ABC of Clinical Reasoning
Nicola Cooper, John Frain, Nicola Cooper, John Frain
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
ABC of Clinical Reasoning
Nicola Cooper, John Frain, Nicola Cooper, John Frain
Über dieses Buch
Being a good clinician is not just about knowledge – how doctors and other healthcare professionals think, reason and make decisions is arguably their most critical skill. While medical schools and postgraduate training programmes teach and assess the knowledge and skills required to practice as a doctor, few offer comprehensive training in clinical reasoning or decision making. This is important because studies suggest that diagnostic error is common and results in significant harm to patients – and errors in reasoning account for the majority of diagnostic errors.
The ABC of Clinical Reasoning covers core elements of the thinking and decision making associated with clinical practice – from what clinical reasoning is, what it involves and how to teach it. Informed by the latest advances in cognitive psychology, education and studies of expertise, the ABC covers:
- Evidence-based history and examination
- Use and interpretation of diagnostic tests
- How doctors think – models of clinical reasoning
- Cognitive and affective biases
- Metacognition and cognitive de-biasing strategies
- Patient-centred evidence based medicine
- Teaching clinical reasoning
From an international team of authors, the ABC of Clinical Reasoning is essential reading for all students, medical professionals and other clinicians involved in diagnosis, in order to improve their decision-making skills and provide better patient care.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
CHAPTER 1
Clinical Reasoning: An Overview
OVERVIEW
- Clinical reasoning describes the thinking and decision-making processes associated with clinical practice
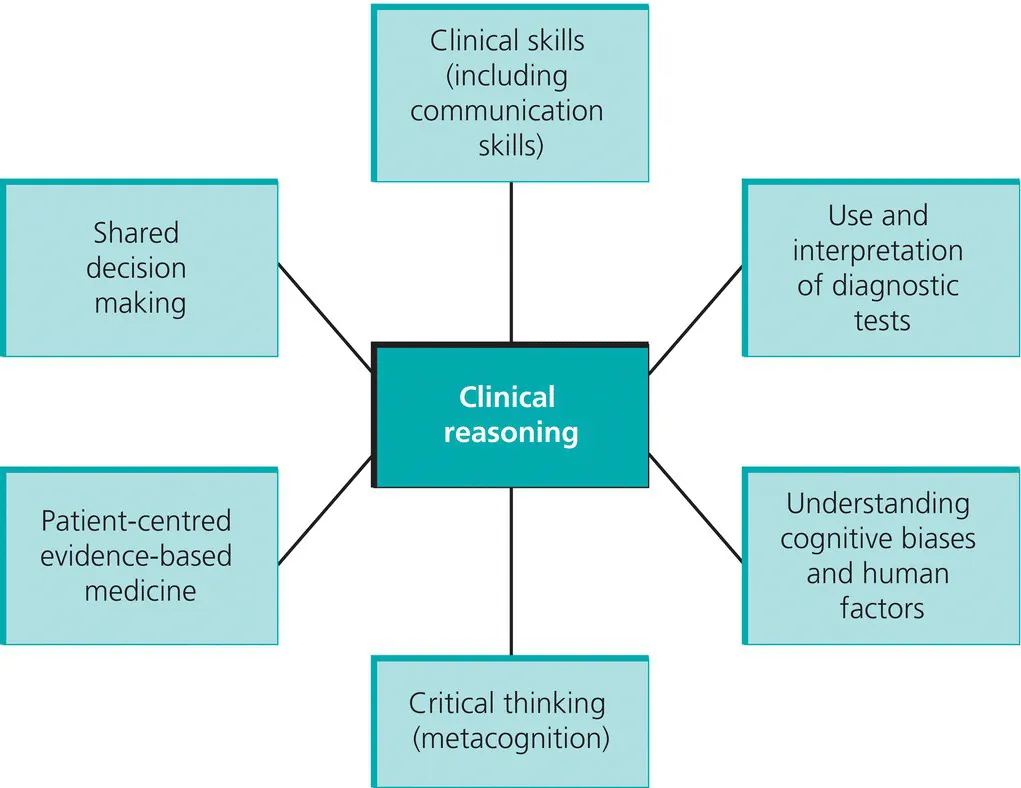
- The core elements of clinical reasoning include: evidence-based clinical skills, use and interpretation of diagnostic tests, understanding cognitive biases, human factors, metacognition (thinking about thinking), and patient-centred evidence-based medicine
- Diagnostic error is common and causes significant harm to patients. Errors in reasoning play a significant role in diagnostic error
- Sound clinical reasoning is directly linked to patient safety and quality of care
Introduction
What is clinical reasoning?
Box 1.1 A definition of clinical reasoning