematical grounding. The purpose of this book is to bridge the gap between the more conceptual and computational oriented undergraduate classes to the more abstract oriented classes. The book begins with systems of linear equations and complex numbers, then relates these to the abstract notion of linear maps on finite-dimensional vector spaces, and covers diagonalization, eigenspaces, determinants, and the Spectral Theorem. Each chapter concludes with both proof-writing and computational exercises.
Request Inspection Copy
This is an introductory textbook designed for undergraduate mathematics majors with an emphasis on abstraction and in particular, the concept of proofs in the setting of linear algebra. Typically such a student would have taken calculus, though the only prerequisite is suitable mathematical grounding. The purpose of this book is to bridge the gap between the more conceptual and computational oriented undergraduate classes to the more abstract oriented classes. The book begins with systems of linear equations and complex numbers, then relates these to the abstract notion of linear maps on finite-dimensional vector spaces, and covers diagonalization, eigenspaces, determinants, and the Spectral Theorem. Each chapter concludes with both proof-writing and computational exercises.
Request Inspection Copy
Readership: Undergraduates in mathematics.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
Chapter 1
What is Linear Algebra?
1.1Introduction
1.2What is Linear Algebra?
- Characterization of solutions: Are there solutions to a given system of linear equations? How many solutions are there?
- Finding solutions: How does the solution set look? What are the solutions?