![]()
Fats and fatty acids
You are probably reading this booklet because you or your child has been diagnosed with a long-chain fatty acid oxidation disorder (LC-FAOD) or this diagnosis is suspected.
With an LC-FAOD, the body is unable to properly break down fats in the diet.
Fat as an energy source
Our bodies need energy to keep muscles, organs and normal processes working.
The three types of food that provide energy are carbohydrates (in the form of sugars and starches), protein and fats.
The body stores fat under the skin and around the organs so that it can be used to provide energy when needed.
Fatty acids are building blocks
Fats are made up of building blocks called fatty acids. Fatty acids are usually joined in groups of three (tri) to a glycerol backbone – this is called a triglyceride. Each fatty acid is made up of a chain of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached.
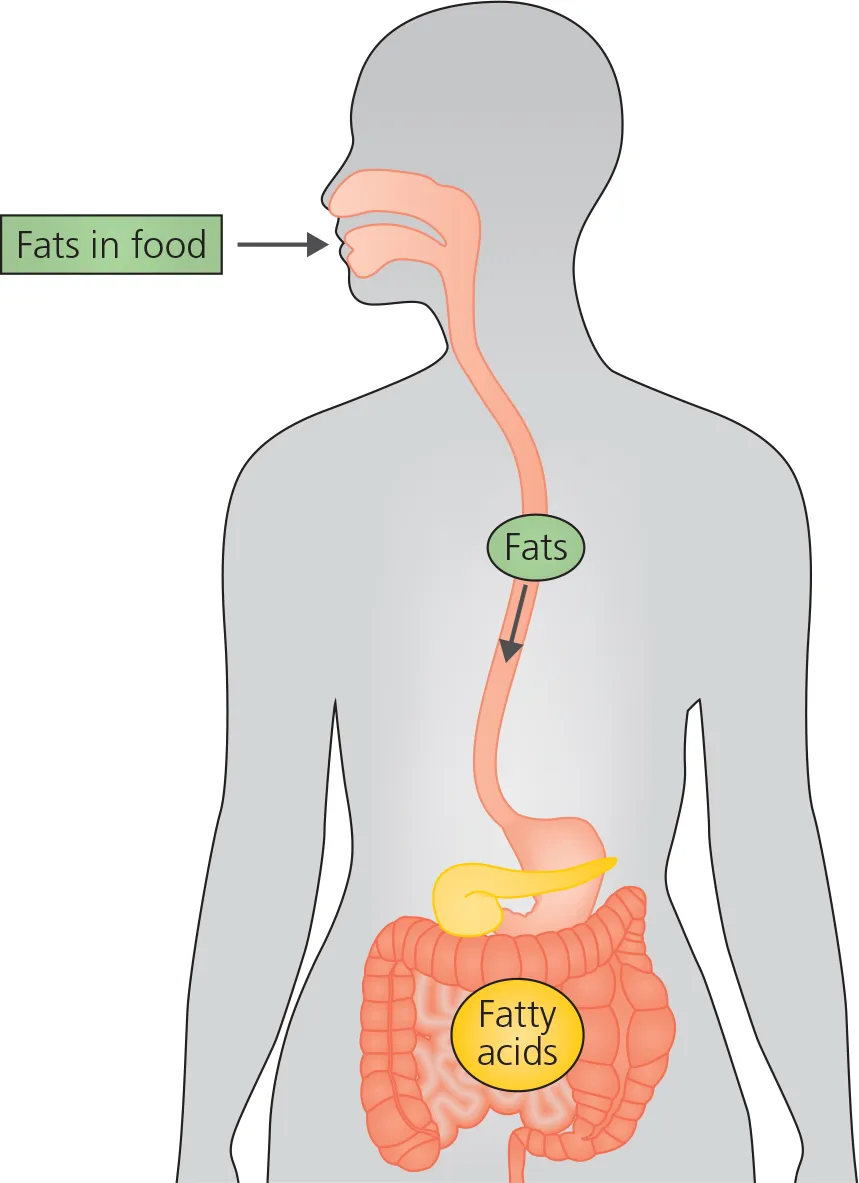
Fats enter the body from our diet. Fatty acids are released from triglycerides. They are either stored as fat or used as a source of energy in the body.
The number of carbon atoms varies between different fatty acids; for example…
Palmitic acid has 16 carbons and is found in palm oil
Oleic acid has 18 carbons and is found in olive oil
Arachidonic acid has 20 carbons and is found in meat and dairy products
![]()
Fatty acids for energy
When the body needs to use fat as an energy source, it breaks down the triglyceride and releases fatty acids. These fatty acids then travel in the blood to the muscles and organs where they can be used for energy.
Introducing beta oxidation
Once the fatty acids are in the muscle or organ where they will be used for energy, they go through a complicated process called beta oxidation. This takes place in mitochondria, which are specialized areas in cells.
What is an enzyme?
Enzymes are special proteins that help with a wide range of crucial tasks in the body. Each enzyme – and there are thousands in an average human cell – has a specific task. Examples of enzymes that help digest food are:
![]()
Long-chain fatty acid oxidation disorders
As shown on page 2, each fatty acid contains a chain of carbons. The length of this chain varies, with most fatty acids having between 4 and 24 carbons.
Enzymes are needed to move long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria and process them for energy.
LC-FAODs happen when one of the enzymes involved in breaking down long-chain fatty acids for energy is not made or is not working properly.
As a result, the body is unable to use these fatty acids for energy in the usual way. This can lead to problems with energy supplies.
Not being able to use energy from stored fat can cause harmful effects. Having partially digested fatty acids in the body may also cause problems.
LC-FAODs are named according to the enzyme that is affected. The most common types of LC-FAOD are:
•Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 or CPT1 deficiency (sometimes written as CPT I)
•Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase or CACT deficiency
•Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 or CPT2 deficiency (sometimes written as CPT II)
•Very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase or VLCAD deficiency
•Long-chain 3-hydroxy-acyl-CoA dehydrog...