![]()
1
General Concepts
1.1 Introduction
The concept of separating sample components in a column was first developed in 1903 by Mikhail Tswett, who introduced the term chromatography in 1906. Unfortunately, his contemporaries showed little interest for the idea and almost 30 years went by before scientists in Germany rediscovered the principle of column liquid chromatography (LC). Then, in 1943 Arne Tiselius (in Sweden) classified chromatography into three modes: frontal, elution, and displacement. The elution mode actually became synonymous with almost all chromatography, but in recent years the displacement mode has attracted new interest, particularly in the separation of proteins.
In the years immediately prior to and during the Second World War, the principles of ion exchange chromatography (IEC) and liquid–liquid partition chromatography began to develop into crude technical solutions. Then after the war, in the early 1950s, the new technique of thin layer chromatography (TLC) came to light and gradually improved the partition principles used in paper chromatography. A. Martin and R.L.M. Synge (in the United Kingdom) received the Nobel Prize in 1952 for the invention of partition chromatography. Martin with James had also developed gas–liquid chromatography at this time. Gas chromatography (GC) was readily accepted by research chemists at the major oil companies, who understood the large potential of this technique and participated in developing the new instrumentation.
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) was developed in Sweden by Porath and Flodin with dextrin materials (1959), by Hjertén with polyacrylamide (1961) and agarose (1964) materials, and by Moore in the United States with polystyrene–divinylbenzene (PS-DVB) materials (1964).
Supercritical fluid chromatography was demonstrated as early as 1962, but it did not receive much interest until the technology was improved more than 20 years later.
The introduction of open tubular columns into gas chromatography revolutionized GC, first with glass capillaries in the 1970s and then with fused silica columns in the 1980s. A similar revolution started with the gradual development of new columns and instrumentation in liquid chromatography. With columns filled with small particles, the high-pressure liquid chromatography of the 1970s–1980s was later renamed high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Gel electrophoresis (GE) was developed in the 1940s, while capillary electrophoresis appeared 40 years later. Then chromatography with electric potential-driven liquid flow also developed into micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) and electrochromatography (EC), both with capillary columns. Electrophoresis, thus, is not a chromatographic technique, since there is no stationary phase, except in MEKC and EC.
To date, HPLC has become the dominating chromatographic technique, with capillary GC being second only to it (for the more volatile analytes). Both GC and HPLC are mature separation techniques today; however, HPLC is still being developed toward faster and more efficient separations and also partially toward miniaturized columns, particularly for applications in the life science area. The majority of the other techniques already mentioned are niche techniques today, but still important for a relatively smaller number of users compared to HPLC and GC. Electric potential-driven techniques have an added opportunity for new technology on microchips.
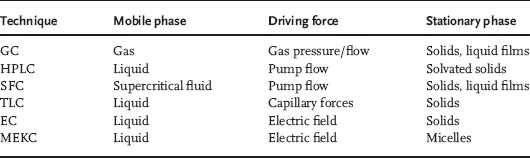
Some of the properties of the chromatographic techniques are shown in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1 Properties of chromatographic techniques.
1.2 Migration and Retention
1.2.1 General
In a chromatographic system, the sample is introduced in a small volume at the inlet of a column or another carrier of the stationary phase. The mobile phase transports the sample components in contact with the stationary phase throughout the column.
Due to different interactions between the sample components and the stationary phase, the sample components migrate through the system at different speeds and elute from the column with different retention times.
The retention time is defined as the time between the sample introduction and the elution from the column.
At the end of the column, a detector provides a signal for all eluting components (universal detection) or for a limited number (selective detection).
In a sample with many components, some compounds will coelute, partly or completely, depending on the complexity of the sample and the peak capacity of the column.
With mass spectrometric detection, even coeluting components can be identified.
1.2.2 Mo...