
eBook - ePub
Key Notes on Plastic Surgery
Adrian Richards, Hywel Dafydd
This is a test
Partager le livre
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Key Notes on Plastic Surgery
Adrian Richards, Hywel Dafydd
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
This is the new edition of the concise but comprehensive handbook that should be owned by all surgical trainees specialising in plastic surgery. Taking a pithy systematic approach, Key Notes on Plastic Surgery offers the latest developments within the field in bullet point form and includes key papers for viva voces. It is informed by the current FRCS (Plast) curriculum, making it ideal preparation for the UK exit examination or equivalent international board exam.
Key features
- Fully covers the entire scope of plastic surgery
- Clearly divided into 10 sections with logical subheadings for easy fact-finding
- Acts as an adjunct to the established longer texts
- Brand new chapter on ethics and the law – a compulsory component of the oral examination
- Illustrations outlining key surgical procedures and relevant anatomy
Fully revised to include all the latest clinical guidelines, Key Notes on Plastic Surgery is the perfect rapid reference tool for trainees in plastic surgery and dermatologic surgery who require quick, accurate answers.
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Key Notes on Plastic Surgery est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Key Notes on Plastic Surgery par Adrian Richards, Hywel Dafydd en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Medicina et Chirurgia plastica e medicina estetica. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
Chapter 1
General Principles
- Embryology, structure and function of the skin
- Blood supply to the skin
- Classification of flaps
- Geometry of local flaps
- Wound healing and skin grafts
- Bone healing and bone grafts
- Cartilage healing and cartilage grafts
- Nerve healing and nerve grafts
- Tendon healing
- Transplantation
- Tissue engineering
- Alloplastic implantation
- Wound dressings
- Sutures and suturing
- Tissue expansion
- Lasers
- Local anaesthesia
- Microsurgery
- Haemostasis and thrombosis
- Further reading
Embryology, structure and function of the skin
- Skin differentiates from ectoderm and mesoderm during the 4th week.
- Skin gives rise to:
- Teeth and hair follicles, derived from epidermis and dermis
- Fingernails and toenails, derived from epidermis only.
- Hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, apocrine glands and mammary glands are ‘epidermal appendages’ because they develop as ingrowths of epidermis into dermis.
- Functions of skin:
- Physical protection
- Protection against UV light
- Protection against microbiological invasion
- Prevention of fluid loss
- Regulation of body temperature
- Sensation
- Immunological surveillance.
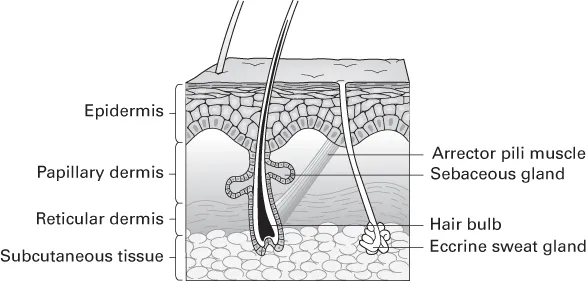
The epidermis
- Composed of stratified squamous epithelium.
- Derived from ectoderm.
- Epidermal cells undergo keratinisation—their cytoplasm is replaced with keratin as the cell dies and becomes more superficial.
- Rete ridges are epidermal thickenings that extend downward between dermal papillae.
- Epidermis is composed of these five layers, from deep to superficial:
- Stratum germinativum
- Also known as the basal layer.
- Cells within this layer have cytoplasmic projections (hemidesmosomes), which firmly link them to the underlying basal lamina.
- The only actively proliferating layer of skin.
- Stratum germinativum also contains melanocytes.
- Stratum spinosum
- Also known as the prickle cell layer.
- Contains large keratinocytes, which synthesise cytokeratin.
- Cytokeratin accumulates in aggregates called tonofibrils.
- Bundles of tonofibrils converge into numerous desmosomes (prickles), forming strong intercellular contacts.
- Stratum granulosum
- Contains mature keratinocytes, with cytoplasmic granules of keratohyalin.
- The predominant site of protein synthesis.
- Combination of cytokeratin tonofibrils with keratohyalin produces keratin.
- Stratum lucidum
- A clear layer, only present in the thick glabrous skin of palms and feet.
- Stratum corneum
- Contains non-viable keratinised cells, having lost their nuclei and cytoplasm.
- Protects against trauma.
- Insulates against fluid loss.
- Protects against bacterial invasion and mechanical stress.
Cellular composition of the epidermis
- Keratinocytes—the predominant cell type in the epidermis.
- Langerhans cells—antigen-presenting cells (APCs) of the immune system.
- Merkel cells—mechanoreceptors of neural crest origin.
- Melanocytes—neural crest derivatives:
- Usually located in the stratum germinativum.
- Produce melanin packaged in melanosomes, which is delivered along dendrites to surrounding keratinocytes.
- Melanosomes form a cap over the nucleus of keratinocytes, protecting DNA from UV light.
The dermis
- Accounts for 95% of the skin's thickness.
- Derived from mesoderm.
- Papillary dermis is superficial; contains more cells and finer collagen fibres.
- Reticular dermis is deeper; ...