
Advanced Common Core Math Explorations
Factors and Multiples (Grades 5-8)
Jerry Burkhart
- 168 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Advanced Common Core Math Explorations
Factors and Multiples (Grades 5-8)
Jerry Burkhart
Información del libro
Students become mathematical adventurers in these challenging and engaging activities designed to deepen and extend their understanding of concepts from the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics. The investigations in this book stretch students' mathematical imaginations to their limits as they explore mystifying patterns of colored blocks, analyze paths of pool balls, solve mathematical word puzzles, and unravel a baffling mathematical code. Each activity comes with detailed support for classroom implementation including learning goals, discussion guides, detailed solutions, and suggestions for extending the investigation. There is also a free supplemental e-book offering strategies for motivation, assessment, parent communication, and suggestions for using the materials in different learning environments.Grades 5-8
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
Exploration 1
Building Blocks
INTRODUCTION
Materials
- » Colored pencils
Prior Knowledge
- » Identify and find factors and multiples of one- and two-digit numbers.
- » Understand the concept of a prime number (optional, but recommended).
Learning Goals
- » Understand prime numbers as building blocks of the natural (counting) numbers.
- » Analyze connections between prime factorizations of different numbers.
- » Analyze and extend complex patterns.
- » Persist in solving challenging problems.
Launching the Exploration
STUDENT HANDOUT
Stage 1
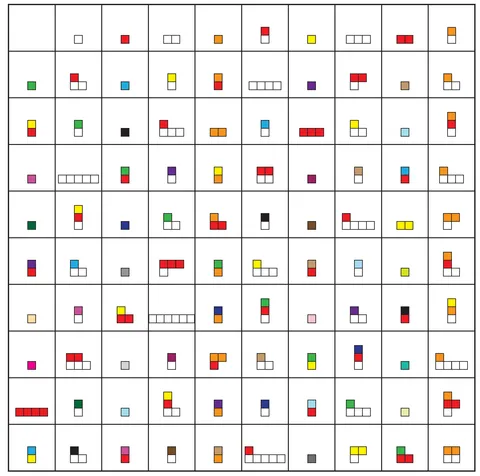
- Analyze patterns in the colored blocks for the top 50 squares of this grid. Extend the patterns to fill in the remaining 50 squares.
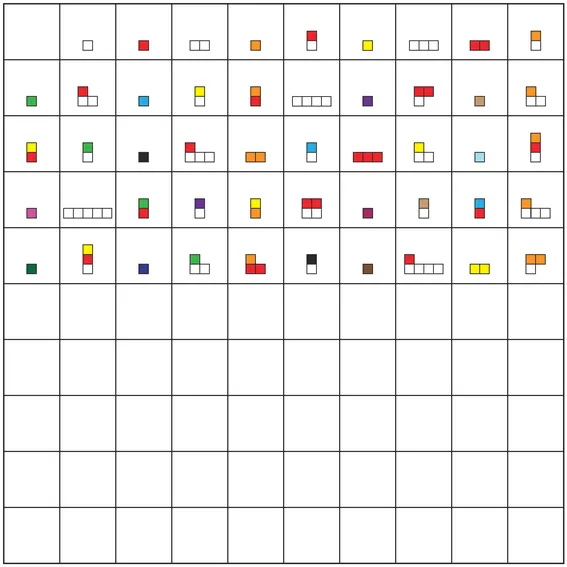
Stage 2
- 2. Draw the correct block pattern into the two empty squares and fill in the correct colors for all blocks in the grid. Include any additional information that you think is important.
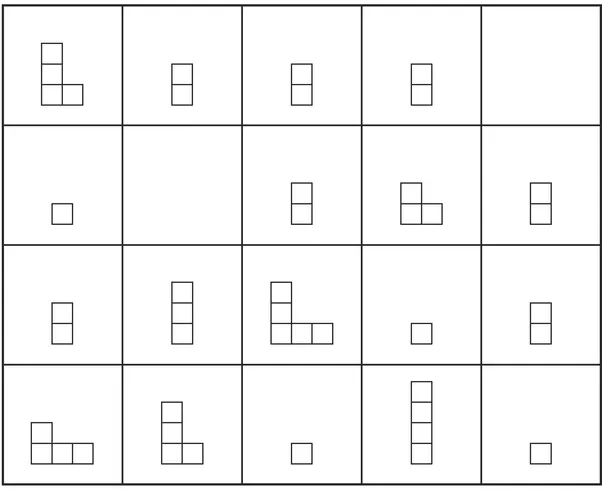
Stage 3
- 3. Look at the grid in Stage 1 and focus on the squares that have just one block. Can you find a method that will always predict when the next one will come?
TEACHER’S GUIDE
STAGE 1
Problem # 1
- Analyze patterns in the colored blocks for the top 50 squares of this grid. Extend the patterns to fill in the remaining 50 squares.
Questions and Conversations for # 1
- » Is it important to keep the blank square in the upper left corner? Yes. The pattern will be easier to understand if you keep it there.
- » Are there patterns in rows, columns, diagonals, etc.? Yes, there are many vertical and diagonal patterns. For example, white blocks appear in alternating columns. What pattern do you see for red blocks?
- » Does every color show some pattern? Yes, every color follows some distinctive pattern. Try to think about what might cause these patterns.
- » Will it help to count the total number of blocks in each row or column? You might make interesting observations by counting these, but it will probably not help you complete the grid.
- » Will it help to look for a pattern in the number of white blocks in the squares? It might, but it's a complicated pattern. Reading from left to right, top to bottom, it looks like this: 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 4, 1,2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 5, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 4,... Every natural number will eventually appear in this list! You might find the pattern hard to unravel without more information.
- » Can it help to focus on patterns in squares in which all blocks are the same color? Yes. This will probably help the most for squares with white blocks because you can't see many squares of this type for the other colors.
- » Should I look at the squares in a particular order? Yes, try reading the grid from left to right, top to bottom, just as you would read a book.
- » Will two different squares ever have exactly the same collection of colored blocks? No.
- » What always happens the first time a new color appears? Every color appears by itself the first time.
- » What always happens the second time a new color appearst Every color appears with a white block the second time. Can you see how this pattern continues?
- » Does the main pattern have anything to do with numbers? Yes. Try numbering the squares in order from left to right, top to bottom.
- » Should the first square be numbered "0" since it contains no blocks? This is an important question. Experiment before deciding. (It turns out that the blank square at the beginning should be numbered 1, not 0.)
- » Look at the squares numbered 2, 3, and 6 or 3, 4, and 12. What happens? Look at how the block diagrams combine. Under what circumstances does this happen in general?
- » In which square will the next white block go? What about the next red block? Students might notice that white blocks occur every 2 squares, red blocks come every 3 squares, orange ones appear every 5 squares, etc. (This is a key pattern.)
- » Once you know that a square contains a certain color, how can you figure how many blocks of that color it has? Look at the squares that have at least two white blocks. What about three white blocks? Ask the same types of questions for other colors.
- » Is there anything special about the squares with just one block? Yes! Try writing down the numbers of these squares. (These squares are all labeled as prime numbers!)
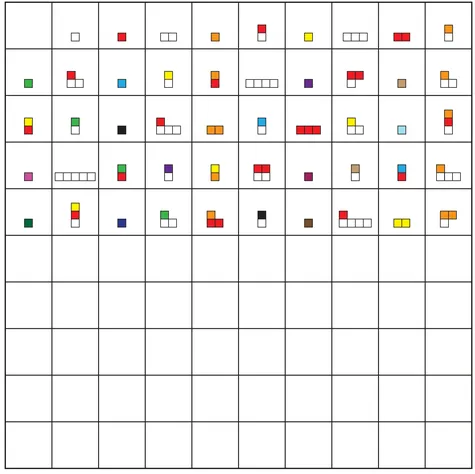
Solution for # 1
STAGE 2
Problem #2
- 2. Draw the correct block pattern into the two empty squares and fill in the correct colors for all blocks in the grid. Include any additional information that you think is important.
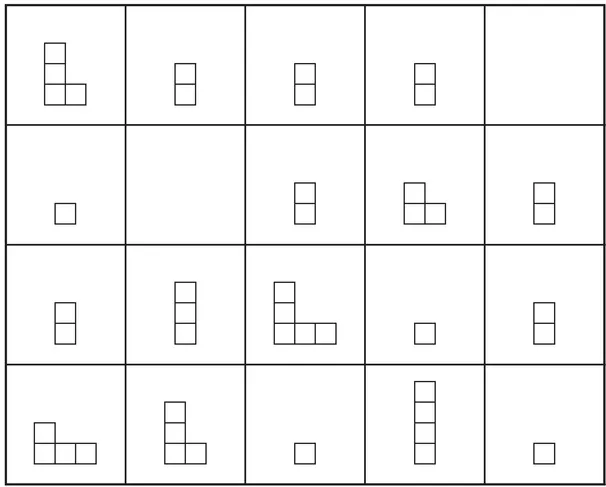
Questions and Conversations for #2
- » How are the blocks arranged in each square? Each row of blocks contains only one prime number value. The smallest prime number is i...