
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to Differential Geometry
T. J. Willmore
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 336 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to Differential Geometry
T. J. Willmore
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
A solid introduction to the methods of differential geometry and tensor calculus, this volume is suitable for advanced undergraduate and graduate students of mathematics, physics, and engineering. Rather than a comprehensive account, it offers an introduction to the essential ideas and methods of differential geometry.
Part 1 begins by employing vector methods to explore the classical theory of curves and surfaces. An introduction to the differential geometry of surfaces in the large provides students with ideas and techniques involved in global research. Part 2 introduces the concept of a tensor, first in algebra, then in calculus. It covers the basic theory of the absolute calculus and the fundamentals of Riemannian geometry. Worked examples and exercises appear throughout the text.
Part 1 begins by employing vector methods to explore the classical theory of curves and surfaces. An introduction to the differential geometry of surfaces in the large provides students with ideas and techniques involved in global research. Part 2 introduces the concept of a tensor, first in algebra, then in calculus. It covers the basic theory of the absolute calculus and the fundamentals of Riemannian geometry. Worked examples and exercises appear throughout the text.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist An Introduction to Differential Geometry als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu An Introduction to Differential Geometry von T. J. Willmore im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Matematica & Geometria differenziale. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Thema
MatematicaPart 1
THE THEORY OF CURVES AND SURFACES IN
THREE-DIMENSIONAL EUCLIDEAN SPACE
I
THE THEORY OF SPACE CURVES
1. Introductory remarks about space curves
IN the theory of plane curves, a curve is usually specified either by means of a single equation or else by a parametric representation. For example, the circle centre (0, 0) and radius a is specified in Cartesian coordinates (x, y) by the single equation
x2+y2 = a2,
or else by the parametric representation
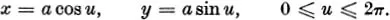
In the theory of space curves similar alternatives are available. However, in three-dimensional Euclidean space E3, a single equation generally represents a surface, and two equations are needed to specify a curve. Thus the curve appears as the intersection of the two surfaces represented by the two equations. Parametrically the curve may be specified in Cartesian coordinates by equations
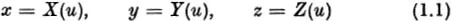
where X, Y, Z are real-valued functions of the real parameter u which is restricted to some interval. Alternatively, in vector notation the curve is specified by a vector-valued function
r = R(u).
Suppose a curve is defined by equations F(x, y, z) = 0, G(x, y, z) = 0, and it is required to find parametric equations for the curve. If F and G have continuous first derivatives and if at least one of the Jacobian determinants
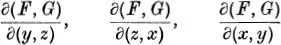
is not zero at a point (x0, y0, z0) on the curve, it is known from the theory of implicit functions that the equations F = 0, G = 0 can be solved for two of the variables in terms of the third. For example, when the first Jacobian is non-zero, the variables y and z may be expressed as functions of x, say y = Y(x), z = Z(x), which leads to the parametrization x = u, y = Y(u), z = Z(u). However, this solution is valid only for a certain range of x and it will not in general give a parametrization of the whole curve.
Conversely, suppose a curve is given parametrically by equations (1.1) and it is required to find two equations which specify the curve. The straightforward method of solving the first equation to obtain u = f(x) and substituting in the other two equations gives y = Y(f(x)), z = Z(f(x)), but this solution m...