![]()
Chapter 1
Overview of Near Field Communication
WHAT’S IN THIS CHAPTER?
- A background for NFC technology
- Ubiquitous computing and wireless communication aspects for NFC
- Evolution of NFC technology: RFID and contactless smart card technologies
- An introduction to NFC technology and NFC devices: NFC tag, NFC reader, and NFC mobile
- NFC operating modes with generic usage models
- Examples for NFC applications in terms of operating modes
Currently, Near Field Communication (NFC) is one of the enablers for ubiquitous computing. This technology simplifies and secures interaction with the automation ubiquitously around you. Many applications you use daily such as credit cards, car keys, tickets, health cards, and hotel room access cards will presumably cease to exist because NFC-enabled mobile phones will provide all these functionalities.
The NFC ecosystem is designed from the synergy of several technologies, including wireless communications, mobile devices, mobile applications, and smart card technologies. Also, server-side programming, web and cloud services, and XML technologies contribute to the improvement and spread of NFC technology and its applications.
This chapter provides a brief background of the fundamentals and evolution of NFC technology. Then it gives a brief overview of NFC technology and the touching paradigm, including a comparison of NFC with other wireless technologies, and an introduction to smart NFC devices and operating modes with novel NFC applications in the industry.
UBIQUITOUS COMPUTING AND NFC
The history of modern computers comprises work that’s been performed over the past 200 years. Personal computers (PCs) were an important step after early computers, changing the way that users interact with computers by using keyboards and monitors for input and output instead of primitive options such as punch cards and cables. The mouse also changed the way that humans interact with computers because it enables users to input spatial data in to a computer. Users became accustomed to using their hands to hold the mouse and pointing their fingers to click it. The movements of the pointing device are echoed on the screen by the movements of the cursor, creating a simple and intuitive way to navigate a computer’s graphical user interface (GUI).
Touch screens changed the form of interaction even further and did so in a dramatic way. They removed the need for earlier input devices, and the interaction was performed by directly touching the screen, which became the new input device. In the meantime, mobile phones were introduced, initially for voice communication. Early forms of mobile phones contained a keypad. Those mobile phones with touch screens are considered to be state of the art because the screen is used for both input and output, which is more intuitive for users.
Ubiquitous computing is the highest level of interaction between humans and computers, in which computing devices are completely integrated into everyday life. Ubiquitous computing is a model in which humans do not design their activities according to the machines they need to use; instead, the machines are adjusted to human needs. Eventually, the primary aim is that humans using machines will not need to change their daily behaviors and will not even notice that they are performing activities with the help of machines.
As in modern computers and interfaces, increasing mobility of computing devices provided by mobile communications is also an important step in the development of ubiquitous computing capabilities and NFC. Mobile phones already had several communications options with the external environments before the introduction of NFC. When mobile phones were initially introduced, their primary goal was to enable voice communication. GSM (Global System for Mobile) communication further enabled functionality of mobile phones for several services, such as voice communication, short messaging service (SMS), multimedia message service (MMS), and Internet access. Also, the introduction of Global Positioning System (GPS) and Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) technologies (e.g., Infrared Data Association or IrDA) changed the way we use mobile phones. One communication option between mobile phones and computers was data transfer by USB — a physical port was used for this purpose, and cable was used for data transfer.
Later, Bluetooth technology was introduced, creating personal area networks that connect peripherals with computing devices such as mobile phones. Bluetooth became very popular in the early 2000s. Perhaps the most widely used function of Bluetooth is data exchange among mobile phones or between a mobile phone and another Bluetooth-enabled device such as a computer. Bluetooth enables communication among devices within a particular vicinity. However, secure data transfer cannot be performed completely with this technology because it is designed for wireless communication up to 10 meters, which allows malicious devices to alter the communication.
Currently, a new way of interacting has entered everyone’s daily life: NFC technology can be identified as a combination of contactless identification and interconnection technologies. NFC operates between two devices in a short communication range via a touching paradigm. It requires touching two NFC-compatible devices together over a few centimeters. NFC communication occurs between an NFC mobile device on one side and an NFC tag (a passive RFID tag), an NFC reader, or an NFC mobile device on the other side. RFID is capable of accepting and transmitting beyond a few meters and has a wide range of uses. However, NFC is restricted for use within close proximity (up to a few centimeters) and also designed for secure data transfer. Currently, integration of NFC technology into mobile phones is considered a practical solution because almost everyone carries a mobile phone.
The main vision of NFC is the integration of personal and private information such as credit card or cash card data into the mobile phones. Therefore, security is the most important concern, and even the short wireless communication range provided by RFID technology is considered too long. Shielding is necessary to prevent unauthorized people from eavesdropping on private conversations because even nonpowered, passive tags still can be read over 10 meters. This is the point where NFC comes in.
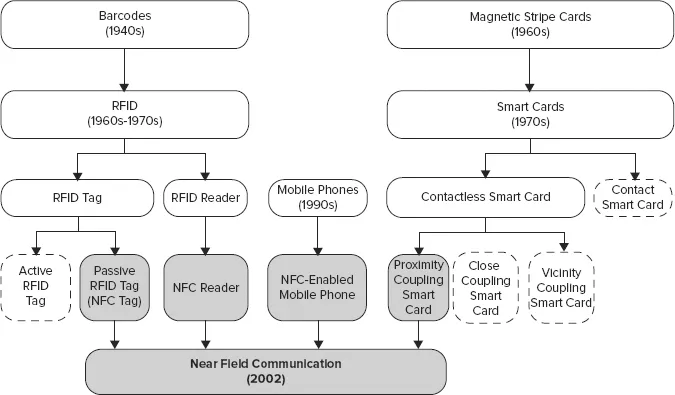
NFC integrates RFID technology and contactless smart technologies within mobile phones. The evolution of NFC technology is illustrated in Figure 1-1. The gray areas in the figure indicate the technological developments that support the NFC environment directly. This chapter provides a brief overview of the technologies that make NFC evolution possible.
WIRELESS COMMUNICATION AS NFC
NFC technology also can be evaluated using a wireless communication aspect. Wireless communication refers to data transfer without using any cables. When communication is impossible or impractical through the use of cables, wireless communication is the solution. The range may vary from a few centimeters to many kilometers.
Wireless communication devices include various types of fixed, mobile, and portable two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants, GPS units, wireless computer mice, keyboards and headsets, satellite television, and cordless telephones. Wireless communication allows communication without requiring a physical connection to the network.
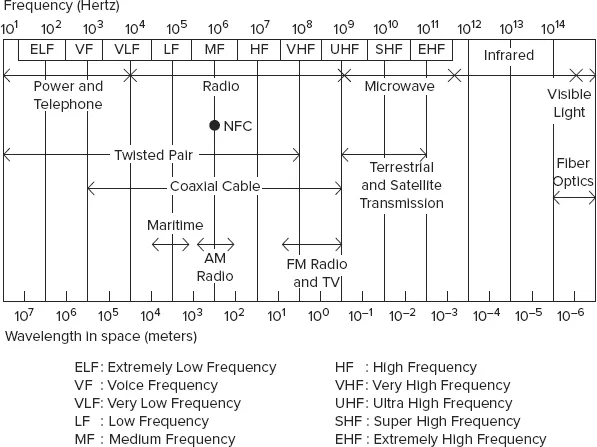
Wireless communication introduces challenges that are somewhat harder to handle compared to wired communication; these challenges include interference, attenuation, unreliability, cost, and security. Wireless communication makes use of transmission of data over electromagnetic waves within the electromagnetic spectrum, as depicted in Figure 1-2.
The most straightforward b...