Finite Difference Methods in Financial Engineering
A Partial Differential Equation Approach
Daniel J. Duffy
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Finite Difference Methods in Financial Engineering
A Partial Differential Equation Approach
Daniel J. Duffy
Información del libro
The world of quantitative finance (QF) is one of the fastest growing areas of research and its practical applications to derivatives pricing problem. Since the discovery of the famous Black-Scholes equation in the 1970's we have seen a surge in the number of models for a wide range of products such as plain and exotic options, interest rate derivatives, real options and many others. Gone are the days when it was possible to price these derivatives analytically. For most problems we must resort to some kind of approximate method.
In this book we employ partial differential equations (PDE) to describe a range of one-factor and multi-factor derivatives products such as plain European and American options, multi-asset options, Asian options, interest rate options and real options. PDE techniques allow us to create a framework for modeling complex and interesting derivatives products. Having defined the PDE problem we then approximate it using the Finite Difference Method (FDM). This method has been used for many application areas such as fluid dynamics, heat transfer, semiconductor simulation and astrophysics, to name just a few. In this book we apply the same techniques to pricing real-life derivative products. We use both traditional (or well-known) methods as well as a number of advanced schemes that are making their way into the QF literature:
- Crank-Nicolson, exponentially fitted and higher-order schemes for one-factor and multi-factor options
- Early exercise features and approximation using front-fixing, penalty and variational methods
- Modelling stochastic volatility models using Splitting methods
- Critique of ADI and Crank-Nicolson schemes; when they work and when they don't work
- Modelling jumps using Partial Integro Differential Equations (PIDE)
- Free and moving boundary value problems in QF
Included with the book is a CD containing information on how to set up FDM algorithms, how to map these algorithms to C++ as well as several working programs for one-factor and two-factor models. We also provide source code so that you can customize the applications to suit your own needs.
Preguntas frecuentes
Part I
The Continuous Theory of Partial Differential Equations
Chapter 1
An Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations
1.1 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES
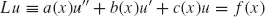
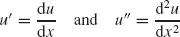
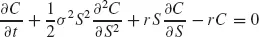
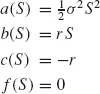
1.2 TWO-POINT BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM