Salivary Gland Pathology
Diagnosis and Management
Eric R. Carlson, Robert A. Ord
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Salivary Gland Pathology
Diagnosis and Management
Eric R. Carlson, Robert A. Ord
Über dieses Buch
Salivary Gland Pathology: Diagnosis and Management, Second Edition, updates the landmark text in this important discipline within oral and maxillofacial surgery, otolaryngology/head and neck surgery, and general surgery. Written by well-established clinicians, educators, and researchers in oral and maxillofacial surgery, this book brings together information on the etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of all types of salivary gland pathology. Clear and comprehensive, Salivary Gland Pathology: Diagnosis and Management offers complete explanation of all points, supported by a wealth of clinical and surgical illustrations to allow the reader to gain insight into every facet of each pathologic entity and its diagnosis and treatment. Salivary Gland Pathology: Diagnosis and Management offers comprehensive coverage of all aspects of this topic. Beginning with the embryology, anatomy and physiology of the salivary glands, the first section of the book discusses radiographic imaging, infections, cystic conditions, sialoadenitis and sialolithiasis, and systemic diseases. The second section of the book is devoted to the classification of salivary gland tumors and devotes individual chapters to the discussion of each type. Additions for this section of the second edition include molecular biology of salivary gland neoplasia, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy and targeted therapy for salivary gland malignancies. The book closes with a discussion of pediatric salivary gland pathology, traumatic injuries of the salivary glands and miscellaneous pathologic processes of the salivary glands and ducts, including a section on saliva as a diagnostic fluid. The book is intended for a very diverse audience, including academic oral and maxillofacial surgeons, otolaryngologists / head and neck surgeons, general surgeons, as well as residents in these disciplines. Private practitioners will want to place this publication on the bookshelves of their offices so as to consult the textbook when evaluating a patient with salivary gland pathology.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
Chapter 1
Surgical Anatomy, Embryology, and Physiology of the Salivary Glands
Outline
- Introduction
- The Parotid Gland
- Embryology
- Anatomy
- Contents of the Parotid Gland
- The Facial Nerve
- Auriculotemporal Nerve
- Retromandibular Vein
- External Carotid Artery
- Parotid Lymph Nodes
- Parotid Duct
- Nerve Supply to the Parotid
- The Submandibular Gland
- Embryology
- Anatomy
- The Superficial Lobe
- The Deep Lobe
- The Submandibular Duct
- Blood Supply and Lymphatic Drainage
- Nerve Supply to the Submandibular Gland
- Parasympathetic Innervation
- Sympathetic Innervation
- Sensory Innervation
- The Sublingual Gland
- Embryology
- Anatomy
- Sublingual Ducts
- Blood Supply, Innervation, and Lymphatic Drainage
- Minor Salivary Glands
- Histology of the Salivary Glands
- Control of Salivation
- Summary
- References
Introduction
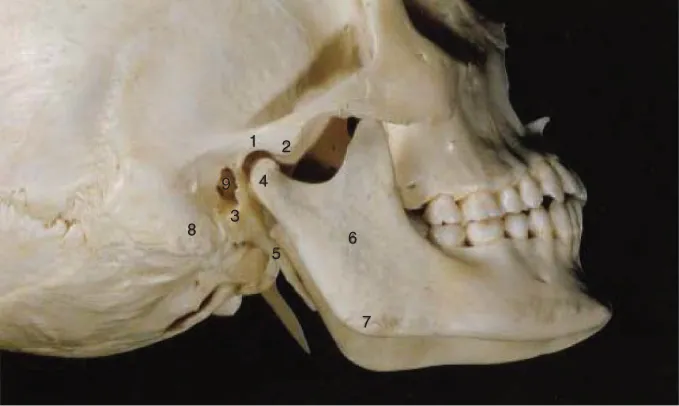
The Parotid Gland
Embryology
Anatomy