
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to Differential Geometry
T. J. Willmore
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 336 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to Differential Geometry
T. J. Willmore
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
A solid introduction to the methods of differential geometry and tensor calculus, this volume is suitable for advanced undergraduate and graduate students of mathematics, physics, and engineering. Rather than a comprehensive account, it offers an introduction to the essential ideas and methods of differential geometry.
Part 1 begins by employing vector methods to explore the classical theory of curves and surfaces. An introduction to the differential geometry of surfaces in the large provides students with ideas and techniques involved in global research. Part 2 introduces the concept of a tensor, first in algebra, then in calculus. It covers the basic theory of the absolute calculus and the fundamentals of Riemannian geometry. Worked examples and exercises appear throughout the text.
Part 1 begins by employing vector methods to explore the classical theory of curves and surfaces. An introduction to the differential geometry of surfaces in the large provides students with ideas and techniques involved in global research. Part 2 introduces the concept of a tensor, first in algebra, then in calculus. It covers the basic theory of the absolute calculus and the fundamentals of Riemannian geometry. Worked examples and exercises appear throughout the text.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es An Introduction to Differential Geometry un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a An Introduction to Differential Geometry de T. J. Willmore en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Matematica y Geometria differenziale. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
Categoría
MatematicaCategoría
Geometria differenzialePart 1
THE THEORY OF CURVES AND SURFACES IN
THREE-DIMENSIONAL EUCLIDEAN SPACE
I
THE THEORY OF SPACE CURVES
1. Introductory remarks about space curves
IN the theory of plane curves, a curve is usually specified either by means of a single equation or else by a parametric representation. For example, the circle centre (0, 0) and radius a is specified in Cartesian coordinates (x, y) by the single equation
x2+y2 = a2,
or else by the parametric representation
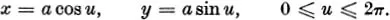
In the theory of space curves similar alternatives are available. However, in three-dimensional Euclidean space E3, a single equation generally represents a surface, and two equations are needed to specify a curve. Thus the curve appears as the intersection of the two surfaces represented by the two equations. Parametrically the curve may be specified in Cartesian coordinates by equations
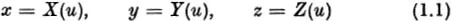
where X, Y, Z are real-valued functions of the real parameter u which is restricted to some interval. Alternatively, in vector notation the curve is specified by a vector-valued function
r = R(u).
Suppose a curve is defined by equations F(x, y, z) = 0, G(x, y, z) = 0, and it is required to find parametric equations for the curve. If F and G have continuous first derivatives and if at least one of the Jacobian determinants
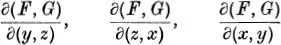
is not zero at a point (x0, y0, z0) on the curve, it is known from the theory of implicit functions that the equations F = 0, G = 0 can be solved for two of the variables in terms of the third. For example, when the first Jacobian is non-zero, the variables y and z may be expressed as functions of x, say y = Y(x), z = Z(x), which leads to the parametrization x = u, y = Y(u), z = Z(u). However, this solution is valid only for a certain range of x and it will not in general give a parametrization of the whole curve.
Conversely, suppose a curve is given parametrically by equations (1.1) and it is required to find two equations which specify the curve. The straightforward method of solving the first equation to obtain u = f(x) and substituting in the other two equations gives y = Y(f(x)), z = Z(f(x)), but this solution m...