
eBook - ePub
Digital Logic Design
Brian Holdsworth, Clive Woods
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 519 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Digital Logic Design
Brian Holdsworth, Clive Woods
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
New, updated and expanded topics in the fourth edition include: EBCDIC, Grey code, practical applications of flip-flops, linear and shaft encoders, memory elements and FPGAs. The section on fault-finding has been expanded. A new chapter is dedicated to the interface between digital components and analog voltages.
- A highly accessible, comprehensive and fully up to date digital systems text
- A well known and respected text now revamped for current courses
- Part of the Newnes suite of texts for HND/1st year modules
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Digital Logic Design un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Digital Logic Design de Brian Holdsworth, Clive Woods en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Design y Industriedesign. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
1
Number systems and codes
1.1 Introduction
A digital logic system may well have a numerical computation capability as well as its inherent logical capability and consequently it must be able to implement the four basic arithmetic processes of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Human beings normally perform arithmetic operations using the decimal number system, but, by comparison, a digital machine is inherently binary in nature and its numerical calculations are executed using a binary number system.
Since the decimal system has ten digits, a ten-state device is required to represent the decimal digits, one state being allocated to each of the decimal digits. Ten-state devices are not readily available in the electrical world, however two-state devices such as a transistor operating in a switching mode are, and it is for this reason that the binary number system is of great importance to the digital engineer. In addition to the binary system, a number of other systems such as the hexadecimal system are used in conjunction with programmable logic devices, consequently the digital engineer must be familiar with a variety of different number systems.
It is also true that arithmetic processes executed by a digital machine are not necessarily identical to the pencil and paper methods which are normally employed by humans. For example the process of subtraction is carried out as an addition and this involves the use of complement arithmetic.
Again, a frequent requirement is that the output of a digital machine should be a decimal display, for obvious reasons. Since the machine normally computes in pure binary, a way has to be found to represent decimal numbers in terms of binary digits and this requires a binary coded decimal system. Methods have to be devised so that any numerical computations carried out in pure binary can be converted into binary coded decimal so that at the interface with the outside world a decimal display or readout is available.
Coding of information is a basic consideration in the use of a digital system. Codes are required for decimal numbers, the letters of the alphabet and a variety of other well used symbols such as =, ?, etc. We previously referred to binary coded decimal as a coded representation for decimal numbers. This is an example of a weighted code of which there are a number of examples. In addition to weighted codes there are a variety of other codes available, for example the XS3 code, and the choice of a suitable code is not arbitrary. Its properties have to be considered before selection for use. In practice the most widely used code is the 8-4-2-1 weighted code which is referred to as naturally binary coded decimal.
The aim of this chapter is to describe the various number systems in common usage and to develop methods for implementing the four fundamental arithmetic operations on a machine. Additionally, a brief survey of some of the more common codes will be presented.
1.2 Number systems
The number system most familiar to man is the decimal system. A decimal number such as (473.85)10 may be expressed in the following form:
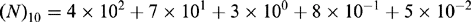
The number (N)10 consists of a series of decimal digits multiplied by the number (10)10 raised to some power that depends upon the pos...