![]()
CHAPTER 1
Introduction of Intellectual Property
Intellectual Property (IP) is an integral and invaluable building block of many industries. It is an intangible key asset and a primary method for securing business’ return-on-investment (ROI) from innovation and reputation. Besides protecting a company’s innovations from competitors (including counterfeiters), IP assets are also an important source of cash-flow through licensing arrangements or sales. For start-ups, in particular, IP is also a significant asset by which to attract investors.
In addition, IP is a significant ingredient in a company’s ethos or “brand.” Brands are the means by which goods and service providers develop relationships with consumers. Brands are often described as having strong or weak equity. This equity has been defined by such factors as consumer loyalty, consumer awareness, association with quality, societal relevance, consumer engagement, and leadership among peers. Counterfeiting and grey markets dilute the equity of the brand by interfering and often destroying the factors noted above.
What Are IP Assets?
Patents, trademarks, copyrights, designs, trade secrets, including confidential and proprietary (business critical) information such as product specifications, new product release plans, marketing, pricing, client and customer confidential information.
The survival of many companies depends on robust and diverse measures to protect it. Companies proactively investing in securing their IP from the beginning will benefit enormously in the long run.
What Are the Most Common Threats to IP and How to Address Them?
1. IP and confidential information divulgence. The costs of recovering lost or leaked IP is much higher than the cost usually needed to protect it. Protection is often achieved by implementing cybersecurity or other technological measures or some simpler protection methods such as:
(a) Restricting critical information to the leadership team only;
(b) Safely storing confidential documents in a highly secure online repository providing detailed tracking of the site’s access and use; and
(c) Assigning permissions-based roles for data access.
Protection may also be enhanced by requiring extremely rigorous nondisclosure and confidentiality agreements to deter employees and third parties from divulging sensitive data.
2. Patents are an important part of the overall IP protection strategy. However, they should not be the sole protective method employed (The number of patents being invalidated is increasing with estimates suggesting that over half of U.S. patents granted are struck down1).
3. Free-riding. Whether IP is leaked via employee, obtained illicitly or incidentally, any opportunistic free rider can exploit it for their own gain.
Business growth and preventing potential revenue losses in the future from leaked, stolen, or copied IP depends on defining a clear and early IP strategy, which should include:
• Identifying IP assets to protect;
• Registering the core IP as soon as possible;
• Prioritize IP protection needs by locale (operating markets);
• Adapt to the local IP protection competencies and practices;
• Deploy technology to “fight technology” (cybersecurity, analytics);
• Identify and catalog your trade secrets;
• Online protection; and
• Budget accordingly.
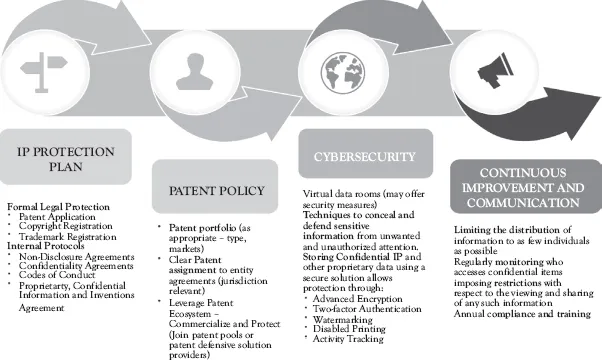
Good IP protection strategy should include the 4 components as shown in Figure 1.1.
Figure 1.1 IP protection strategy components
Where and When to Protect IP?
Owing to a “first-to-file system” in most countries, local formal legal protection/registrations are usually necessary to protect IP. Therefore, ideally the IP protection strategy has to be in place at least 12 months (in order to obtain necessary registrations) before entering local markets. Late-obtained IP registrations will limit the options of preventive measures and risk and associated costs will be higher.
It is absolutely essential to understand that IP rights are territorial. And as result IP rights are often enforceable only upon valid domestic registration. (Exceptions include the European Union where multicountry patent filing is available, or Myanmar where IP filing is not yet available.)
While much of this book provides det...