Applications of Nano Materials, Organic Semiconductor Complexes and Composites Based Devices
1. Introduction
During the last years, many efforts were devoted to the fabrication of new nanostructures and their composites with organic materials and semiconductors. Based on these materials, a number of electronic devices having sufficient sensitivity and efficiency for practical application were designed and investigated. In this chapter, results of authors investigations and obtained from the literature regarding effect of humidity to electric properties of Cu2O-PEPC (poly-N-epoxypropylcarbazole) nanocomposite films, ITO/CuPc/NiPc/Al and ITO/NiPc/CuPc/Al junction cells with double junction, surface-type Al/CNT/Al pressure sensors, resistive-type displacement sensor based on composite of vanadium complex (VO2 (3-fl)) and CNT, the CNT and Cu2O strain sensors based on composites are presented and discussed. Data on properties of thin film organic field effect transistors (OFETs), can be used not only for amplification of the voltage but, OFETs having Schottky junction, as MESFET, a number of sensors can be fabricated. In addition, properties of OFET as a temperature sensor are discussed in detail.
The structure and properties of organic solar cells with Schottky junction and p-n heterojunction, bulk heterojunction solar cells, and based on TiO2 nanostructure dye sensitized solar cells (DSSC) are discussed. Special attention was given to the properties of rectifying antennas, rectennas and based solar cells unlike to the conventional solar cells; if it will be fabricated using nanotechnology can convert the energy of light into electric power with very high efficiency.
In addition, structure and properties of a single layer organic light-emitting diode (OLED) fabricated on the base of Poly(p-phenylene vinylene (PPV), two-layer organic light-emitting diode which uses Alq3 (tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato) aluminum, and NPB (N,N’-di(naphthalene-1-yl)-N,N’diphenyl-benzidine (e-electrons, h- holes), OLEDs with three CuPc/NPB/Alq3 layers and five layers OLET with structure CuPc/NPB/CBP+Ir(ppy)3/BCP/Alq3 are discussed.
2. SENSORS
2.1. Humidity Sensor
Humidity sensors are used for the evaluation of the environmental parameters in different industrial applications [1 - 3]. There are different kinds of humidity sensors such as capacitive, resistive, hydrometric, gravimetric, optical and integrated types operating on different principles [4 - 6]. Capacitive humidity sensors are one of the simplest, less power consuming and reliable. Properties of these sensors depend on hygroscopic material used in the capacitance as insulator, and on the construction of plates. Unusually surface type electrodes are more popular [7].
For the fabrication of humidity sensors, a number of techniques and materials are used [8 - 5], e.g. for capacitive humidity sensors, surface and bulk micromachining techniques are popular for the production of porous silicon-based sensors [8, 9]. For the manufacturing of humidity and temperature sensors a thin-film surface micromachining technique was proposed by Park et al. [10]. Cellulose acetate butyrate [11, 12] and polyimide [13, 14] materials are commonly used as sensing materials for capacitive-type humidity sensors. Karimov et al. [15] fabricated a surface-type capacitive humidity sensor based on copper phthalocyanine (CuPc). As relative humidity is increased from 35% to 92%, the capacitance of the detector is also increased continuously by 200 times.
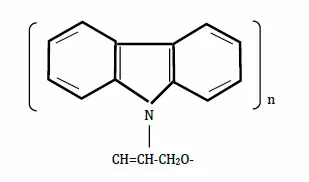
The complexes of poly-N-epoxypropylcarbazole (PEPC) as one of the photosensitive materials are known. The solar cells and photo capacitors are PEPC based on their good adhesive properties [16]. Another photosensitive semiconductor copper oxide (Cu2O), p-type, with a band gap of 2 eV, is nontoxic and is available in nature in large scale is used for the fabrication of nanodots and nanostructure thin films [17 - 20]. Humidity sensors with high sensitivity, stability and linearity of characteristics, potentially can be fabricated with composites of different materials and can be realized by investigating the effects of humidity on copper oxide composites. The results of the investigations of the effect of humidity on the electric properties of the copper oxide nanoparticles and poly-N-epoxypropylcarbazole (Cu2O-PEPC) nanocomposite films are presented in this chapter.
For experiments Cu2O nanopowder was commercially purchased from WINLAB UK. PEPC was synthesized in laboratory [16]. Fig. (1) shows molecular structure of PEPC. The glass substrates were prepared by cleaning ultrasonically by acetone for 10 minutes and then by plasma cleaning for 5 minutes. The blend of copper oxide nanopowder (3.0 wt.%) and poly-N-epoxypropylcarbazole (2.0 wt.%) in benzol was prepared. By drop-casting, a thin film on glass substrates was deposited with pre-deposited surface-type silver electrodes. The gap between silver electrodes was 40 μm for the fabrication of Cu2O-PEPC nanocomposite thin films. It was found that deposited films were stable and had good adhesion to the substrate.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) micrographs of Cu2O-PEPC nanocomposite thin film shows porosity that make this material a potential candidate for humidity sensors fabrications and is shown in Fig. (2)(a-b) at different magnifications. The Cu2O-PEPC nanocomposite thin films were investigated by X-ray differaction (XRD) technique. Fig. (3) shows the pattern of XRD of the nanocomposite thin film obtained from “Panalytical Xpert pro”. It was found that with the ICDD reference card “00-001-1142” the indexed peaks of the XRD pattern a...