Getting Started with Kubernetes - Second Edition
Jonathan Baier
- 286 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Getting Started with Kubernetes - Second Edition
Jonathan Baier
À propos de ce livre
Learn how to schedule and run application containers using Kubernetes.About This Book• Get well-versed with the fundamentals of Kubernetes and get it production-ready for deployments• Confidently manage your container clusters and networks using Kubernetes• This practical guide will show you container application examples throughout to illustrate the concepts and features of KubernetesWho This Book Is ForThis book is for developers, sys admins, and DevOps engineers who want to automate the deployment process and scale their applications. You do not need any knowledge about Kubernetes.What You Will Learn• Download, install, and configure the Kubernetes codebase• Understand the core concepts of a Kubernetes cluster• Be able to set up and access monitoring and logging for Kubernetes clusters• Set up external access to applications running in the cluster• Understand how CoreOS and Kubernetes can help you achieve greater performance and container implementation agility• Run multiple clusters and manage from a single control plane• Explore container security as well as securing Kubernetes clusters• Work with third-party extensions and toolsIn DetailKubernetes has continued to grow and achieve broad adoption across various industries, helping you to orchestrate and automate container deployments on a massive scale.This book will give you a complete understanding of Kubernetes and how to get a cluster up and running. You will develop an understanding of the installation and configuration process. The book will then focus on the core Kubernetes constructs such as pods, services, replica sets, replication controllers, and labels. You will also understand how cluster level networking is done in Kubernetes.The book will also show you how to manage deployments and perform updates with minimal downtime. Additionally, you will learn about operational aspects of Kubernetes such as monitoring and logging. Advanced concepts such as container security and cluster federation will also be covered. Finally, you will learn about the wider Kubernetes ecosystem with OCP, CoreOS, and Tectonic and explore the third-party extensions and tools that can be used with Kubernetes.By the end of the book, you will have a complete understanding of the Kubernetes platform and will start deploying applications on it.Style and approachThis straightforward guide will help you understand how to move your container applications into production through best practices and a step-by-step walkthrough tied to real-world operational strategies.
Foire aux questions
Informations
Introduction to Kubernetes
- Introducing container operations and management
- Why container management is important?
- The advantages of Kubernetes
- Downloading the latest Kubernetes
- Installing and starting up a new Kubernetes cluster
- The components of a Kubernetes cluster
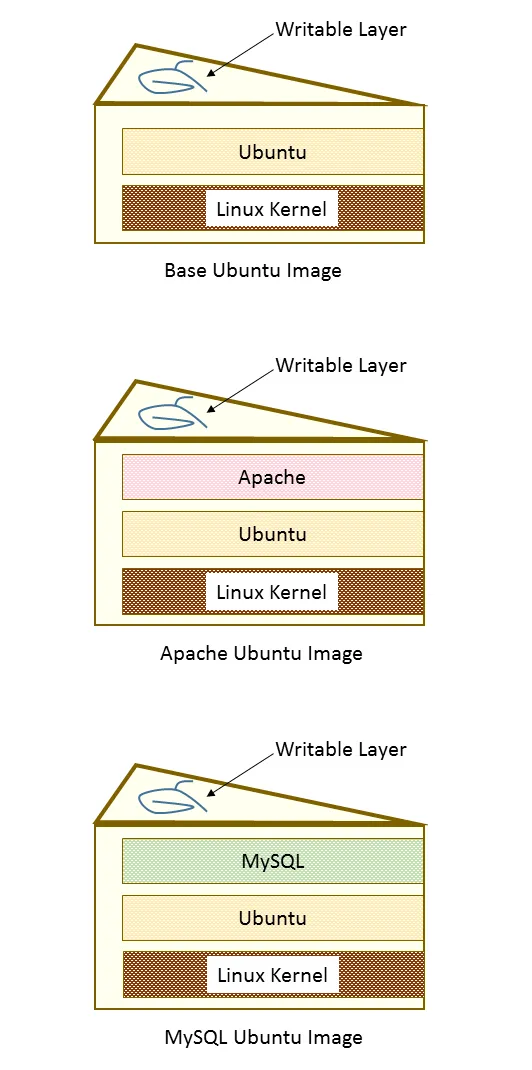
A brief overview of containers
What is a container?