
Applied Mathematics in Hydrogeology
Tien-Chang Lee
- 400 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Applied Mathematics in Hydrogeology
Tien-Chang Lee
À propos de ce livre
As introduced in Dr. Lee's 10-week class, Applied Mathematics in Hydrogeology is written for professionals and graduate students who have a keen interest in the application of mathematics in hydrogeology.
Its first seven chapters cover analytical solutions for problems commonly encountered in the study of quantitative hydrogeology, while the final three chapters focus on solving linear simultaneous equations, finite element analysis, and inversion for parameter determination.
Dr. Lee provides various equation-solving methods that are of interest to hydrogeologists, geophysicists, soil scientists, and civil engineers, as well as applied physicists and mathematicians. In the classroom, this same information will help students realize how familiar equations in hydrogeology are derived-an important step toward development of a student's own mathematical models.
Unlike other applied mathematics books that are structured according to systematic methodology, Applied Mathematics in Hydrogeology emphasizes equation-solving methods according to topics. Hydrogeological problems and governing differential equations are introduced, including hydraulic responses to pumping in confined and unconfined aquifers, as well as transport of heat and solute in flowing groundwater.
Foire aux questions
Informations
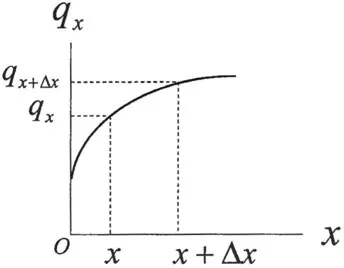
(1.1) |
(1.2) |