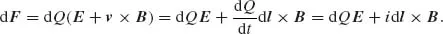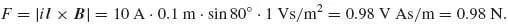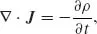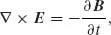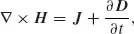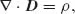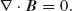Design of Rotating Electrical Machines
Juha Pyrhonen, Tapani Jokinen, Valeria Hrabovcova
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Design of Rotating Electrical Machines
Juha Pyrhonen, Tapani Jokinen, Valeria Hrabovcova
Über dieses Buch
In one complete volume, this essential reference presents an in-depth overview of the theoretical principles and techniques of electrical machine design. This timely new edition offers up-to-date theory and guidelines for the design of electrical machines, taking into account recent advances in permanent magnet machines as well as synchronous reluctance machines.
New coverage includes:
- Brand new material on the ecological impact of the motors, covering the eco-design principles of rotating electrical machines
- An expanded section on the design of permanent magnet synchronous machines, now reporting on the design of tooth-coil, high-torque permanent magnet machines and their properties
- Large updates and new material on synchronous reluctance machines, air-gap inductance, losses in and resistivity of permanent magnets (PM), operating point of loaded PM circuit, PM machine design, and minimizing the losses in electrical machines>
- End-of-chapter exercises and new direct design examples with methods and solutions to real design problems>
- A supplementary website hosts two machine design examples created with MATHCAD: rotor surface magnet permanent magnet machine and squirrel cage induction machine calculations. Also a MATLAB code for optimizing the design of an induction motor is provided
Outlining a step-by-step sequence of machine design, this book enables electrical machine designers to design rotating electrical machines. With a thorough treatment of all existing and emerging technologies in the field, it is a useful manual for professionals working in the diagnosis of electrical machines and drives. A rigorous introduction to the theoretical principles and techniques makes the book invaluable to senior electrical engineering students, postgraduates, researchers and university lecturers involved in electrical drives technology and electromechanical energy conversion.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
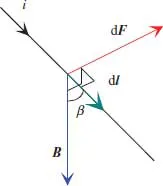
| Electric field strength | E | [V/m] |
| Magnetic field strength | H | [A/m] |
| Electric flux density | D | [C/m2] |
| Magnetic flux density | B | [Vs/m2], [T] |
| Current density | J | [A/m2] |
| Electric charge density, dQ/dV | ρ | [C/m3] |