Abstract
With the emergence of the Internet of things (IoT) and machine-to-machine (M2M) communications, massive growth in the sensor node deployment is expected soon. According to IHS Markit forecast, the number of connected IoT devices would grow to 125 billion by 2030. The exponential growth in IoT is impacting virtually all stages of industry and nearly all market areas. It is redefining the ways to design, manage, and maintain the networks, data, clouds, and connections. To support the requirements of new applications, an innovative paradigm called low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) is evolved. The LPWAN is a class of wireless IoT communication standards and solutions with characteristics such as large coverage areas, low transmission data rates with small packet data sizes, and long battery life operation. The LPWAN technologies are being deployed and have shown enormous potential for the vast range of applications in IoT and M2M, especially in constrained environments. This chapter focuses on a general introduction to LPWANs, innovative applications and services, requirements, wireless access, and characteristics.
1.1 Introduction
With the emergence of the Internet of things (IoT) and machine-to-machine (M2M) communications, massive growth in the sensor node deployment is expected soon. According to the forecast by Ericsson [1], around 29 billion devices will be connected to the Internet by 2022. These connected IoT devices include connected cars, machines, meters, sensors, point-of-sale terminals, consumer electronics products, wearables, and others. IoT survey reported on the Forbes website [2] forecasts more than 75 billion IoT device connections by 2025. HIS Markit [3] forecasted that the number of connected IoT devices would grow to 125 billion in 2030. The exponential growth in IoT is impacting virtually all stages of industry and nearly all market areas. It is redefining the ways to design, manage, and maintain the networks, data, clouds, and connections.
With highly anticipated developments in the fields of artificial intelligence, machine learning, data analytics, and blockchain technologies, there is immense potential to exponentially grow the deployments and its applications in almost all the sectors of society, profession, and industry. Such progression allows any things such as sensors, vehicles, robots, machines, or any such objects to connect to the Internet. It enables them to send the sensed data and parameters to the remote centralized device or server, which provides intelligence for making an appropriate decision or actuating action.
In general, IoT applications require energy-efficient and low-complexity nodes for a variety of uses that are to be deployed on scalable networks. Currently, wireless technologies such as IEEE 802.11 wireless local area networks (WLAN), IEEE 802.15.1 Bluetooth, IEEE 802.15.3 ZigBee, low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPAN), and others are being used for sensing applications in the short-range environments. In contrast, wireless cellular technologies such as 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G can be extended to long-range applications. Primarily, WLAN and Bluetooth were designed for high-speed data communication, whereas ZigBee and LR-WPAN were designed for wireless sensing applications in the local environments and are used for low data–rate application for communication distances ranging from a few meters to a few hundred meters, depending on the line of sight, obstacles in the path, interference, transmit power, etc. Wireless cellular networks such as 2G, 3G, and 4G are designed for voice and data communication, not primarily for wireless sensing applications. Although these technologies are used for sensing for one or other ways in some of the applications, their performance in terms of performance metrics used in the wireless sensor networks may not be acceptable.
Hence, to support such requirements, a new paradigm of IoT, called low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) is evolved. The LPWAN is a class of wireless IoT communication standards and solutions with characteristics such as large coverage areas, low transmission data rates with small packet data sizes, and long battery life operation [4]. The LPWAN technologies are being deployed and have shown enormous potential for the vast range of applications in IoT and M2M, especially in constrained environments.
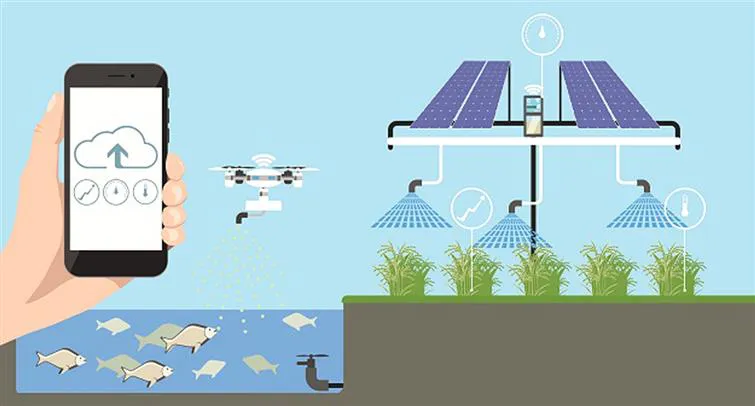
1.2 Intelligent applications and services
The growing popularity of IoT use cases in domains that rely on connectivity spanning large areas and able to handle a massive number of connections is driving the demand for massive IoT technologies. With the advancement in the field of miniaturized electronics, communication, computing, sensing, actuating, and battery technologies, it is possible to design low-power, long-range networking technologies with many years of battery life and tens of kilometers coverage. These technologies have to be Internet-compatible so that data, device, and network management can be undertaken through cloud-based platforms. The most critical requirements of wireless IoT/M2M devices are low power consumption with extended transmission range, support to massive number of devices, the capability to handle RF interference, low cost, easy deployment, and robust security for the both, applications and network level. LPWAN technologies are promising and can be deployed for a broad range of smart and intelligent applications, including environment monitoring, smart cities, smart utilities, agriculture, health care, industrial automation, asset tracking, logistics and transportation, and many more as given in Table 1–1.
Table 1–1
Applications of LPWANs.| Field | Major applications |
|---|
| Smart cities | | Smart parking, structural health of the buildings, bridges and historical monuments, air quality measurement, sound noise level measurement, traffic congestion and traffic light control, road toll control, smart lighting, trash collection optimization, waste management, utility meters, fire detection, elevator monitoring and control, manhole cover monitoring, construction equipment and labor health monitoring, environment and public safety |
| Smart environment | | Water quality, air pollution, temperature, forest fire, landslide, animal tracking, snow level monitoring, and earthquake early detection |
| Smart water | | Water quality, water leakage, river flood monitoring, swimming pool management, and chemical leakage |
| Smart... |