Geometry Of The Octonions, The
Tevian Dray, Corinne A Manogue
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Geometry Of The Octonions, The
Tevian Dray, Corinne A Manogue
Información del libro
There are precisely two further generalizations of the real and complex numbers, namely, the quaternions and the octonions. The quaternions naturally describe rotations in three dimensions. In fact, all (continuous) symmetry groups are based on one of these four number systems. This book provides an elementary introduction to the properties of the octonions, with emphasis on their geometric structure. Elementary applications covered include the rotation groups and their spacetime generalization, the Lorentz group, as well as the eigenvalue problem for Hermitian matrices. In addition, more sophisticated applications include the exceptional Lie groups, octonionic projective spaces, and applications to particle physics including the remarkable fact that classical supersymmetry only exists in particular spacetime dimensions.
Contents:
-
- Introduction
- Number Systems:
- The Geometry of the Complex Numbers
- The Geometry of the Quaternions
- The Geometry of the Octonions
- Other Number Systems
- Symmetry Groups:
- Some Orthogonal Groups
- Some Unitary Groups
- Some Symplectic Groups
- Symmetry Groups over Other Division Algebras
- Lie Groups and Lie Algebras
- The Exceptional Groups
- Applications:
- Division Algebras in Mathematics
- Octonionic Eigenvalue Problems
- The Physics of the Octonions
- Magic Squares
Readership: Advanced undergraduate and graduate students and faculty in mathematics and physics; non-experts with moderately sophisticated mathematics background.
Key Features:
- This book is easily digestible by a large audience wanting to know the elementary introduction to octanions
- Suitable for any reader with a grasp of the complex numbers, although familiarity with non-octonionic versions of some of the other topics would be helpful
- Many open problems are very accessible
- Advanced topics covered are quite sophisticated, leading up to a clear discussion of (one representation of) the exceptional Lie algebras and their associated root diagrams, and of the octonionic projective spaces on which they act
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
Chapter 1
Introduction

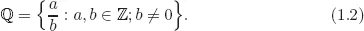

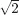

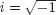
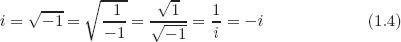
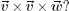
PART I
Number Systems
Chapter 2
The Geometry of the Complex Numbers
2.1Complex Numbers