
An Introduction to Aspects of Thermodynamics and Kinetics Relevant to Materials Science
Eugene Machlin
- 480 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
An Introduction to Aspects of Thermodynamics and Kinetics Relevant to Materials Science
Eugene Machlin
Información del libro
This book is based on a set of notes developed over many years for an introductory course taught to seniors and entering graduate students in materials science. An Introduction to Aspects of Thermodynamics and Kinetics Relevant to Materials Science is about the application of thermodynamics and kinetics to solve problems within Materials Science. Emphasis is to provide a physical understanding of the phenomenon under discussion, with the mathematics presented as a guide.
The problems are used to provide practice in quantitative application of principles, and also to give examples of applications of the general subject matter to problems having current interest and to emphasize the important physical concepts.
End of chapter problems are included, as are references, and bibliography to reinforce the text. This book provides students with the theory and mathematics to understand the important physical understanding of phenomena.
- Based on a set of notes developed over many years for an introductory course taught to seniors and entering graduate students in materials science
- Provides students with the theory and mathematics to understand the important physical understanding of phenomena
- Includes end of chapter problems, references, and bibliography to reinforce the text
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
Thermodynamics of Phases having Constant Composition
Publisher Summary
Introduction
| Thermodynamic potential | Constrained variables |
| Gibbs free energy (G) | P,T,N |
| Helmholtz free energy (F) | V,T,N |
| Enthalpy (H) | P,S,N |
| Internal energy (E) | V,S,N |
| Grand (Ω) | V,T,μ |
| X | Y | Z | 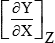 | X | Y | Z | 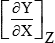 |
| T | V | p | αV | T | p | V | α/β |
| T | S | p | Cp/T | T | S | V | Cp/T – α2V/β |
| T | V | p | Cp – αpV | T | U | V | Cp – α2VT/β |
| T | H | p | CP | T | H | V | Cp – α2VT/β + αV/β |
| T | F | p | − αpV – S | T | F | V | −S |
| T | G | p | −S | T | G | V | αV/β – S |
| p | V | T | −βV | T | p | S | Cp/αVT |
| p | S | T | −αV | T | V | S | −βCp/αT + αV |
| p | U | T | βpV – αVT | T | U | S | βpCp/αT – αpV |
| p | H | T | V – αVT | T | H | S | Cp/αT |
| p | F | T | β... |