
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Number Theory
Anthony Vazzana, David Garth
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 426 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Number Theory
Anthony Vazzana, David Garth
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
Introduction to Number Theory is a classroom-tested, student-friendly text that covers a diverse array of number theory topics, from the ancient Euclidean algorithm for finding the greatest common divisor of two integers to recent developments such as cryptography, the theory of elliptic curves, and the negative solution of Hilbert's tenth problem.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Introduction to Number Theory un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Introduction to Number Theory de Anthony Vazzana, David Garth en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Mathématiques y Mathématiques générales. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
Chapter 1
Introduction
Die ganzen Zahlen hat der liebe Gott gemacht, alles andere ist Menschenwerk.[The good Lord made the whole numbers; all else is the work of man.]
1.1 What is number theory?
The natural numbers (i.e., the positive integers) are the counting numbers
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, ….
These numbers are one of the oldest, most universal concepts of mathematics. Number theory is the study of properties of the natural numbers.
One of the central issues of number theory is that of factorization and in particular prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. Thus, the prime numbers are
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, ….
We will show that every positive integer greater than 1 can be (uniquely) written as the product of prime numbers. Therefore, understanding prime numbers is crucial.
A particularly appealing aspect of number theory is that one can start with a simple concept and quickly come upon deep, difficult-to-solve problems. Another attractive feature is that many interesting patterns are revealed through example calculations that are easy to carry out.
We illustrate these two points with a few questions about prime numbers. First, how many prime numbers are there? Over two thousand years ago, Euclid provided a simple, elegant proof that there are infinitely many. (We will give this proof in Section 4.3.)
Let’s delve a little deeper. Apart from the number 2, all primes are odd. Consequently, when we divide any prime greater than 2 by the number 4, the remainder must be either 1 or 3. In other words, any prime other than 2 can be written in the form 4k + 1 or 4k + 3, for some integer k. For example, 13 = 4 · 3 + 1 and 19 = 4 · 4 + 3. One can easily work out representations for the first few primes, as shown below.

We see that four of the first ten odd primes are of the form 4k + 1 while the remaining six are of the form 4k + 3. With the aid of a computer one can easily make similar calculations for a much larger sample. The table below indicates how the first n odd primes are divided between the two sets.
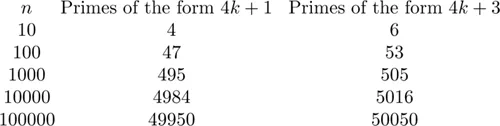
By modifying Euclid’s proof one can show without substantial effort that there are an infinite number of primes of the form 4k+3 (see Proposition 4.9). Strangely, it is not as easy to show that there are an infinite number of primes of the form 4k + 1. However, with the introduction of some mathematical machinery, we will be able to prove that there are an infinite number of such primes. Our data above suggest that there is more to the issue than the infinitude of both sets. For each value of n, approximately half of the primes are in each set. Moreover, the larger n is in our table, the closer the percentage of each type is to 50%. Developing even heavier machinery (which is beyond the scope of this book), one can show that this pattern continues. That is, the percentage of the first n primes of the form 4k + 1 approaches 50% as n grows larger.
One can ask similar questions about the number of primes of the form ak + b, for fixed integers a and b. Again, with a good deal of effort one can give a satisfactory description of what goes on. If we modify things a bit in a different dir...