
Inherited Bleeding Disorders in Women
Rezan A. Kadir, Paula D. James, Christine A. Lee, Rezan A. Kadir, Paula D. James, Christine A. Lee
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Inherited Bleeding Disorders in Women
Rezan A. Kadir, Paula D. James, Christine A. Lee, Rezan A. Kadir, Paula D. James, Christine A. Lee
Información del libro
The essential guide for understanding and treating women with inherited bleeding disorders, revised and updated
Now in its second edition, Inherited Bleeding Disorders in Women includes the most recent developments and research in the field. This important guide offers the most current information available for the effective management of these complex and difficult to diagnose disorders. Treating women with inherited bleeding disorders can be challenging and requires close collaboration among practitioners in different specialties.
This important guide is written by a team of international experts who offer advice and practical suggestions for treating women with inherited bleeding disorders. Inherited Bleeding Disorders in Women comprehensively covers obstetric and gynecological issues for carriers of hemophilia, women with von Willebrand disease, rare bleeding disorders and inherited platelet disorders. This important resource:
- Offers an updated guide for hematologists, obstetricans and gynecologists and other clinicians treating women with inherited bleeding disorders
- Includes information for treating both common and rare bleeding disorders
- Contains the most recent developments and advances in the field for the treatment and management of inherited bleeding disorders in women
- Presents information from noted experts in the field
- Offers a multidisciplinary approach to the topic
Written for hematologists, obstetricians and gynecologists and other clinicians working with women, Inherited Bleeding Disorders in Women has been fully revised and updated and continues to serve as a trusted guide for the management and treatment of women with inherited bleeding disorders.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
1
Hematological Assessment of a Patient with an Inherited Bleeding Disorder
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Normal Hemostasis
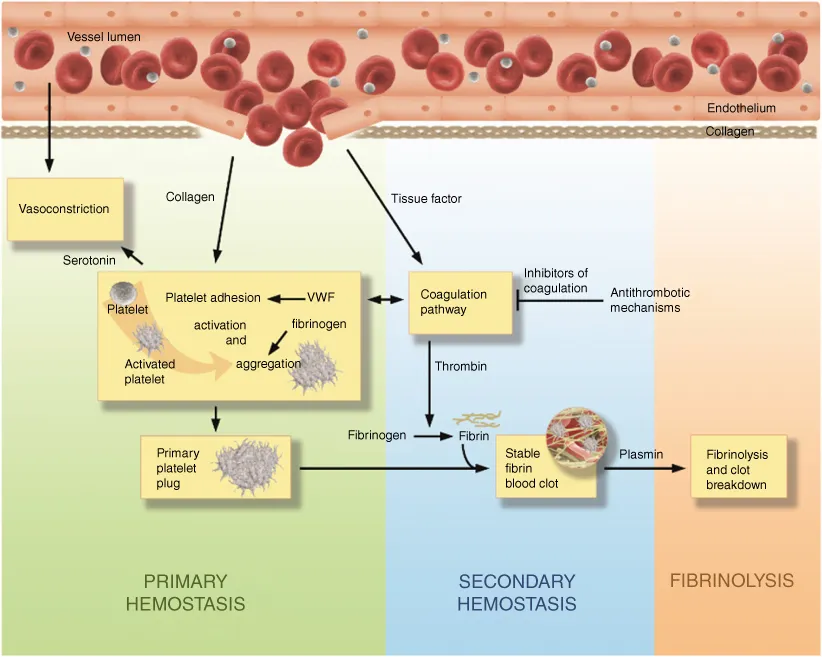
1.2.1 Primary Hemostasis
- Platelet adhesion: following vessel injury, von Willebrand factor (VWF) binds to specific sites on exposed collagen. Platelets adhere to the exposed subendothelial matrix (directly or indirectly via VWF). This is mediated through binding of VWF with the platelet glycoprotein GP1b, while GPVI interacts with collagen, and platelet β1 integrin with laminin, collagen, and fibronectin. These interactions enable firm adhesion of platelets to the exposed subendothelial matrix [3].
- Platelet activation: platelet adhesion to the subendothelium triggers shape change and release of platelet α and dense granule contents. This activation recruits and activates additional platelets to the injured site. (Thrombin, produced by the coagulation pathway, adds to the activation of platelets.)
- Platelet aggregation and platelet plug formation: thrombin cleaves fibrinogen and the resulting fibrin monomers form a bridge between activated platelets, causing platelets to aggregate together, forming a platelet plug. The GPIIb/IIIa platelet receptor is converted into its high‐affinity conformation, allowing for stable interactions between the receptor and fibrin, VWF, and fibronectin.