
eBook - ePub
Digital Logic Design
Brian Holdsworth, Clive Woods
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 519 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Digital Logic Design
Brian Holdsworth, Clive Woods
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
New, updated and expanded topics in the fourth edition include: EBCDIC, Grey code, practical applications of flip-flops, linear and shaft encoders, memory elements and FPGAs. The section on fault-finding has been expanded. A new chapter is dedicated to the interface between digital components and analog voltages.
- A highly accessible, comprehensive and fully up to date digital systems text
- A well known and respected text now revamped for current courses
- Part of the Newnes suite of texts for HND/1st year modules
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Digital Logic Design è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Digital Logic Design di Brian Holdsworth, Clive Woods in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Design e Industriedesign. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
1
Number systems and codes
1.1 Introduction
A digital logic system may well have a numerical computation capability as well as its inherent logical capability and consequently it must be able to implement the four basic arithmetic processes of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Human beings normally perform arithmetic operations using the decimal number system, but, by comparison, a digital machine is inherently binary in nature and its numerical calculations are executed using a binary number system.
Since the decimal system has ten digits, a ten-state device is required to represent the decimal digits, one state being allocated to each of the decimal digits. Ten-state devices are not readily available in the electrical world, however two-state devices such as a transistor operating in a switching mode are, and it is for this reason that the binary number system is of great importance to the digital engineer. In addition to the binary system, a number of other systems such as the hexadecimal system are used in conjunction with programmable logic devices, consequently the digital engineer must be familiar with a variety of different number systems.
It is also true that arithmetic processes executed by a digital machine are not necessarily identical to the pencil and paper methods which are normally employed by humans. For example the process of subtraction is carried out as an addition and this involves the use of complement arithmetic.
Again, a frequent requirement is that the output of a digital machine should be a decimal display, for obvious reasons. Since the machine normally computes in pure binary, a way has to be found to represent decimal numbers in terms of binary digits and this requires a binary coded decimal system. Methods have to be devised so that any numerical computations carried out in pure binary can be converted into binary coded decimal so that at the interface with the outside world a decimal display or readout is available.
Coding of information is a basic consideration in the use of a digital system. Codes are required for decimal numbers, the letters of the alphabet and a variety of other well used symbols such as =, ?, etc. We previously referred to binary coded decimal as a coded representation for decimal numbers. This is an example of a weighted code of which there are a number of examples. In addition to weighted codes there are a variety of other codes available, for example the XS3 code, and the choice of a suitable code is not arbitrary. Its properties have to be considered before selection for use. In practice the most widely used code is the 8-4-2-1 weighted code which is referred to as naturally binary coded decimal.
The aim of this chapter is to describe the various number systems in common usage and to develop methods for implementing the four fundamental arithmetic operations on a machine. Additionally, a brief survey of some of the more common codes will be presented.
1.2 Number systems
The number system most familiar to man is the decimal system. A decimal number such as (473.85)10 may be expressed in the following form:
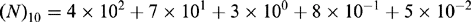
The number (N)10 consists of a series of decimal digits multiplied by the number (10)10 raised to some power that depends upon the pos...