
eBook - ePub
The Forex Options Course
A Self-Study Guide to Trading Currency Options
Abe Cofnas
This is a test
Partager le livre
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
The Forex Options Course
A Self-Study Guide to Trading Currency Options
Abe Cofnas
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
The Forex Options Course is a practical, hands-on guide to understanding and trading forex options. Designed to build a trader's knowledge base in a step-by-step manner, this reliable resource moves from the straightforward to the more sophisticated with discussions of everything from basic plain vanilla calls and puts to intriguing first-generation exotic binary options. Written in a straightforward and accessible style, The Forex Options Course will help you develop the skills and strategies needed to succeed in today's dynamic forex market.
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que The Forex Options Course est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à The Forex Options Course par Abe Cofnas en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Business et Foreign Exchange. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
PART ONE
Key Option Elements
The objective of Part One is to provide a knowledge base for learning about the key elements of forex options. This includes a description of plain vanilla options and how option premiums are impacted by volatility. To prepare the forex trader for shaping option trades, Part One also provides a detailed outline on the basic elements of “the Greeks,” which are the components that provide insight on how forex option prices change with time and volatility.
CHAPTER 1
The Elements of an Option Trade
PLAIN VANILLA OPTIONS
This chapter provides a review of the key elements that comprise an option trade. The simplest form of option trading is called plain vanilla. Plain vanilla options in all markets include calls and puts and are exactly the same as in forex trading.
PURCHASING AN OPTION
First, let’s talk about purchasing an option. Purchasing an option means holding an option. A trader purchases an option by paying a premium for it.
Calls
Once a trader has purchased (gone long) and is holding a call, he has the right but not the obligation to buy the underlying spot forex upon expiration. If it’s a European-style option, exercising rights are on expiration and not before. If it’s an American-style option, exercising rights are any time up to and including expiration.
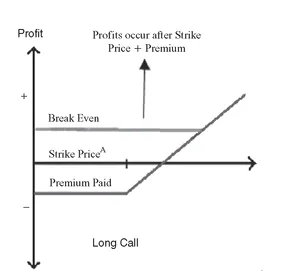
The key concept is that a buyer of a call anticipates an upward move or is bullish. The trader selects a target called a strike price. If the price of the spot forex moves through and beyond the strike price, the position will be in profits. If the spot price is beyond the strike price at the time of expiration, the position is known as “in the money.” We can see in the profit payout graph (see Figure 1.1) that a call option becomes profitable once the price is beyond the strike price and beyond the cost of the position. This is a generic example for any call.
FIGURE 1.1 Currency Call Option Example
Let’s begin to examine the elements of an option trade by looking at the following example involving the EURUSD.
After scanning the weekly chart of the EURUSD, a trader is anticipating a stronger EUR against the dollar and has selected a 1.47 strike price for a February 14 expiration. The premium charged for this is calculated to be $790 USD. Notice that the EURUSD spot position is at 1.4419. To be clear, the example as shown in Figures 1.2 and 1.3 would mean the trader expects the EURUSD to move to and beyond 1.47 by the expiration date. Actually, to be profitable if held to expiration, the spot position needs to be 79 pips beyond that, or 1.4779 to recover the costs of the premium since each pip is worth $10. But the most that the trader would lose is the premium paid and any associated other fees (source of the premium price example: www.ikongm.com).
Puts
Once a trader has purchased (gone long) and is holding a put, he has the right but not the obligation to buy the underlying spot forex upon expiration. If it’s a European-style option, exercising rights are on expiration and not before. If it’s an American-style option, exercising rights are any time up to and including expiration.
What is important about purchasing an option is the element of risk control. Once an option is purchased and the premium is paid (along with any other fees), this total cost is the maximum risk facing the trader. No matter what happens to the price action, the most the trader can lose is the cost of the premium paid.
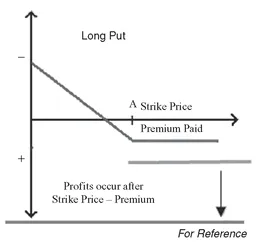
The key concept is that a buyer of a put anticipates a downward move or is bearish. The trader selects a target called a strike price. If the price of the spot forex moves toward, and possibly through and beyond the strike price, the position will be in profits. If the spot price is beyond the strike price at the position is known as “in the money.” We can see in the generic profit payout graph (see Figure 1.4) that a put option becomes profitable once the price is beyond the strike price and beyond the cost of the position.
FIGURE 1.2 Placing a Call on the EURUSD
Source: © ProRealTime.com, web-based charting software
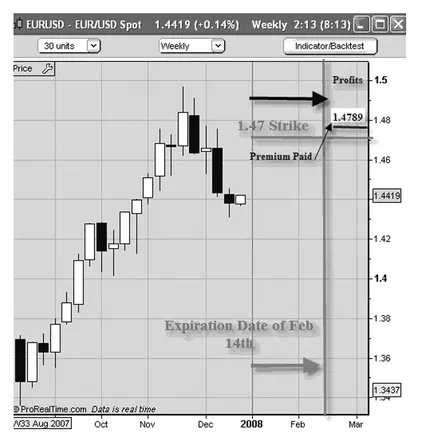
FIGURE 1.3 Trader Expects EURUSD to Move Beyond 1.47
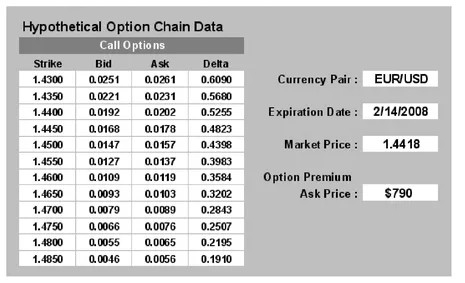
FIGURE 1.4 Profit Region on Puts
In Figures 1.5 and 1.6 we see an example regarding the GBPUSD. The market price is at 1.9816. The strike price selected is at 1.9400. The expiration date is February 14. The cost of a put is $1290. The trader placing this put will pay in pip terms 129 pips if trading a standard lot of 100,000. This means that the break-even point will be 1.9400-0.0129, or 1.9271 if the trade is allowed to go to expiration. It is possible that the premium price could move up in value if volatility in the market increased and the GBPUSD fell quickly and early toward the strike point (source of premium price examples: www.ikongm.com).
The trader needs to always remember that time itself is important. The longer the time to expiration, the greater the risk that the strategy can go wrong and a new event will interfere and change the price direction. However, more time can allow the trade to work out and overcome periods where the price movements go against the trader. Time is a double-edged sword for the forex option trader.
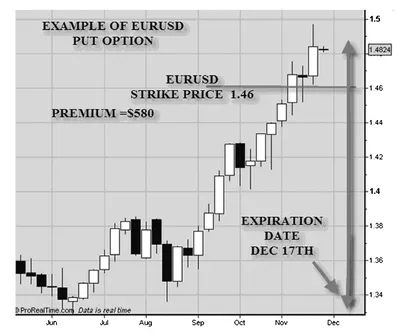
Figure 1.7 shows an example of a put option on the EURUSD. The trader expects a fall in the EURUSD and has selected 1.46 for the strike price. The amount of the premium charged is estimated to be $580. Remember this is 200 pips away from the spot price which is at 1.4829 (see Figure 1.8).
Compare the premium price of this put to the call that was at 150 or 180 pips away, which was at 763. In other words, the market expected the move to be up because the price of an option almost the same distance was much higher for the call.
FIGURE 1.5 Profit Range for Put on GBPUSD
Source: © ProRealTime.com, web-based charting software
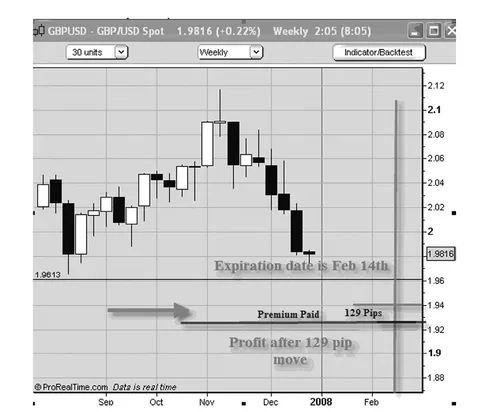
FIGURE 1.6 Put Option Chain for GBPUSD
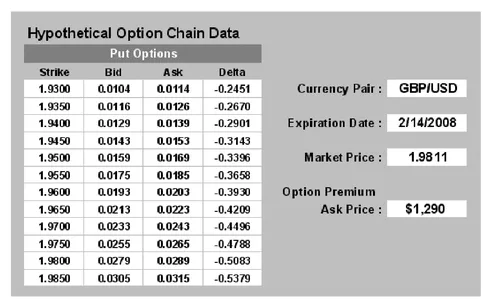
FIGURE 1.7 EURUSD Put Option
Source: © ProRealTime.com, web-based charting software
When there is a difference in the premiums between a call and a put at the same distance from the market, this is an important sentiment indicator that we will discuss in detail.
WRITING AN OPTION—BEGINNERS DON’T
When an option trade is undertaken, there are, of course, two parties to the trade. The trader purchases an option, but from whom? In forex, the other side is the forex firm that makes the market and establishes the premium prices. (In the future it might become direct matching between buyers and writer or options.) The writer originates the option trade and is looking for a buyer. The writer of a call is anticipating that the price of the underlying spot forex position will not get any higher than the strike price at expiration. The writer of the put is ant...