Section 1:Introduction to AWS AI NLP Services
In this section, we introduce the NLP construct and the business value of using NLP, leading to an overview of the AWS AI stack, along with the key NLP services.
This section comprises the following chapters:
- Chapter 1, NLP in the Business Context and Introduction to AWS AI Services
- Chapter 2, Introducing Amazon Textract
- Chapter 3, Introducing Amazon Comprehend
Chapter 1: NLP in the Business Context and Introduction to AWS AI Services
Natural language processing, or NLP, is quite popular in the scientific community, but the value of using this Artificial Intelligence (AI) technique to gain business benefits is not immediately obvious to mainstream users. Our focus will be to raise awareness and educate you on the business context of NLP, provide examples of the proliferation of data in unstructured text, and show how NLP can help derive meaningful insights to inform strategic decisions within an enterprise.
In this introductory chapter, we will be establishing the basic context to familiarize you with some of the underlying concepts of AI and Machine Learning (ML), the types of challenges that NLP can help solve, common pitfalls when building NLP solutions, and how NLP works and what it's really good at doing, with examples.
In this chapter, we will cover the following:
- Introducing NLP
- Overcoming the challenges in building NLP solutions
- Understanding why NLP is becoming mainstream
- Introducing the AWS ML stack
Introducing NLP
Language is as old as civilization itself and no other communication tool is as effective as the spoken or written word. In their childhood days, the authors were enamored with The Arabian Nights, a centuries-old collection of stories from India, Persia, and Arabia. In one famous story, Ali Baba and the Forty Thieves, Ali Baba is a poor man who discovers a thieves' den containing hordes of treasure hidden in a cave that can only be opened by saying the magic words open sesame. In the authors' experience, this was the first recollection of a voice-activated application. Though purely a work of fiction, it was indeed an inspiration to explore the art of the possible.
Recently, in the last two decades, the popularity of the internet and the proliferation of smart devices has fueled significant technological advancements in digital communications. In parallel, the long-running research to develop AI made rapid strides with the advent of ML. Arthur Lee Samuel was the first to coin the term machine learning, in 1959, and helped make it mainstream in the field of computer science by creating a checkers playing program that demonstrated how computers can be taught.
The concept that machines can be taught to mimic human cognition, though, was popularized a little earlier in 1950 by Alan Turing in his paper Computing Machinery and Intelligence. This paper introduced the Turing Test, a variation of a common party game of the time. The purpose of the test was for an interpreter to ask questions and compare responses from a human participant and a computer. The trick was that the interpreter was not aware which was which, considering all three were isolated in different rooms. If the interpreter was unable to differentiate the two participants because the responses matched closely, the Turing Test had successfully validated that the computer possessed AI.
Of course, the field of AI has progressed leaps and bounds since then, largely due to the success of ML algorithms in solving real-world problems. An algorithm, at its simplest, is a programmatic function that converts inputs to outputs based on conditions. In contradiction to regular programmable algorithms, ML algorithms have learned the ability to alter their processing based on the data they encounter. There are different ML algorithms to choose from based on requirements, for example, Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), a popular algorithm for regression and classification problems, Exponential Smoothing (ETS), for statistical time series forecasting, Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD), for computer vision problems, and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), for topic modeling in NLP problems.
For more complex problems, ML has evolved into deep learning with the introduction of Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), which have the ability to solve highly challenging tasks by learning from massive volumes of data. For example, AWS DeepComposer (https://aws.amazon.com/deepcomposer/), an ML service from Amazon Web Services (AWS), educates developers with music as a medium of instruction. One of the ML models that DeepComposer uses is trained with a type of neural network called the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to create new and unique musical compositions from a simple input melody using AutoRegressive (AR) techniques:
Figure 1.1 – Composing music with AWS DeepComposer and ML
A piano roll is an image representation of music, and AR-CNN considers music generation as a sequence of these piano roll images:
Figure 1.2 – Piano roll representation of music
While there is broad adoption of ML across organizations of all sizes and industries spurred by the democratization of advanced technologies, the potential to solve many types of problems, and the breadth and depth of capabilities in AWS, ML is only a subset of what is possible today with AI. According to one report (https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2019-01-21-gartner-survey-shows-37-percent-of-organizations-have, accessed on March 23, 2021), AI adoption grew by 270% in the period 2015 to 2019. And it is continuing to grow at a rapid pace. AI is no longer a peripheral technology only available to those enterprises that have the economic resources to afford high-performance computers. Today, AI is a mainstream option for organizations looking to add cognitive intelligence to their applications to accelerate business value. For example, ExxonMobil in partnership with Amazon created an innovative and efficient way for customers to pay at gas stations. The Alexa pay for gas skill uses the car's Alexa-enabled device or your smartphone's Alexa app to communicate with the gas pump to manage the payment. The authors paid a visit to a local ExxonMobil gas station to try it out, and it was an awesome experience. For more details, please refer to https://www.exxon.com/en/amazon-alexa-pay-for-gas.
AI addresses a broad spectrum of tasks similar to human intelligence, both sensory and cognitive. Typically, these are grouped into categories, for example, computer vision (mimics human vision), NLP (mimics human speech, writing, and auditory processes), conversational interfaces (such as chatbots, mimics dialogue-based interactions), and personalization (mimics human intuition). For example, C-SPAN, a broadcaster that reports on proceedings at the US Senate and the House of Representatives, uses Amazon Rekognition (a computer vision-based image and video analysis service) to tag who is speaking/on camera at each time. With Amazon Rekognition, C-SPAN was able to index twice as much content compared to what they were doing previously. In addition, AWS offers AI services for intelligent search, forecasting, fraud detection, anomaly detection, predictive maintenance, and much more, which is why AWS was named the leader in the first Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud AI.
While language is inherently structured and well defined, the usage or interpretation of language is subjective, and may inadvertently cause an unintended influence that you need to be cognizant of when building natural language solutions. Consider, for example, the Telephone Game, which shows how conversations are involuntarily embellished, resulting in an entirely different version compared to how it began. Each participant repeats exactly what they think they heard, but not what they actually heard. It is fun when played as a party game but may have more serious repercussions in real life. Computers, too, will repeat what they heard, based on how their underlying ML model interprets language.
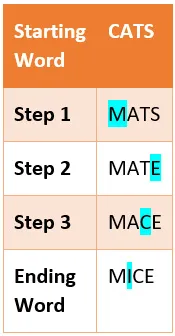
To understand how small incremental changes can completely change the meaning, let's look at another popular game: Word Ladder (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Word_ladder). The objective is to convert one word into a different word, often one with the opposite meaning, in as few steps as possible with only one letter in the word changing in one step.
An example is illustrated in the following table:
Figure 1.3 – The Word Ladder game
Adapting AI to wor...