
Deep Learning By Example
Ahmed Menshawy
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Deep Learning By Example
Ahmed Menshawy
Información del libro
Grasp the fundamental concepts of deep learning using Tensorflow in a hands-on mannerAbout This Book• Get a first-hand experience of the deep learning concepts and techniques with this easy-to-follow guide• Train different types of neural networks using Tensorflow for real-world problems in language processing, computer vision, transfer learning, and more• Designed for those who believe in the concept of 'learn by doing', this book is a perfect blend of theory and code examplesWho This Book Is ForThis book targets data scientists and machine learning developers who wish to get started with deep learning. If you know what deep learning is but are not quite sure of how to use it, this book will help you as well. An understanding of statistics and data science concepts is required. Some familiarity with Python programming will also be beneficial.What You Will Learn• Understand the fundamentals of deep learning and how it is different from machine learning• Get familiarized with Tensorflow, one of the most popular libraries for advanced machine learning• Increase the predictive power of your model using feature engineering• Understand the basics of deep learning by solving a digit classification problem of MNIST• Demonstrate face generation based on the CelebA database, a promising application of generative models• Apply deep learning to other domains like language modeling, sentiment analysis, and machine translationIn DetailDeep learning is a popular subset of machine learning, and it allows you to build complex models that are faster and give more accurate predictions. This book is your companion to take your first steps into the world of deep learning, with hands-on examples to boost your understanding of the topic.This book starts with a quick overview of the essential concepts of data science and machine learning which are required to get started with deep learning. It introduces you to Tensorflow, the most widely used machine learning library for training deep learning models. You will then work on your first deep learning problem by training a deep feed-forward neural network for digit classification, and move on to tackle other real-world problems in computer vision, language processing, sentiment analysis, and more. Advanced deep learning models such as generative adversarial networks and their applications are also covered in this book.By the end of this book, you will have a solid understanding of all the essential concepts in deep learning. With the help of the examples and code provided in this book, you will be equipped to train your own deep learning models with more confidence.Style and approachA step-by-step guide filled with multiple examples to help you get started with data science and deep learning.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
TensorFlow in Action - Some Basic Examples
- Capacity of a single neuron and activation functions
- Activation functions
- Feed-forward neural network
- The need for a multilayer network
- TensorFlow terminologies—recap
- Linear regression model—building and training
- Logistic regression model—building and training
Capacity of a single neuron
Biological motivation and connections
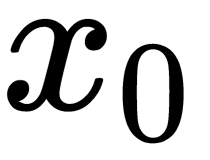
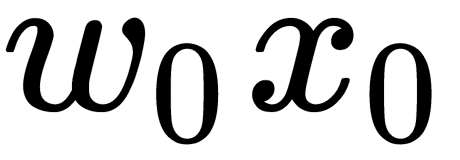
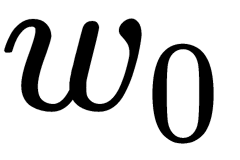

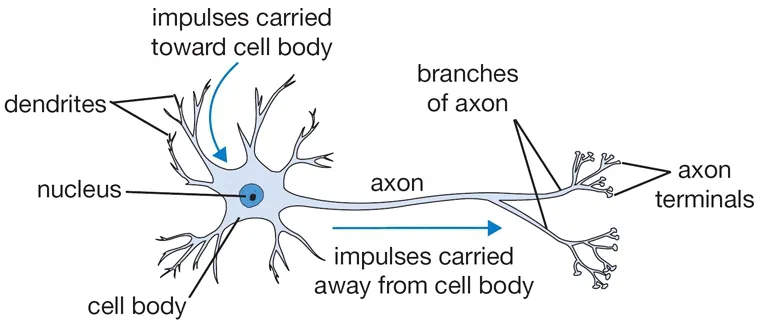
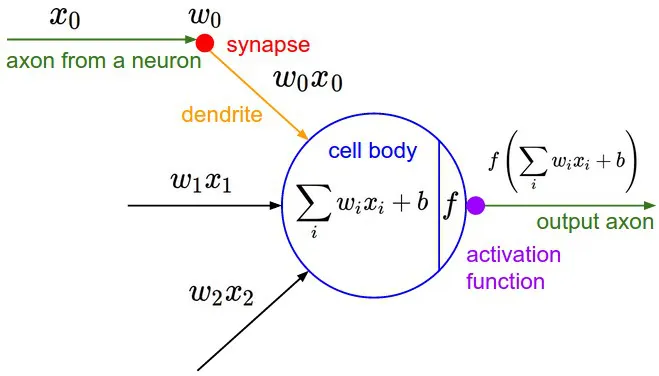

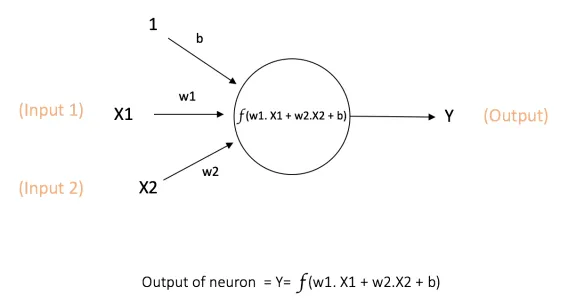
Activation functions
- Introduce nonlinearity into the output of a neuron. This is important because most real-world data is nonlinear and we want neurons to learn these nonlinear representations.
- Squash the output to be in a specific range.