
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Number Theory
Anthony Vazzana, David Garth
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 426 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Number Theory
Anthony Vazzana, David Garth
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Introduction to Number Theory is a classroom-tested, student-friendly text that covers a diverse array of number theory topics, from the ancient Euclidean algorithm for finding the greatest common divisor of two integers to recent developments such as cryptography, the theory of elliptic curves, and the negative solution of Hilbert's tenth problem.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Introduction to Number Theory als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Introduction to Number Theory von Anthony Vazzana, David Garth im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Mathématiques & Mathématiques générales. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
Die ganzen Zahlen hat der liebe Gott gemacht, alles andere ist Menschenwerk.[The good Lord made the whole numbers; all else is the work of man.]
1.1 What is number theory?
The natural numbers (i.e., the positive integers) are the counting numbers
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, ….
These numbers are one of the oldest, most universal concepts of mathematics. Number theory is the study of properties of the natural numbers.
One of the central issues of number theory is that of factorization and in particular prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. Thus, the prime numbers are
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, ….
We will show that every positive integer greater than 1 can be (uniquely) written as the product of prime numbers. Therefore, understanding prime numbers is crucial.
A particularly appealing aspect of number theory is that one can start with a simple concept and quickly come upon deep, difficult-to-solve problems. Another attractive feature is that many interesting patterns are revealed through example calculations that are easy to carry out.
We illustrate these two points with a few questions about prime numbers. First, how many prime numbers are there? Over two thousand years ago, Euclid provided a simple, elegant proof that there are infinitely many. (We will give this proof in Section 4.3.)
Let’s delve a little deeper. Apart from the number 2, all primes are odd. Consequently, when we divide any prime greater than 2 by the number 4, the remainder must be either 1 or 3. In other words, any prime other than 2 can be written in the form 4k + 1 or 4k + 3, for some integer k. For example, 13 = 4 · 3 + 1 and 19 = 4 · 4 + 3. One can easily work out representations for the first few primes, as shown below.

We see that four of the first ten odd primes are of the form 4k + 1 while the remaining six are of the form 4k + 3. With the aid of a computer one can easily make similar calculations for a much larger sample. The table below indicates how the first n odd primes are divided between the two sets.
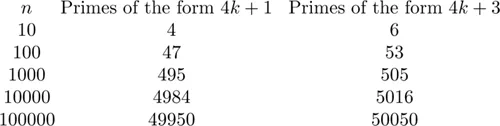
By modifying Euclid’s proof one can show without substantial effort that there are an infinite number of primes of the form 4k+3 (see Proposition 4.9). Strangely, it is not as easy to show that there are an infinite number of primes of the form 4k + 1. However, with the introduction of some mathematical machinery, we will be able to prove that there are an infinite number of such primes. Our data above suggest that there is more to the issue than the infinitude of both sets. For each value of n, approximately half of the primes are in each set. Moreover, the larger n is in our table, the closer the percentage of each type is to 50%. Developing even heavier machinery (which is beyond the scope of this book), one can show that this pattern continues. That is, the percentage of the first n primes of the form 4k + 1 approaches 50% as n grows larger.
One can ask similar questions about the number of primes of the form ak + b, for fixed integers a and b. Again, with a good deal of effort one can give a satisfactory description of what goes on. If we modify things a bit in a different dir...